Sampling distributions
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the concepts of populations and samples in statistics, emphasizing the importance of sampling distributions. It explains how we estimate population parameters using sample statistics and illustrates the impact of sample size on accuracy. Through a relatable example involving cat weights, the video demonstrates that larger samples yield more reliable estimates. It highlights the Central Limit Theorem, assuring that sample means will approximate a normal distribution with sufficient sample size, even when the original data isn't normally distributed. This foundational understanding is crucial for effective statistical inference.
Takeaways
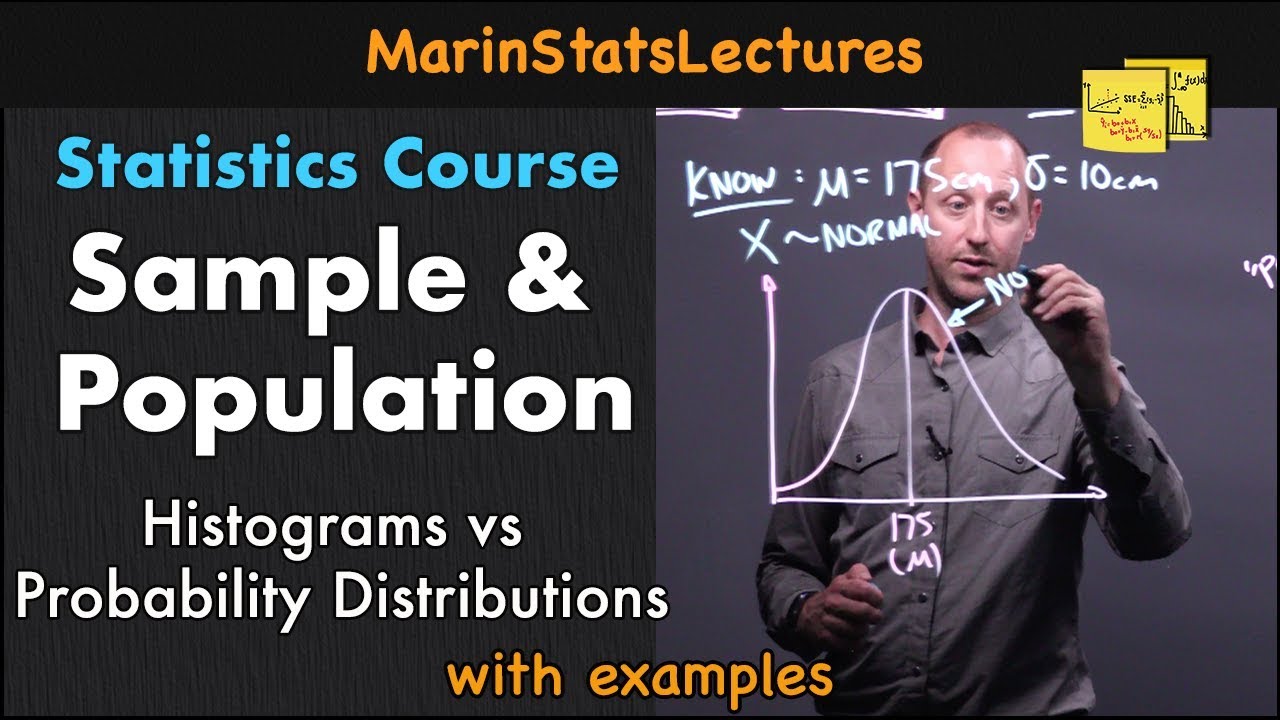
- 📊 Understanding populations and samples is crucial in statistics; we use samples to infer about entire populations since measuring every member is often impractical.
- 🔍 Sample statistics (like mean, standard deviation) are estimates of population parameters, and they can vary with each sample taken.
