A "Crash Course" to Spatial Interpolation
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Anastasios Dardis from Ezra Canada explores spatial interpolation in ArcGIS Pro, a technique for estimating values at unsampled locations using geocoded sample points. He explains two main methods: deterministic, which uses mathematical formulas, and geostatistical, employing statistical models with spatial autocorrelation. The tutorial covers popular models like IDW and Kriging, discussing their applications, advantages, and limitations. Dardis also guides viewers through the iterative process of selecting a model, setting parameters, and validating results using cross-validation, ultimately helping users apply spatial interpolation effectively.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Spatial interpolation is a technique used to estimate values at unknown points or areas based on geocoded sample points with known values.
- 📈 It is more efficient and cost-effective to use spatial interpolation to map unknown values at unsampled locations rather than extracting samples at every location.
- 🔍 Spatial interpolation applies Tobler's First Law of Geography, which states that everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things.
- 💧 It is widely used in various disciplines such as hydrology, soil, agriculture, weather, climate, atmosphere, land use, and topography.
- 🛠️ There are two types of spatial interpolation techniques: deterministic (mathematics-based formulas) and geostatistical (statistical models with spatial autocorrelation).
- 📊 Deterministic methods like IDW provide smooth interpolated surfaces and are easier to understand and process, while geostatistical methods like Kriging are more complex but consider distance and variation between data points.
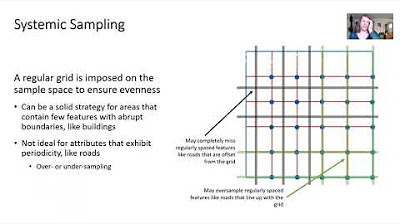
- 📉 IDW is efficient for large datasets and good for high spatial density, but it may not be suitable for small datasets or areas with abrupt changes.
- 🔍 Kriging is excellent for smaller datasets, identifies interpolation errors, and considers spatial autocorrelation, but it can be computationally intensive and requires knowledge of geostatistics.
- 🔄 The process of spatial interpolation is iterative and includes visualizing data, exploring for outliers or skewness, selecting a model, checking its accuracy, and comparing multiple models if necessary.
- 📊 Decision trees developed by ESRI can guide the selection of the most appropriate spatial interpolation model based on various factors such as the type of information required, method complexity, and desired level of smoothness.
- 📈 A semi-variogram is used in geostatistical methods to visualize spatial autocorrelation and help determine parameters such as the sill, range, and nugget effect.
Q & A
What is spatial interpolation?
-Spatial interpolation is a technique that uses geocoded sample points with known values to estimate values at unknown points or areas. It's more efficient and cost-effective than extracting samples at every location.
Why is spatial interpolation important?
-Spatial interpolation is important because it allows for the prediction of values at unsampled locations, which can be costly or impractical to directly measure. It's widely used across various disciplines such as hydrology, soil science, agriculture, weather, and climate.
What is Tobler's First Law of Geography, and how does it relate to spatial interpolation?
-Tobler's First Law of Geography states that 'everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things.' This law is fundamental to spatial interpolation as it suggests that the value at an unknown location can be estimated based on the values of nearby locations.
What are the two types of techniques used in spatial interpolation?
-The two types of techniques used in spatial interpolation are deterministic and geostatistical. Deterministic methods use mathematical formulas, while geostatistical methods use statistical models that consider spatial autocorrelation.
What is the difference between deterministic and geostatistical methods?
-Deterministic methods, like Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW), assign values based on surrounding measured values, and they are smooth and simple to understand. Geostatistical methods, like Kriging, consider distance and variation between known data points, predict with accuracy, and identify interpolation errors, but they are more complex and computationally intensive.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of IDW?
-IDW is efficient for large datasets, easy to understand, and good for high spatial density. However, it is not suitable for small datasets, assumes similar values for closer points (not good for abrupt changes), and does not consider spatial autocorrelation.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Kriging?
-Kriging considers distance and variation between data points, is prediction-based, and identifies interpolation errors. It is excellent for smaller datasets. However, it can be complex, requires knowledge of geostatistics, and cannot identify absolute min or max values outside the current range.
What is the role of cross-validation in spatial interpolation?
-Cross-validation is used to check the accuracy of the spatial interpolation model by comparing the predicted values with the actual values. It helps to fine-tune the model parameters and select the best-performing model.
How does the semi-variogram help in spatial interpolation?
-The semi-variogram visualizes spatial autocorrelation and helps in determining the model parameters such as the sill, range, and nugget. It aids in understanding the spatial structure of the data and in fitting the best semi-variogram model to predict values at unsampled locations.
What are the key parameters to consider when performing spatial interpolation?
-Key parameters include lag size, lag tolerance, direction, angle tolerance, bandwidth, and the type of semi-variogram model (e.g., spherical, Gaussian, exponential). These parameters influence how spatial autocorrelation is measured and how values at unknown locations are predicted.
What tools are available in ArcGIS Pro for spatial interpolation?
-ArcGIS Pro offers the Interpolation toolset in the Spatial Analyst toolbox for deterministic methods, the Interpolation toolset in the Geostatistical Analyst toolbox for geostatistical methods, and the Geostatistical Wizard for an interactive approach to spatial interpolation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)