Intro to Generative AI for Busy People
Summary
TLDRThis video explores generative AI, explaining it as a subset of AI that creates new content like text and images. It highlights the role of GPUs in revolutionizing AI performance and the significance of breakthroughs like the transformer model. The script distinguishes between supervised and unsupervised machine learning, introduces deep learning and neural networks, and explains how generative AI models, like large language models, learn from data to produce new content.
Takeaways
- 🤖 Generative AI refers to creating new content such as text, images, and videos using artificial intelligence.
- 💡 AI is a branch of computer science that aims to make computers behave like humans by understanding language and recognizing objects and patterns.
- 🚀 The recent buzz around generative AI is due to advancements in hardware (GPUs), software, and the availability of large datasets.
- 💼 GPUs are preferred for AI tasks because they can handle many operations simultaneously, unlike CPUs which are better at complex, single tasks.
- 📈 The introduction of transformers in 2016 led to significant breakthroughs in AI, particularly in the development of models like GPT.
- 📚 Large language models (LLMs) are trained on vast amounts of text data from the internet, including books, articles, and Wikipedia.
- 🧠 Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data without explicit programming, similar to human learning.
- 🔍 There are two main types of machine learning models: supervised (data with labels) and unsupervised (data without labels).
- 🧬 Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns from data.
- 🌐 Generative AI is a type of deep learning that can process both labeled and unlabeled data to generate new content.
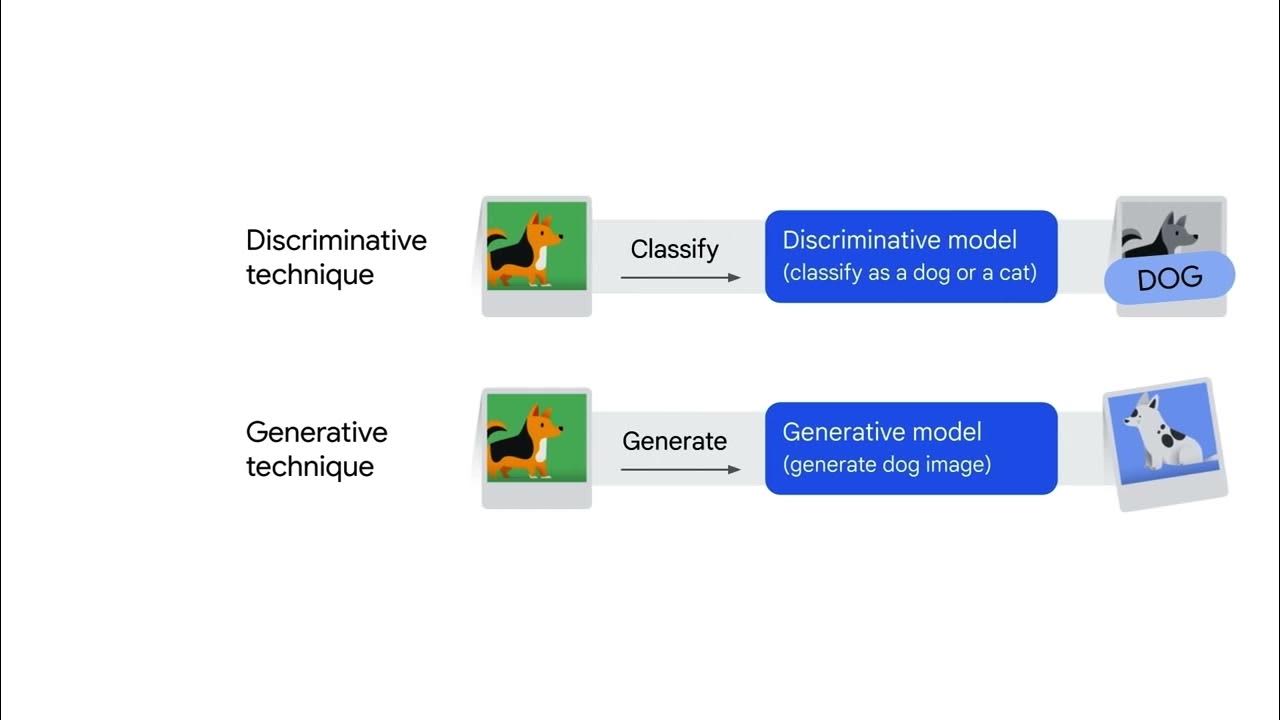
- 🏥 Discriminative models predict labels for data points, while generative models understand and reproduce data characteristics to create new instances.
Q & A
What is generative AI?
-Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content such as text, images, and videos.
What is the difference between a CPU and a GPU?
-A CPU is like a CEO that handles complex tasks one at a time, while a GPU is like a team of workers that can handle many simpler, repetitive tasks simultaneously.
Why are GPUs important for AI?
-GPUs are important for AI because their ability to handle multiple operations at once makes them ideal for tasks such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
What is a transformer in the context of AI?
-A transformer is a significant breakthrough in AI research introduced in 2016, which is the foundation of GPT-Generative Pre-Trained Transformer.
How does a generative AI model like GPD-4 pass tests like the SATs and bar exams?
-GPD-4 passes such tests because it was trained on a large corpus of text data from the internet, including thousands of books, millions of articles, and the entirety of Wikipedia.
What is machine learning and how is it related to AI?
-Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on building systems that learn from data and behave like humans. It allows computers to learn without explicit programming.
What are the two most common types of machine learning models?
-The two most common types of machine learning models are supervised and unsupervised models. Supervised models have labeled data, while unsupervised models have unlabeled data.
How are deep learning and machine learning related?
-Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns from both labeled and unlabeled data.
What are artificial neural networks and how do they work?
-Artificial neural networks are inspired by the human brain and are made up of interconnected nodes called neurons that can learn to perform tasks by processing data and making predictions.
What is the difference between generative and discriminative machine learning models?
-Generative models understand and reproduce the characteristics of data to generate new content, while discriminative models classify or predict labels for data points.
How are large language models like GPT related to generative AI?
-Large language models are a specific type of generative model that focuses on language. They are trained on large amounts of text data and can generate new, coherent text.
What are the key components that have contributed to the rise of generative AI?
-The key components contributing to the rise of generative AI are advancements in hardware (like GPUs), software, and the availability of large amounts of data.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Introduction to Generative AI

Introduction to Generative AI

Generative AI Vs NLP Vs LLM - Explained in less than 2 min !!!

Generative AI Explained In 5 Minutes | What Is GenAI? | Introduction To Generative AI | Simplilearn
Generative AI for Absolute Beginners : Types of Generative AI

Apa Itu Generative AI? Pahami dalam 2 Menit!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
