22. Física e Introducción a la Biofísica. Principio de Pascal
Summary
TLDRIn this segment, we explore Pascal's Principle, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid and to the walls of its container. The principle explains that when pressure is applied to a small area within a container, it maintains constancy across different areas. This concept is illustrated with an example of varying surface areas, showing that increasing surface area results in greater force. This principle underpins devices like hydraulic presses and dental chairs, where small forces generate larger ones. The next segment will apply this principle in a practical exercise.
Takeaways
- 📚 Pascal's principle states that the pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted without reduction throughout the fluid and onto the walls of the container.
- 💡 Key terms include pressure, fluid, and transmission without reduction, which are essential to understand the concept.
- 🔑 The pressure in a fluid remains constant throughout, meaning it doesn't diminish as it is transmitted.
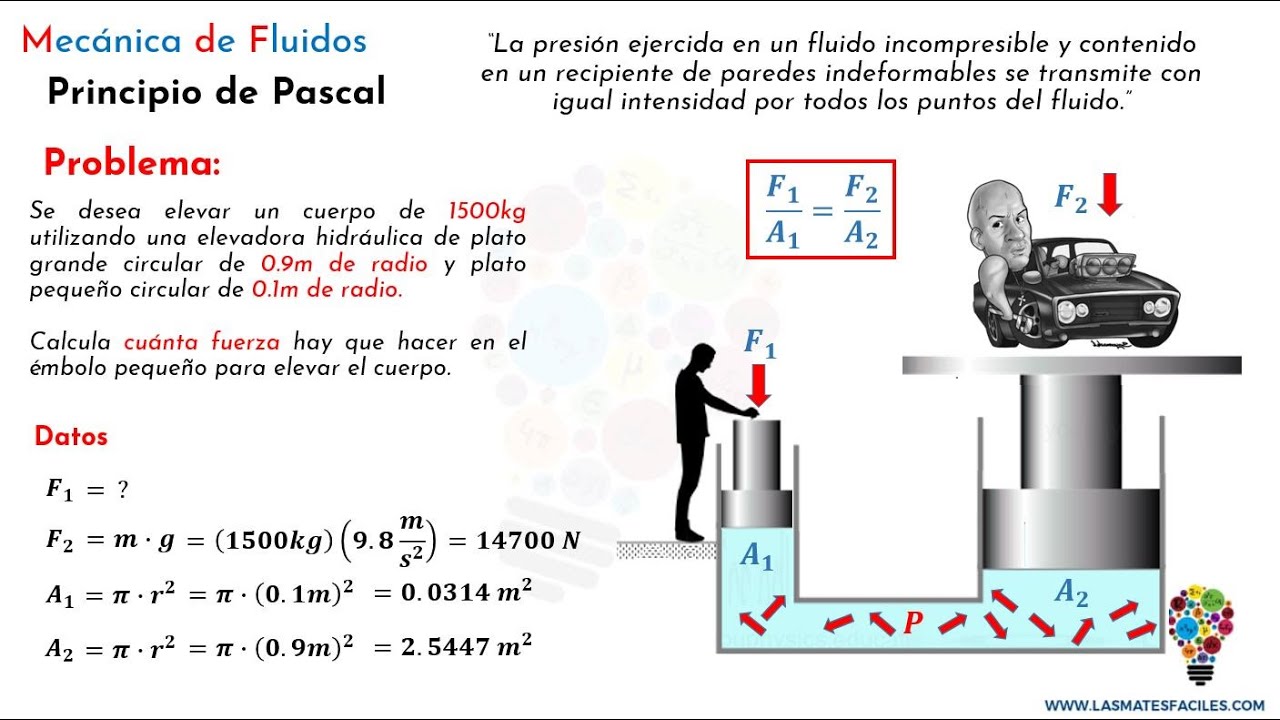
- 📊 The principle can be explained mathematically: Pressure equals force divided by area (P = F/A).
- ⚖️ This equation shows that if the pressure is constant and the area increases, the force must also increase.
- 🛠️ Pascal's principle is the foundation for hydraulic presses, where small forces applied to small areas can result in much larger forces being generated over larger areas.
- 🦷 An example of Pascal's principle in action is the dental chair, where a small force applied to a pedal can lift the entire chair.
- ⚙️ In practical applications, Pascal's principle allows for the amplification of force by manipulating the area of application.
- 🔄 The pressure in a confined fluid is uniformly distributed and maintained across different areas of the container.
- 📘 The next section will cover a practical exercise applying Pascal's principle to solidify understanding.
Q & A
What is Pascal's principle as explained in the transcript?
-Pascal's principle states that the pressure applied to a fluid enclosed in a container is transmitted undiminished to all parts of the liquid and to the walls of the container.
What are the key terms mentioned in Pascal's principle?
-The key terms are 'pressure,' 'fluid,' and the fact that this pressure is transmitted without loss.
How does the transcript explain the relationship between pressure, force, and surface area?
-Pressure is defined as force over surface area. In Pascal's principle, the pressure remains constant, so if the surface area increases, the force must increase to maintain the constant pressure.
What example is given to explain Pascal's principle?
-An example given is the hydraulic press, like the dentist's chair, where a small force applied to a small area can elevate the chair by increasing the surface area, resulting in a greater output force.
What does Pascal's principle suggest about pressure in a fluid-filled container?
-Pascal's principle suggests that the pressure remains constant throughout the fluid in the container.
How is Pascal's principle applied in hydraulic systems?
-In hydraulic systems, a small force applied to a smaller surface area can result in a much larger force if applied to a larger surface area, because pressure is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
What mathematical equation is derived from Pascal's principle in the transcript?
-The equation is: Pressure (P) = Force (F) / Surface Area (A). This leads to the formula: F1/A1 = F2/A2, where pressure is constant.
What happens to the force when the surface area increases in a hydraulic system?
-As the surface area increases, the force also increases to maintain constant pressure.
Why is the pressure described as 'transmitted without loss' in Pascal's principle?
-This means that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, it is spread uniformly throughout the fluid without any decrease in its intensity.
What practical applications are mentioned that use Pascal's principle?
-Hydraulic presses and dentist's chairs are examples where Pascal's principle is applied to increase force with minimal effort.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)