Cellular Respiration
Summary
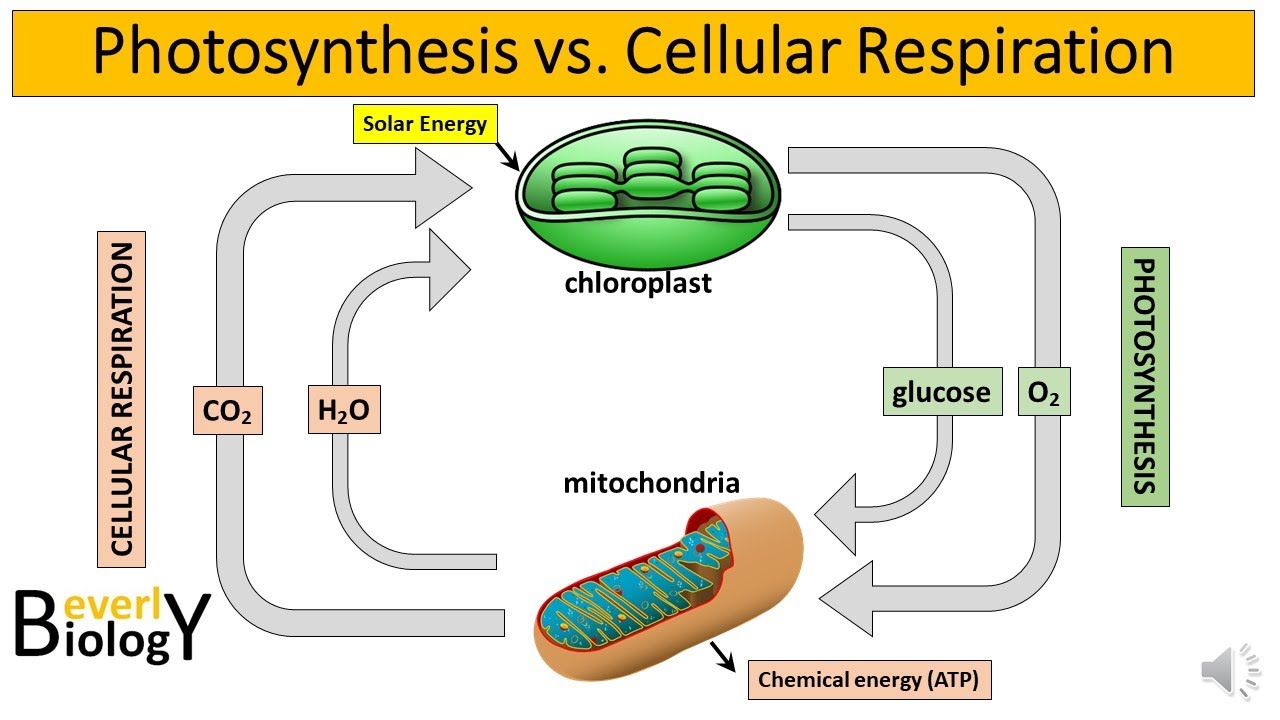
TLDRThis transcript explains the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen, while cellular respiration takes oxygen and glucose to produce water, carbon dioxide, and ATP—the cell's energy. These two processes are cyclical and opposite, supporting life by converting solar energy into usable energy for cells. The transcript also introduces aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, and anaerobic respiration, which doesn't. While anaerobic respiration is less efficient, it allows ATP production when oxygen is scarce.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Plants produce carbohydrates like glucose through photosynthesis.
- 💡 The bonds in glucose are broken down to create ATP, the energy molecule used by cells.
- 🏭 Cellular respiration happens in the mitochondria, where oxygen and glucose are used.
- 🔄 The products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the reactants of cellular respiration, and vice versa.
- ⚡ The main purpose of photosynthesis and cellular respiration is to convert the Sun’s energy into ATP.
- 🌬️ Cellular respiration requires oxygen and produces water, carbon dioxide, and lots of ATP.
- 🧬 Oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration, which is the normal, efficient way cells produce ATP.
- ❌ Anaerobic respiration means 'not requiring oxygen' and occurs when oxygen levels are low.
- ⚙️ Anaerobic respiration is less efficient but allows ATP production in low-oxygen environments.
- 📆 More details on anaerobic respiration will be discussed next time.
Q & A
What is the main product of photosynthesis?
-The main product of photosynthesis is glucose, a carbohydrate.
Where does cellular respiration occur within the cell?
-Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of the cell.
What are the reactants needed for cellular respiration?
-The reactants needed for cellular respiration are oxygen and glucose.
What are the products of cellular respiration?
-The products of cellular respiration are water, carbon dioxide, and lots of ATP (energy).
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
-Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite processes. The products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the reactants for cellular respiration, and vice versa.
What is the overall purpose of photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-The purpose of photosynthesis and cellular respiration is to convert energy from the Sun into ATP, which is the usable energy for cells.
What happens when oxygen is present in cellular respiration?
-When oxygen is present, cells perform aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen and produces a lot of ATP.
What does the term 'anaerobic respiration' mean?
-Anaerobic respiration means 'not requiring oxygen'. It allows cells to make ATP in the absence of oxygen, but it is less efficient.
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
-The equation for photosynthesis is carbon dioxide + water + light energy = glucose + oxygen.
Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient than aerobic respiration?
-Anaerobic respiration is less efficient because it produces much less ATP compared to aerobic respiration, which uses oxygen.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hubungan Respirasi dan Fotosintesis & Tahapan Respirasi

Celademhaling en fotosynthese
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration

Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration

Bioenergetics: The transformation of free energy in living systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
AP Biology Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Complete Review
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)