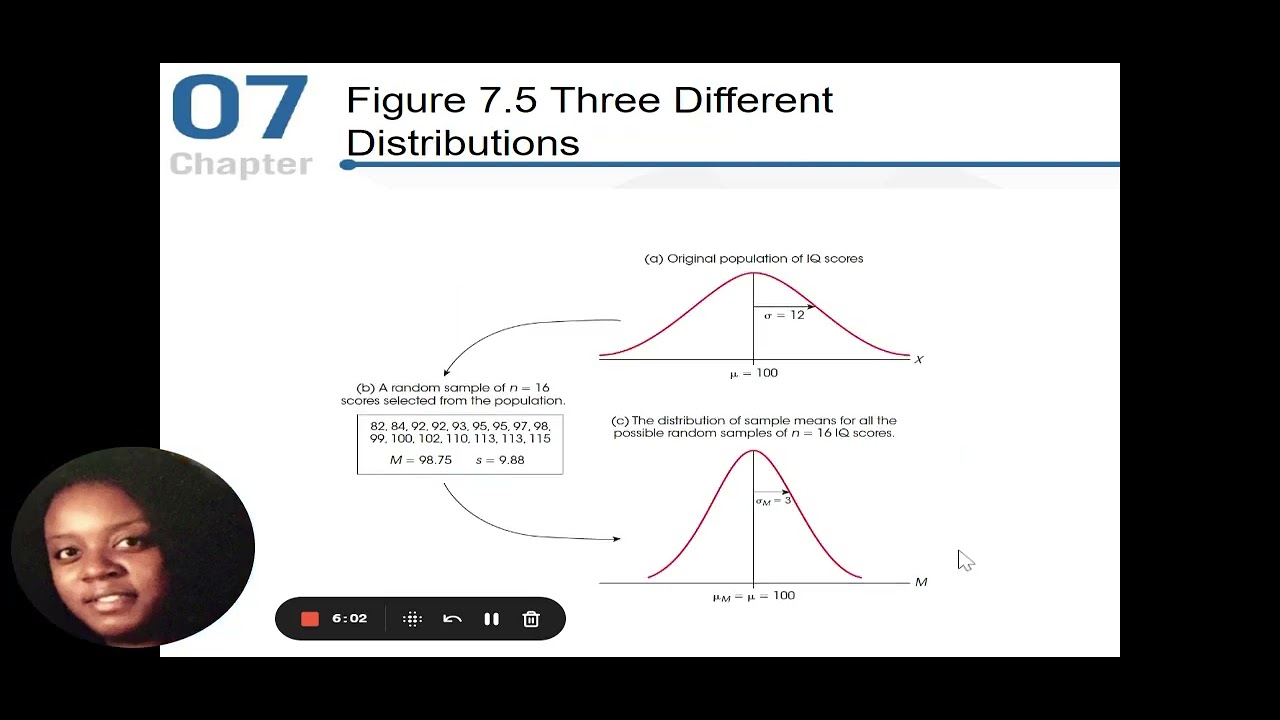
- 📈 The distribution of sample statistics forms a sampling distribution, which shows how sample means vary across different samples.
- 🐱 An example using cat weights illustrates how random samples provide varying mean estimates and how those estimates approach the true population mean with larger sample sizes.
- 💡 The larger the sample size, the more reliable the sample mean will be as an estimate of the true population mean.
- ⚖️ Sample means from multiple samples will converge towards the population mean, demonstrating an unbiased estimate principle.
- 📉 The standard deviation of the sample mean decreases as sample size increases, leading to greater confidence in the estimates.
- 📏 The Central Limit Theorem states that for large enough samples, the distribution of the sample mean will be approximately normal, even if the population distribution is not.
- 🧪 In real-world applications, many data distributions are not normal; however, large sample sizes allow us to treat sample means as normally distributed.
- 🔑 Key takeaway: As sample size increases (typically n ≥ 30), the sampling distribution becomes more normal, enabling effective statistical inference.
Q & A
What is general anesthesia?
-General anesthesia is a medically induced state of unconsciousness accompanied by a loss of sensation throughout the body, typically used during surgical procedures.
What are the common methods of administering general anesthesia?
-General anesthesia can be administered through inhalation of anesthetic gases or intravenous injections of anesthetic drugs.
What is the role of the anesthesiologist during surgery?
-The anesthesiologist is responsible for monitoring the patient's vital signs, managing anesthesia delivery, and ensuring the patient's safety and comfort throughout the surgical procedure.
What are some common anesthetic agents used in general anesthesia?
-Common anesthetic agents include propofol, sevoflurane, desflurane, and isoflurane, each with specific properties and uses.
What are the potential risks associated with general anesthesia?
-Risks may include allergic reactions, respiratory complications, cardiovascular issues, and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
How does an anesthesiologist assess a patient's suitability for general anesthesia?
-An anesthesiologist evaluates the patient's medical history, current health status, and any underlying conditions to determine the appropriateness of general anesthesia.
What is the process of preoperative assessment in anesthesia?
-Preoperative assessment involves reviewing the patient's medical history, conducting a physical examination, and discussing anesthesia options and risks with the patient.
How do anesthetic agents affect the body during surgery?
-Anesthetic agents induce unconsciousness, relax muscles, and inhibit pain responses, ensuring the patient remains unaware of the surgery and does not experience pain.
What are the stages of general anesthesia?
-The stages of general anesthesia include induction (loss of consciousness), maintenance (sustained anesthesia), and emergence (return to consciousness).
What are some common postoperative considerations following general anesthesia?
-Postoperative considerations include monitoring for recovery from anesthesia, managing pain, and observing for any complications such as nausea or respiratory issues.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)