Hukum Pascal (Definisi, Rumus, Aplikasi, dan Contoh Soal)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host explores Blaise Pascal's law of fluid statics, which states that pressure applied to a confined liquid is transmitted equally in all directions. The video uses a hydraulic press as an example to demonstrate how a small force can be amplified over a larger area, resulting in a greater force. The host also discusses the practical applications of Pascal's law in hydraulic jacks and brakes, highlighting its significance in mechanics and its use in various devices like smartphones.
Takeaways
- 💡 Pascal's Law states that the pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
- 🔧 The law was discovered by Blaise Pascal and is fundamental in the study of static fluids.
- 📐 Pressure (P) is defined as force (F) divided by area (A), and this principle applies uniformly throughout the fluid.
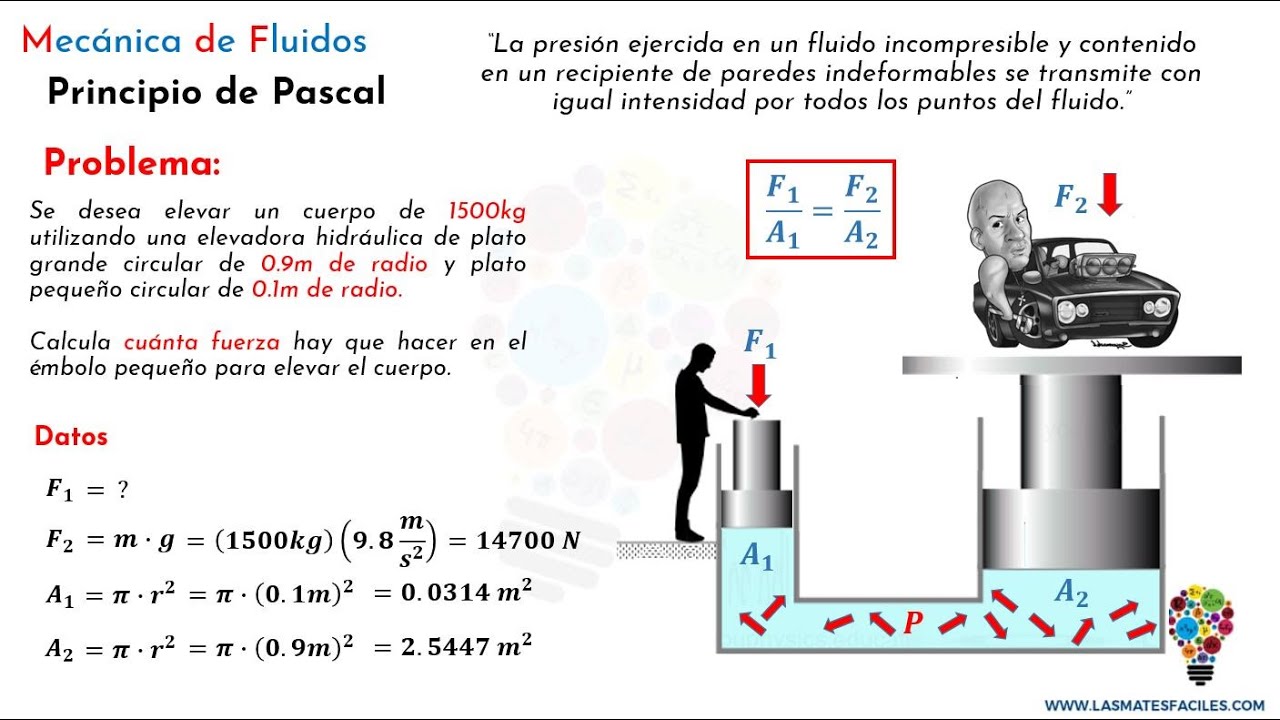
- 🧪 The formula for Pascal's Law can be expressed as P1 = P2, meaning the pressure at two different points in a confined fluid is equal.
- ⚙️ A practical application of Pascal's Law is in hydraulic systems, where a small force applied on a smaller area can produce a larger force over a larger area.
- 📊 The example given shows that applying a force of 1 N over a small area results in a larger force of 3 N when transmitted to a larger area, demonstrating mechanical advantage.
- 🚗 Hydraulic jacks and hydraulic brakes are common examples where Pascal's Law is applied to achieve mechanical advantage.
- 🔄 In the example problem, a hydraulic jack with a small piston diameter of 6 cm and a large piston diameter of 30 cm is used to calculate the output force.
- ⚖️ Using the relationship between the areas of the pistons and the forces applied, the solution shows that a 400 N input force results in an output force of 10,000 N.
- 📚 Pascal's Law is crucial in understanding fluid mechanics and is widely used in hydraulic devices for lifting or applying force efficiently.
Q & A
What is Pascal's Law, as explained in the video?
-Pascal's Law states that pressure exerted on a fluid in a confined space is transmitted equally in all directions within the fluid.
Who discovered Pascal's Law and what does it describe?
-Pascal's Law was discovered by Blaise Pascal. It describes how pressure applied to a fluid in a closed container is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
How is pressure in a fluid transmitted according to Pascal's Law?
-Pressure applied to a fluid in a confined space is transmitted equally in all directions with the same magnitude.
In the video example, how does applying a force F1 on area A1 affect the force on area A2?
-Applying force F1 on area A1 generates a pressure that is transmitted throughout the fluid, producing a larger force F2 on the larger area A2.
What is the formula used in Pascal’s Law to relate force and area?
-The formula used is F1/A1 = F2/A2, where F is the force applied and A is the area.
What mechanical advantage is highlighted in Pascal's Law?
-Pascal’s Law provides a mechanical advantage by allowing a small input force over a small area to generate a larger output force over a larger area.
What practical applications of Pascal’s Law are mentioned in the video?
-Two practical applications mentioned are the hydraulic jack and hydraulic brakes.
How does a hydraulic jack work according to Pascal’s Law?
-A hydraulic jack works by applying a small force on a small area, which is then transmitted through the fluid to produce a larger force on a larger area, lifting heavy objects.
How are hydraulic brakes an application of Pascal's Law?
-Hydraulic brakes apply pressure to a fluid when the brake pedal is pressed. This pressure is transmitted equally to all brake pads, applying force to stop the vehicle.
In the video’s example calculation, what force F2 is generated if F1 is 400 N and A2 is larger than A1?
-In the example, if F1 is 400 N and A2 is larger than A1, the calculated output force F2 is 10,000 N.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hukum Pascal ( Tekanan Zat Dan Penerapannya Dalam Kehidupan Sehari-hari )

FISIKA Kelas 11 - Hukum Pascal | GIA Academy

PERCOBAAN FLUIDA STATIS |HUKUM PASCAL| PERCOBAAN MANOMETER menggunakan suntikan/spui

I fluidi, la pressione, la legge di Pascal e il torchio idraulico
Principio de Pascal. Explicación

PRAKTIKUM JEMBATAN HIDROLIK KELAS XII MIPA 2 TAHUN PELAJARAN 2021/2022
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)