Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (Grade 9)
Summary
TLDRWelcome to Learning Science Channel! Today, we explore photosynthesis and cellular respiration, essential processes for life. Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and carbohydrates using sunlight, while respiration reverses this process to release energy. Both require enzymes and specific conditions, like chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Understanding these cycles is crucial for grasping how energy flows through ecosystems.
Takeaways
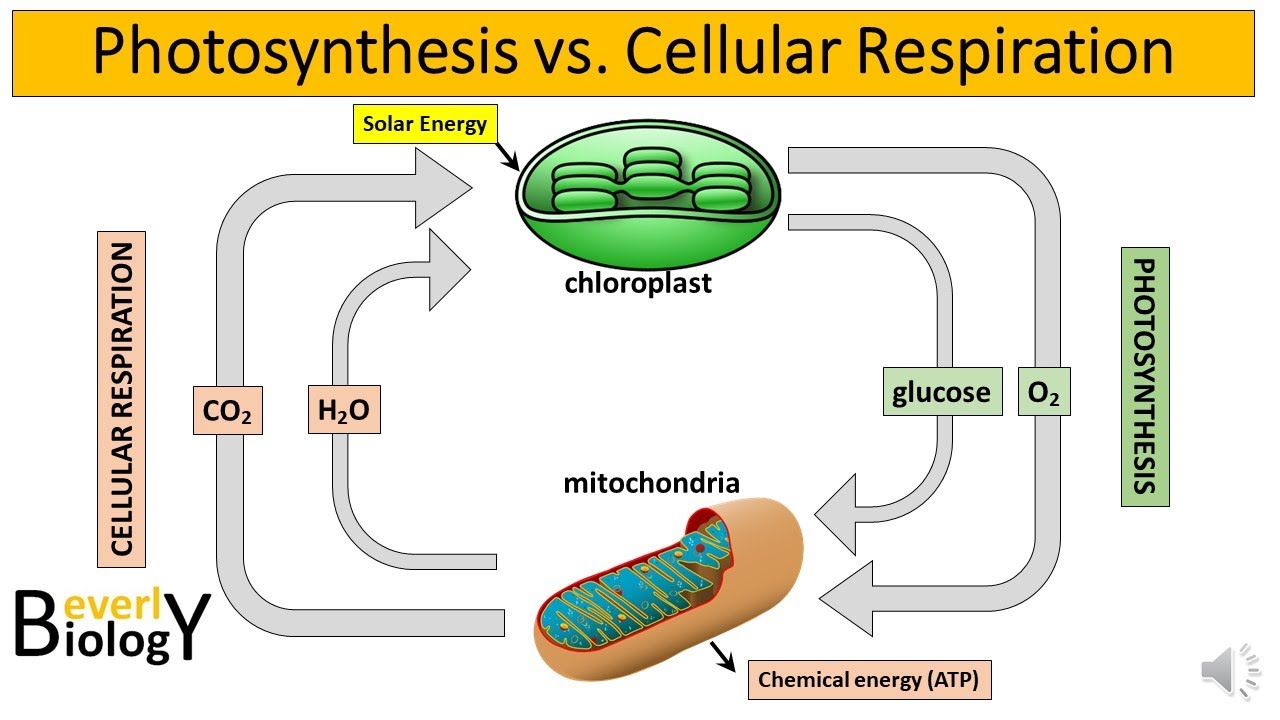
- 🌿 Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and carbohydrates using sunlight.
- 🌱 Cellular respiration is the process where oxygen is combined with carbohydrates to release carbon dioxide and energy.
- 🌍 The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased due to human activities such as the use of fossil fuels.
- 🌱 Plants require sunlight, water, and minerals to grow, and they obtain these elements through photosynthesis.
- 🔍 The chlorophyll pigment in plant chloroplasts plays a crucial role in capturing sunlight for photosynthesis.
- 🔬 Enzymes are necessary catalysts for both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to occur at normal temperatures.
- 🌱 The process of photosynthesis evolved early in Earth's history, and chloroplasts are believed to have evolved from cyanobacteria.
- 🧬 Mitochondria are the sites within cells where cellular respiration occurs, converting food and oxygen into energy.
- 🌱 Plant roots and seeds respire, requiring oxygen, which emphasizes the importance of well-aerated soil for plant health.
- 🌿 In daylight, plants release more oxygen through photosynthesis than they consume through respiration, but they still respire in the dark.
- 🔬 Both photosynthesis and respiration involve the conversion of carbon dioxide and water, but at different stages and for different purposes.
Q & A
What are the main topics covered in today's video on the Learning Science Channel?
-The main topics covered are photosynthesis and cellular respiration, focusing on how stored energy from food is changed to chemical energy for cell use and identifying factors that affect the rate of these processes.
What is the percentage of carbon dioxide in the air today, as mentioned in the script?
-The air contains nearly 0.04% carbon dioxide.
How much carbon dioxide was in the air hundreds of years ago before the use of fossil fuels?
-Hundreds of years ago, before the use of fossil fuels, the air contained only 0.028% carbon dioxide.
What is the most important chemical reaction on the planet according to the script?
-Photosynthesis is referred to as the most important chemical reaction on the planet.
What happens in the chloroplasts of plant leaves during photosynthesis?
-In the chloroplasts, plants use sunlight to pull oxygen away from water and carbon dioxide, allowing the plant to capture the carbon.
What is the name of the process where oxygen is rejoined with a carbohydrate to release energy?
-The process where oxygen is rejoined with a carbohydrate to release energy is called respiration.
What is the simple representation of the carbohydrate molecule mentioned in the script?
-The simple representation of the carbohydrate molecule is CH2O, which stands for a compound of carbon and hydro or water.
What are the two processes that both need catalysts called enzymes to work at normal temperatures?
-The two processes that need enzymes to work at normal temperatures are photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
What pigment is necessary for photosynthesis and what is its active site?
-Chlorophyll is the pigment necessary for photosynthesis, and its active site is a magnesium atom colored green.
How are the chloroplasts in plant leaves related to cyanobacteria?
-The chloroplasts in the green leaves of plants evolved from simple bacteria known as cyanobacteria.
What is the role of oxygen in respiration and how does it relate to the process of combustion?
-In respiration, oxygen is added to the fuel or food, and carbon dioxide is built up. This is similar to combustion, where oxygen is also added to the fuel, but respiration occurs at normal temperatures using enzymes, unlike combustion which requires high temperatures.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration | Week 8 | SCIENCE 9 - QUARTER 1 (MELC 5)

Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Comparison

Science 9: Cellular respiration and its difference from Photosynthesis (Tagalog-English Format)

Grade 9 Science Q1 Ep 7 Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration Part1
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration

Cellular Respiration
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
