Drawing Tutorial - Understanding Light & Shadows
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how different types of light and shadows influence the shading of objects in art. It covers how light sources create a range of contrasting values that define the form and depth of subjects. The video describes key shading concepts, including direct light, highlights, mid-tones, reflected light, core shadows, and cast shadows. By analyzing how light behaves on simple objects, such as an egg, viewers learn to accurately represent 3D forms in their drawings using light and shadow. Understanding these fundamentals helps artists predict light behavior and improve their shading techniques.
Takeaways
- 💡 Light is fundamental to shading, as it determines what we see in a scene.
- 🌞 The type and intensity of light affect the contrast and values in a drawing.
- 🎨 Values represent the lightness or darkness of a color in shading.
- 🆚 Contrast is the difference in values between light and shadow areas.
- 📏 Directional light behaves consistently across different subjects, allowing artists to predict its effects.
- 🥚 Studying simple objects like spheres or eggs can help understand how light interacts with forms.
- 🌟 Direct light is the area facing the light source and receives the most light.
- ✨ Highlights are the brightest areas, often visible on glossy surfaces.
- 🌈 Mid-tones are the transition areas between light and shadow, often showing the object's local color.
- 🔄 Bounce light is light that is reflected into shadow areas from adjacent surfaces.
- 🗻 Shadows are essential for representing 3D forms and are created by the absence of light.
- 🏴 Core shadows are the darkest part of the shadow where no light reaches.
- 📍 Cast shadows are created when an object blocks light, and occlusion shadows are the darkest part of the cast shadow.
Q & A
What is the primary influence on shading in a scene?
-The primary influence on shading in a scene is the type of light present.
Why is light important in a drawing?
-Without light, nothing would be visible, as it allows us to see the subject and creates the values and contrasts that form the basis of shading.
How does shading help convey information to the viewer?
-Shading helps convey the type of light present and the shape and form of the subject matter through the use of values and contrast.
What are 'values' in the context of shading?
-Values refer to how light or dark a color is in a drawing.
What is contrast in shading?
-Contrast is the amount of difference between light and dark values in a shaded area.
What creates contrasting values in a scene?
-When light hits a subject, it creates a range of contrasting values between light and shadow areas.
How does the type and intensity of light affect contrast?
-The intensity and type of light, such as directional or diffused light, determine the amount of contrast between the light and shadow areas.
What is 'direct light' or 'center light' in shading?
-Direct light, or center light, is the area of a subject that is facing the light source and receives the most light.
What is the role of the 'highlight' in shading?
-The highlight is the brightest area of a form and represents the reflection of the light source. It can shift based on the viewer's perspective and the object's surface texture.
What is 'bounce light' or 'reflected light'?
-Bounce light is light that is reflected off a surface back onto the shadow side of a form, softening the shadow area.
What is a 'core shadow' or 'terminator' in shading?
-The core shadow, or terminator, is the darkest part of a shadow where no direct or reflected light reaches. It is located where the light and shadow meet.
What is a 'cast shadow' and how is it created?
-A cast shadow is a shadow that appears on the surface behind or beneath an object, created by the object blocking light from reaching that surface.
What is 'occlusion shadow' in shading?
-Occlusion shadow is the darkest part of a cast shadow, typically found directly beneath an object where no light is able to reach.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Menggambar Konstruksi:Perspektif dengan Pencahayaan | Video pembelajaran kls 9 | Kurikulum Merdeka

Menggambar Konstruksi Perspektif dengan Pencahayaan - Seni Rupa Kelas 9 Fase D
How To Shade and Render The Body - How To Draw

How to Shade with PENCIL for BEGINNERS
Hand Rendering Basics
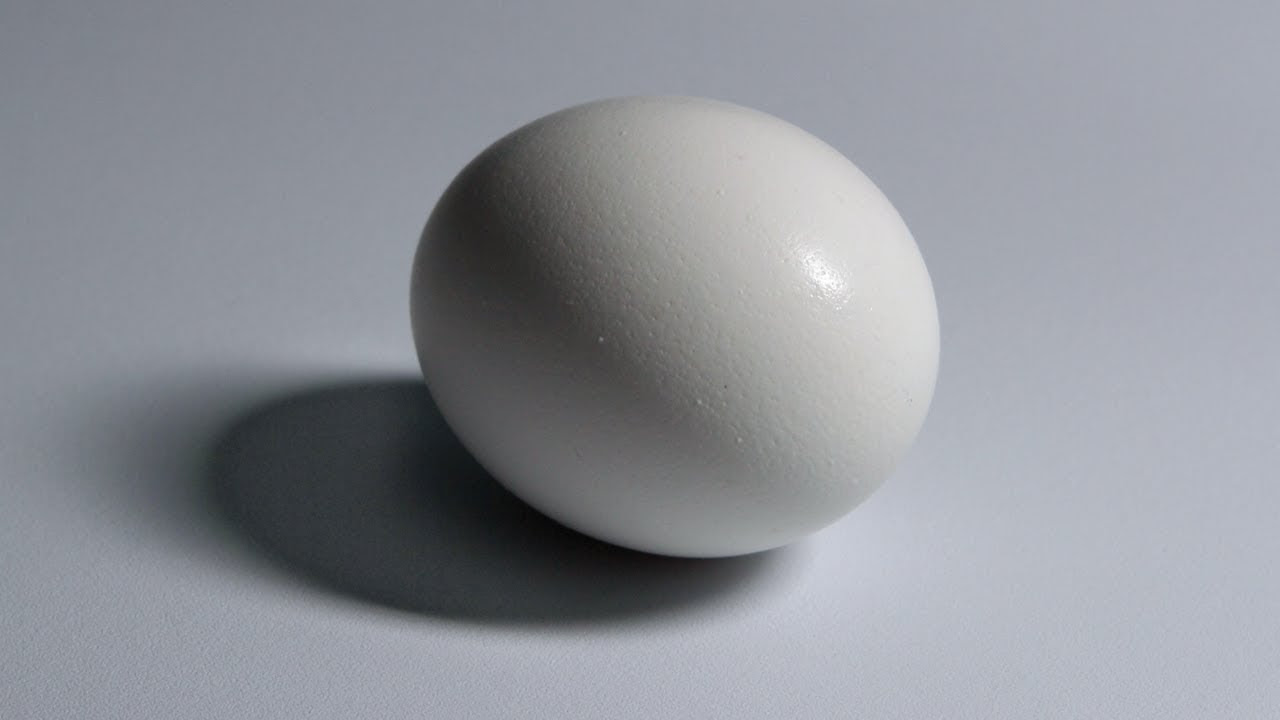

Shading Light and Form - Basics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
