How It's Made: Sugar
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate process of sugar production, from harvesting to packaging. It highlights the roles of sugar cane and sugar beets, the steps involved in cleaning, crushing, extracting juice, and refining sugar, and the techniques of crystallization and centrifugation. The video also discusses the importance of sugar in the food industry, not just as a sweetener but also for its preservative, texture-enhancing, and flavoring properties. The complex steps demonstrate the extensive work behind the sugar you use daily, from the fields to your cup of coffee.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sugar plays a crucial role in the food industry, serving as a preservative, sweetener, texture enhancer, and coloring and flavoring agent.
- 😀 Sugar is primarily obtained from sugar cane and sugar beets, which have been cultivated for thousands of years, with sugar cane being domesticated around 8000 BC.
- 😀 The first sugar cane in America was planted in Louisiana in 1751, establishing a thriving sugar industry in the U.S.
- 😀 The sugar production process involves harvesting sugar cane and sugar beets, followed by thorough cleaning to remove dirt and impurities.
- 😀 After cleaning, sugar cane is crushed using mechanical crushers, and sugar beets are sliced into smaller cassettes to facilitate juice extraction.
- 😀 Juice extraction from both sugar cane and sugar beets is a vital step, involving complex milling and washing processes to separate juice from fibers.
- 😀 The juice extracted from sugar cane is filtered, purified, and clarified through sulfidation and carbonation processes to remove non-sugar impurities.
- 😀 Once purified, the juice undergoes evaporation in vacuum evaporators to create a sugar syrup with a high sugar content.
- 😀 Crystallization follows, where syrup is evaporated until sugar crystals form, using a seeding process to promote crystal growth.
- 😀 After crystallization, centrifugation is employed to separate sugar crystals from molasses, with high-speed centrifuges ensuring efficient separation.
- 😀 The final steps in sugar production include drying the crystals to remove moisture, sorting them by size, and packaging the sugar for sale to consumers.
Q & A
What role does sugar play in the food industry?
-Sugar plays a critical role in the food industry by serving as a preservative, sweetener, texture enhancer, and coloring and flavoring agent.
What are the two main natural sources of sugar?
-The two main natural sources of sugar are sugar cane and sugar beets.
When was sugar first domesticated, and by whom?
-Sugar was first domesticated by native New Guineans around 8000 BC, making it one of the oldest products in existence.
When was the first American sugar cane planted, and where?
-The first American sugar cane was planted in Louisiana in 1751, launching the nation's sugar industry.
What percentage of the world's sugar production comes from sugarcane?
-Around 80% of the total sugar produced worldwide comes from sugarcane, with the remaining portion coming from sugar beets.
What is the first step in the sugar production process?
-The first step in the sugar production process is harvesting, where sugar cane and sugar beets are collected.
How is sugar cane harvested?
-Sugar cane is harvested by mechanized harvesters that cut the stalks into short pieces, called billets, and remove the leafy tops.
What is the cleaning process for sugar cane and sugar beets before processing?
-The raw sugar cane and sugar beets are cleaned by washing them in water-filled flues or rotating drums to remove dirt and impurities.
What happens after the sugar juice is extracted from the plants?
-Once the sugar juice is extracted, it is filtered, clarified, and boiled to separate non-sugar components and reduce protein content before crystallization.
How are sugar crystals formed in the production process?
-Sugar crystals are formed through a process called seeding, where a milky suspension of pure sucrose is added to the syrup, allowing tiny grains to form and attract sugar to create crystals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sering Dikonsumsi, Tapi Ga Tau Prosessnya? Begini Cara Kerja Mesin Gula Pasir Dari Awal Hingga Akhir

How Modern Factory Producing Crystal Sugar Efficiently?

Manisnya Potensi Gula Aren Khas Lombok | Amazing Indonesia Nusa Tenggara Barat

Chemistry Sugar Cane

Pabrik Pembuatan Gula Pasir | SI UNYIL (17/03/20) PART 1
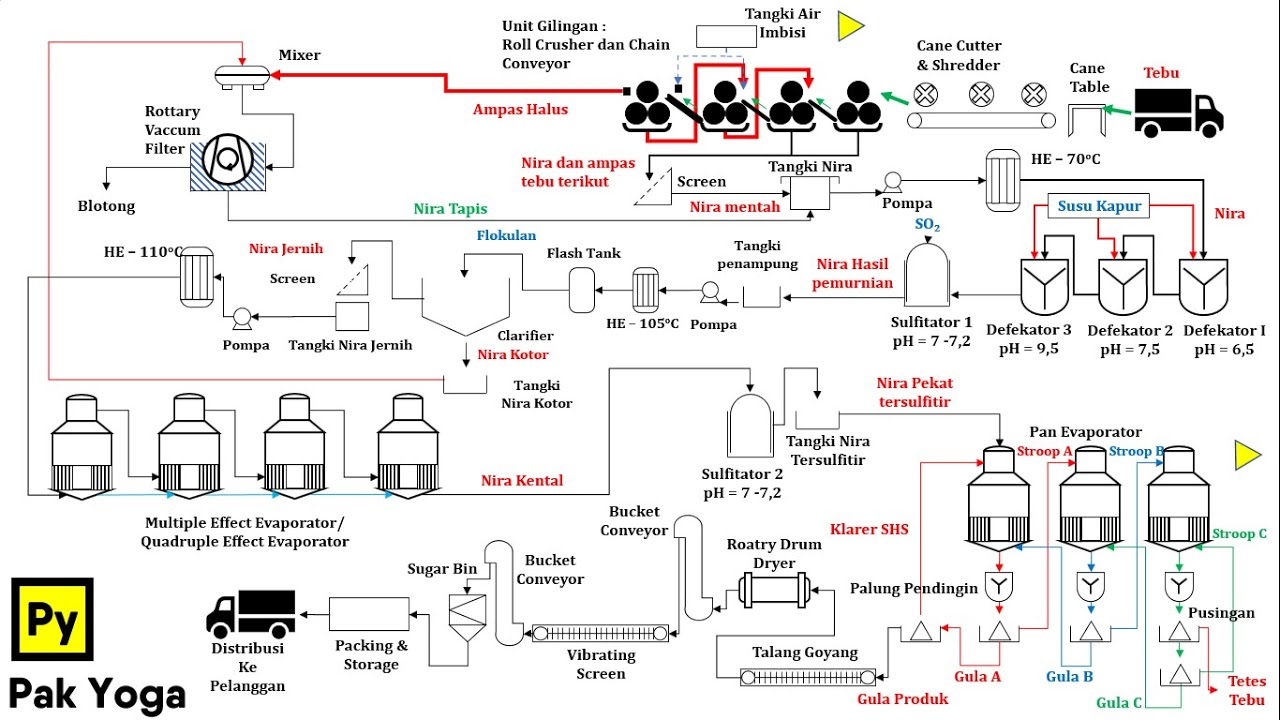
Kimia Industri - Diagram Alir Proses Pembuatan Gula tebu
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)