How Does an MRI Scan Work?
Summary
TLDRThe MRI process utilizes the abundant protons in the human body, which have a magnetic charge due to their spin. When subjected to a strong magnetic field in an MRI machine, these protons align. A radiofrequency pulse then disrupts their alignment, causing them to realign with the magnetic field after the pulse ends, releasing electromagnetic energy. This energy is detected by the MRI, which differentiates tissues based on their energy release speed, providing detailed images.
Takeaways
- 🧲 MRIs rely on the magnetic properties of protons, which are plentiful in the human body.
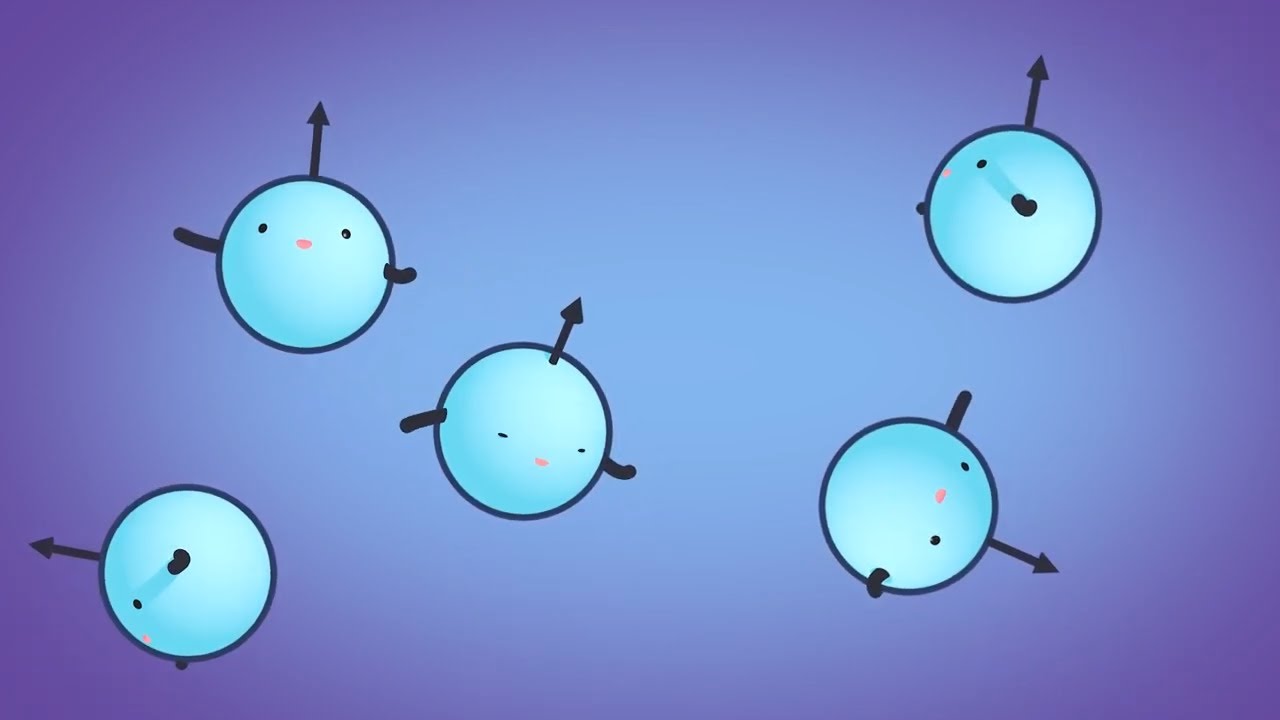
- 🌀 Protons in the body naturally spin, creating a magnetic charge.
- 📡 The MRI machine uses a strong magnetic field to align the protons.
- 🔄 A radiofrequency pulse is introduced to disrupt the alignment of protons.
- 🔄 The pulse can force protons to realign at a 90 or 180-degree angle to the static magnetic field.
- ⏺ Once the radiofrequency pulse is turned off, protons return to their original alignment with the magnetic field.
- 🌐 The realignment of protons releases electromagnetic energy, which the MRI detects.
- 🔎 The MRI differentiates tissues based on the rate at which they release energy after the pulse.
- 🏥 This technology is crucial for medical imaging as it allows for detailed visualization of internal body structures.
- 📈 The speed of energy release is indicative of different tissue types, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Q & A
What are the primary particles used in MRI imaging?
-The primary particles used in MRI imaging are protons, which are abundant in the human body.
How do protons in the human body contribute to MRI imaging?
-Protons in the human body spin, creating a small magnetic charge, which is utilized in MRI imaging.
What happens to protons when a strong magnetic field is introduced during an MRI scan?
-When a strong magnetic field is introduced, protons align with that field, which is part of the MRI scanning process.
What is the purpose of the radiofrequency pulse used by the MRI technician?
-The radiofrequency pulse is used to disrupt the alignment of protons, forcing them into a 90 or 180-degree realignment with the static magnetic field.
Why do protons realign with the magnetic field after the radiofrequency pulse is turned off?
-Protons realign with the magnetic field because the radiofrequency pulse pushes them against their natural alignment, and once the pulse is off, they return to their original state.
What energy is released by protons as they realign with the magnetic field?
-As protons realign with the magnetic field, they release electromagnetic energy, which is detected by the MRI machine.
How does MRI differentiate between various tissues?
-MRI differentiates between various tissues based on how quickly they release energy after the radiofrequency pulse is turned off.
What is the significance of the speed at which protons release energy in MRI imaging?
-The speed at which protons release energy is significant because it allows the MRI to distinguish between different types of tissues, providing detailed images.
How does the MRI machine detect the electromagnetic energy released by protons?
-The MRI machine detects the electromagnetic energy released by protons using sensitive detectors that pick up the signals emitted as the protons realign.
What role does the static magnetic field play in the MRI process?
-The static magnetic field plays a crucial role in the MRI process by providing the initial alignment for protons and serving as the reference for their realignment during the scan.
Can the MRI technique be used to visualize other types of particles besides protons?
-While protons are the most commonly used particles in MRI due to their abundance in water and fat, other types of particles with nuclear magnetic properties can theoretically be used, though they are less common.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Spin, Precession, Resonance and Flip Angle | MRI Physics Course | Radiology Physics Course #3
MRI Physics | Magnetic Resonance and Spin Echo Sequences - Johns Hopkins Radiology

Wie funktioniert MRT? Die Basics

T2 Relaxation, Spin-spin Relaxation, Free Induction Decay, Transverse Decay | MRI Physics Course #4

Signal Processing in MRIs

Prinsip Dasar Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) #MRI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
