Generative AI for Absolute Beginners : Types of Generative AI
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the diverse landscape of generative AI, explaining how it creates novel content like text, images, music, and 3D models. It categorizes these AI systems by task output, architecture, learning approach, and modality, highlighting types such as transformer-based models and GANs. The discussion also touches on open-source versus closed-source models and anticipates future advancements, including more powerful multimodal models and energy-efficient AI.
Takeaways
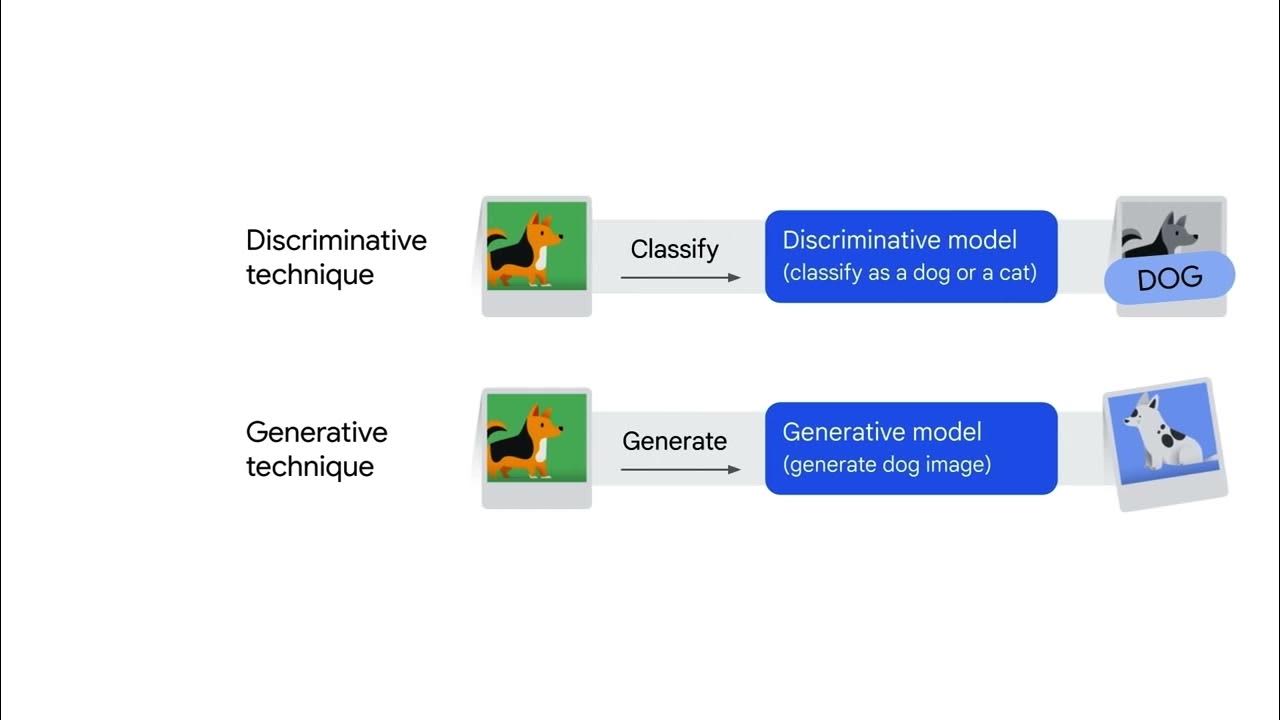
- 🧠 Generative AI is a subset of AI that creates new, original content, unlike conventional AI which primarily analyzes existing data.
- 📄 Text generation models like GPT-3 are used for creative writing and coding, producing human-like text.
- 🖼️ Image generation models such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion create realistic images from text descriptions.
- 🎵 Audio generation systems can produce music, generate speech, or mimic voices, impacting the music industry and aiding speech impairments.
- 🎥 Video generation AI is emerging, creating video clips and animating still images from text descriptions.
- 🤖 Three-dimensional model generation systems are useful in game development, product design, and virtual reality, creating 3D models from descriptions or 2D images.
- 🏗️ Architecture of generative AI systems includes transformer-based models, GANs, VAEs, and diffusion models, each with unique methods for generating content.
- 📚 Learning approaches for generative AI include supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised methods, affecting training and data requirements.
- 🔍 Modality in generative AI refers to the type of data worked with, distinguishing between unimodal systems that handle one data type and multimodal systems that work across different data types.
- 🌐 Open-source versus closed-source generative AI models differ in accessibility, with open-source models offering transparency and community development, while closed-source models provide control and commercialization opportunities.
- 🚀 Future directions for generative AI include more powerful multimodal models, improved control and customization, and the development of energy-efficient models.
Q & A
What is generative AI and how does it differ from conventional AI?
-Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that can create new, original content such as text, images, music, or 3D models. Unlike conventional AI, which primarily analyzes and makes decisions based on existing data, generative AI can produce something entirely new.
What are the different types of content generative AI can produce?
-Generative AI can produce various types of content including text, images, audio, video, and three-dimensional models.
How is generative AI classified by task output?
-Generative AI is classified by task output based on the type of content it generates: text generation, image generation, audio generation, video generation, and three-dimensional model generation.
What is the role of transformer-based models in generative AI?
-Transformer-based models, like GPT, have revolutionized AI, especially in natural language processing. They are excellent at understanding context and generating coherent long-form content.
What are generative adversarial networks (GANs) and how do they work?
-GANs consist of two neural networks: a generator that creates content and a discriminator that tries to distinguish between real and generated content. This adversarial process leads to incredibly realistic outputs, especially in image generation.
What is a variational autoencoder (VAE) and its application in generative AI?
-Variational autoencoders (VAEs) are great at learning compact representations of data and are particularly useful for tasks like image generation and manipulation. They generate new content by sampling from the learned representation.
How do diffusion models function in generative AI?
-Diffusion models learn to generate data by reversing a diffusion process where data is gradually corrupted with noise. The model learns to reverse this corruption step by step, allowing it to generate high-quality samples from random noise.
What is the difference between supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised generative AI?
-Supervised generative AI learns from labeled datasets, unsupervised learns from unlabeled data, and semi-supervised combines both labeled and unlabeled data. Each approach affects how the AI is trained and what kind of data it needs.
What does modality refer to in the context of generative AI?
-Modality refers to the type of data the AI works with. Unimodal generative AI works with a single type of data, while multimodal generative AI can work with multiple types of data, bridging different types of media.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of open-source versus closed-source generative AI?
-Open-source models offer transparency, accessibility, and community development but may have potential misuse and less control. Closed-source models provide control, commercialization opportunities, and potentially reduced risk but are less transparent and accessible.
What are some future directions for the field of generative AI?
-The field of generative AI is evolving towards more powerful multimodal models, improved control and customization, and energy-efficient models, addressing environmental concerns and creating more versatile AI tools.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Intro to Generative AI for Busy People
Introduction to Generative AI

Generative AI Explained In 5 Minutes | What Is GenAI? | Introduction To Generative AI | Simplilearn

Generative AI for Absolute Beginners : Introduction

Introduction to Generative AI

10 INSANE AI Tools You Won't Believe are FREE! AI Tools You Must Try in 2024!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)