CSEC Chemistry: Extracting Sucrose from Sugarcane
Summary
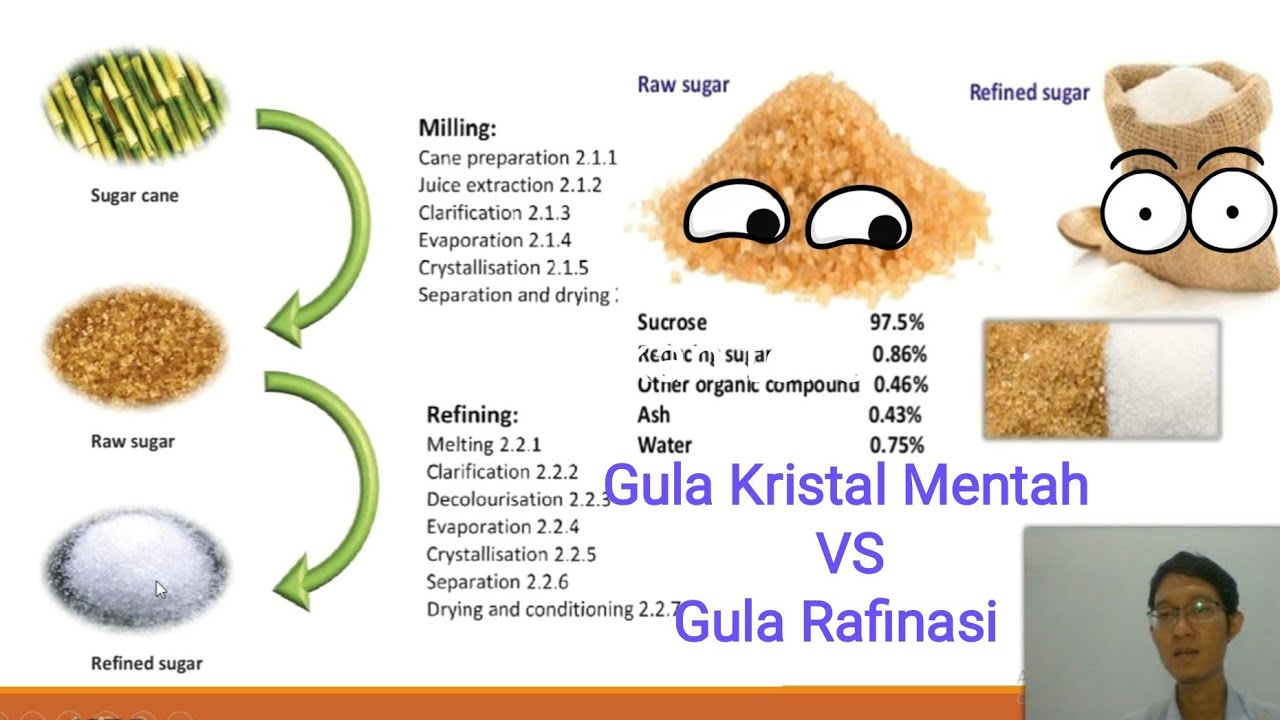
TLDRThis video from the Caribbean Toots series dives into the process of extracting sucrose from sugarcane, covering the steps from harvesting to centrifugation. It begins with cutting sugarcane at a feeder table, crushing it in a roller mill, and spraying with water to release sucrose. The process continues with burning bagasse for energy, using calcium hydroxide in a settling tank to precipitate impurities and neutralize acidity, filtering through a rotary filter, and concentrating the juice in evaporators. The syrup then crystallizes in a vacuum pan, and finally, molasses and sugar crystals are separated by centrifugation, yielding sucrose and byproducts like molasses for further use.
Takeaways
- 🌿 The process of extracting sucrose from sugarcane involves several steps, starting with obtaining sugarcane from the fields.
- ✂️ At the feeder table, sugarcane stalks are cut into smaller pieces to facilitate easier manipulation.
- 🔧 The roller mill crushes the small pieces of sugarcane and sprays them with water to help dissolve the sucrose from the sugarcane cells.
- 🔥 The crushed sugarcane, or bagasse, is used as fuel in furnaces, which generates heat for evaporation and electricity.
- 💧 The dilute juice from the roller mill is treated in a settling tank with calcium hydroxide to precipitate impurities and neutralize acidity.
- 🚱 The rotary filter is used to separate solid particles from the liquid, removing the mud impurities from the juice.
- 🔬 The clear juice is then sent to boilers or evaporators where vacuum distillation occurs to concentrate the sugar and remove excess water.
- 🍯 The concentrated juice, or syrup, is sent to a vacuum pan where crystallization takes place to form sugar crystals.
- 🌀 Centrifugation is used to separate molasses from sugar crystals, resulting in a mixture that can be further processed.
- 🔄 The molasses can be reprocessed in the vacuum pan for further crystallization to extract more sugar crystals.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of the process described in the script?
-The primary goal of the process is to extract sucrose from sugarcane.
What is the first step in the process of extracting sucrose from sugarcane?
-The first step is to get sugarcane from the fields and cut the stalks into smaller pieces at a feeder table.
What happens to the sugarcane stalks after they are cut into smaller pieces?
-The smaller pieces are crushed and sprayed with water in a roller mill to release the sucrose from the sugarcane cells.
What is the purpose of the bagasse produced after the crushing process?
-The bagasse is sent to a furnace where it is burned to generate heat for evaporating water and producing electricity.
Why is calcium hydroxide added to the dilute juice in the settling tank?
-Calcium hydroxide is added to precipitate impurities and neutralize the acidity of the juice, preventing the sucrose from breaking down into glucose and fructose.
How are the mud impurities removed from the juice after the settling tank process?
-The mud impurities are removed through filtration using a rotary filter.
What happens to the clear juice after filtration?
-The clear juice is sent to boilers or evaporators for vacuum distillation to concentrate the juice by removing most of the water.
What is the main process that occurs in a vacuum pan?
-The main process in a vacuum pan is crystallization, where the concentrated juice is turned into sugar crystals.
What is the final step in the extraction process described in the script?
-The final step is centrifugation, which separates the molasses from the sugar crystals.
What can be done with the molasses after it is separated from the sugar crystals?
-The molasses can be further processed to produce alcohol or used as animal feed, and the sugar crystals can be sent to supermarkets or stores.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)