Anatomia do Olho - Como Funciona o Olho Humano
Summary
TLDRIn this video, ophthalmologist Cláudio Del Claro explores the intricate anatomy of the human eye, highlighting its divine creation and complex structures. He explains how each part, from the external muscles to the internal components like the cornea, iris, and retina, plays a crucial role in vision. The video emphasizes the eye's sensitivity, its comparison to a high-performance camera, and the importance of eye care, concluding with a call to action for viewers to subscribe for more eye health content.
Takeaways
- 👁 The human eye is a divine creation and a fantastic organ, providing us with our primary sense of vision.
- 🤔 The eye, despite being small, contains highly complex structures with high metabolic cells, inspiring the invention of the camera.
- 👀 The eye's sensitivity is about 600 times greater than a camera, demonstrating its superior visual capabilities.
- 🔄 The eye's muscles allow for symmetrical and simultaneous movement, ensuring coordinated vision.
- 🛡️ The eye is protected by the orbit, a bony cavity in the skull, and surrounded by fat and orbital skin.
- 👓 Eyelids serve to cover and protect the eyeball, with a blink reflex to prevent foreign objects from entering.
- 🌞 Eyelashes protect the eyes from light and debris, enhancing protection.
- 💧 Blinking helps to spread tears across the eye surface, lubricating and cleaning the eye, which is crucial for eye health.
- 🌈 The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by constricting or dilating the pupil, similar to a camera's diaphragm.
- 🔍 The lens of the eye adjusts focus by contracting and relaxing, similar to a camera's zoom function.
- 👁️🗨️ The retina is the eye's primary organ of vision, capturing light stimuli and transmitting them to the brain via the optic nerve.
Q & A
What makes the human eye such a remarkable organ according to the video?
-The human eye is described as a perfect creation, complex and capable of giving us our primary sense: vision. Its structures are incredibly intricate, and even though cameras have been modeled after the eye, they are still far less sensitive, with the eye being around 600 times more sensitive than a camera.
How does the musculature of the eye function to move it?
-The external muscles of the eye move it in various directions—up, down, left, right, and diagonally. These muscles work simultaneously, meaning when one eye moves in a direction, the other follows in sync, maintaining symmetrical and coordinated movements.
What role do the eyelids play in protecting the eyes?
-Eyelids protect the eyes by covering them, preventing foreign objects from entering. They also blink reflexively when anything approaches the eye, acting as a defense mechanism. Additionally, they help keep the eyes moist by spreading tears over the surface.
Why are eyelashes and eyebrows important for eye protection?
-Eyelashes help block dust, pollen, and other particles from entering the eyes, acting like a protective screen. Eyebrows help prevent sweat and rain from running into the eyes, offering further protection from external elements.
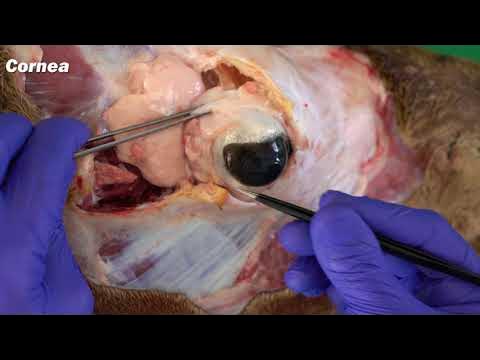
What is the function of the cornea, and why is it crucial for vision?
-The cornea is the eye's most powerful lens, playing a critical role in focusing light onto the retina. Any injury or irregularity in the cornea can severely impact vision, causing blurriness or distortion. It is also highly sensitive, filled with nerve endings that make even minor injuries very painful.
How does the iris control the amount of light entering the eye?
-The iris, the colored part of the eye, controls the size of the pupil to regulate light entry. In bright conditions, it contracts to reduce the light entering the eye, while in darker conditions, it dilates to let more light in, functioning similarly to a camera’s aperture.
What role does the crystalline lens play in vision?
-The crystalline lens focuses light onto the retina by adjusting its shape to accommodate near and far objects. It works like the zoom function on a camera, changing its shape to help the eye focus at different distances.
What is the function of the vitreous body in the eye?
-The vitreous body is a transparent gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina, helping maintain the eye’s shape. It also provides cushioning to protect the retina from potential damage in case of injury.
What happens in the retina, and why is it considered the key structure for vision?
-The retina contains photoreceptors that capture light and convert it into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The retina is essential for processing visual information, and any issues with it can severely affect vision.
What is the optic nerve’s role in the visual process?
-The optic nerve transmits visual information from the retina to the brain, where it is processed into recognizable images. Any damage to the optic nerve can disrupt this process, leading to vision loss, which is a major concern in conditions like glaucoma.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)