Hunter-Gatherers and the Neolithic Revolution
Summary
TLDRThis episode explores the evolution of humans from hunter-gatherer societies to the advent of agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution. It discusses human origins in Africa, the Out of Africa migration, and the shift to a settled lifestyle with the discovery of farming. The video highlights how this transition led to the development of cities, technological advancements, and the emergence of social classes, contrasting the benefits and challenges it brought to human existence.
Takeaways
- 🌏 The first humans evolved in Africa at least 195,000 years ago, with the oldest known fossil being 'OMA one' discovered by Richard Leakey.
- 🧬 Mitochondrial DNA suggests humans could be as old as 338,000 years, but archaeological evidence is yet to confirm this.
- 🌱 The 'Out of Africa' theory posits that humans originated in Africa and migrated to all other continents, driven by population pressure and resource scarcity.
- 🌐 Humans reached Asia around 100,000 years ago, Australia around 50,000 years ago, and the Americas around 14,000 years ago during the Ice Age.
- 🏞️ Hunter-gatherer societies, the first on Earth, were nomadic due to the need to follow food sources, which limited their technological advancements.
- 🔍 Hunter-gatherers had a division of labor with men hunting and tool-making, and women gathering food, making clothing, and tending to children.
- 🍲 Persistence hunting was a method used by early humans, leveraging bipedalism and superior stamina to outlast prey.
- 🌾 The Neolithic Revolution, marked by the discovery of agriculture around 10,000 BCE in southern Iraq, led to permanent settlements and the formation of cities.
- 🏛️ The establishment of agriculture allowed for food surplus, storage, and the growth of the global population, but also introduced new risks like famine and disease.
- 🏗️ With the advent of agriculture, technology advanced, and social classes emerged, leading to inequality and the end of the egalitarian nature of hunter-gatherer societies.
Q & A
How old are humans according to fossil records?
-Fossil records show that humans evolved at least 195,000 years ago.
Who discovered the fossilized remains of OHA-1, and in which year?
-Archaeologist Richard Leakey discovered the fossilized remains of OHA-1 in 1967 CE.
Where were the oldest human remains, OHA-1, found?
-The oldest human remains, OHA-1, were discovered within the lower Omo Valley in modern-day Ethiopia.
What does the Out of Africa theory propose about human origins and migration?
-The Out of Africa theory states that humans originated in Africa and migrated to other continents by walking.
How did population pressure influence the movement of early humans?
-Population pressure, due to slow population growth and scarcity of resources, forced early humans to move and migrate to new areas for survival.
What challenges did the Ice Age pose to early humans migrating to Europe?
-The Ice Age made the Northern Hemisphere extremely cold, covered in glaciers and ice sheets, which early humans had to cross to reach Europe.
How did the lifestyle of hunter-gatherer societies limit their technological advancements?
-The nomadic lifestyle of hunter-gatherer societies, due to the need to follow food sources, limited their ability to develop advanced technologies.
What is the significance of the Neolithic Revolution in human history?
-The Neolithic Revolution marked the discovery of agriculture, which revolutionized human existence by allowing the establishment of permanent residences and the formation of cities.
How did the Neolithic Revolution impact the global population and the risk of famine?
-The Neolithic Revolution allowed for the growth of a surplus of food, leading to an increase in the global population, but also made humans vulnerable to environmental changes that could lead to famine.
What were the social implications of the shift from hunter-gatherer societies to agricultural societies?
-The shift to agricultural societies led to the formation of social classes, the emergence of new jobs, and a move away from egalitarianism, as some jobs became more valued than others.
How did the adoption of agriculture affect the health and lifestyle of early humans?
-Agriculture led to a less active lifestyle, poorer diet, and increased health issues such as cavities, obesity, and heart disease, compared to the hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

The Neolithic Age Explained: Global History Review
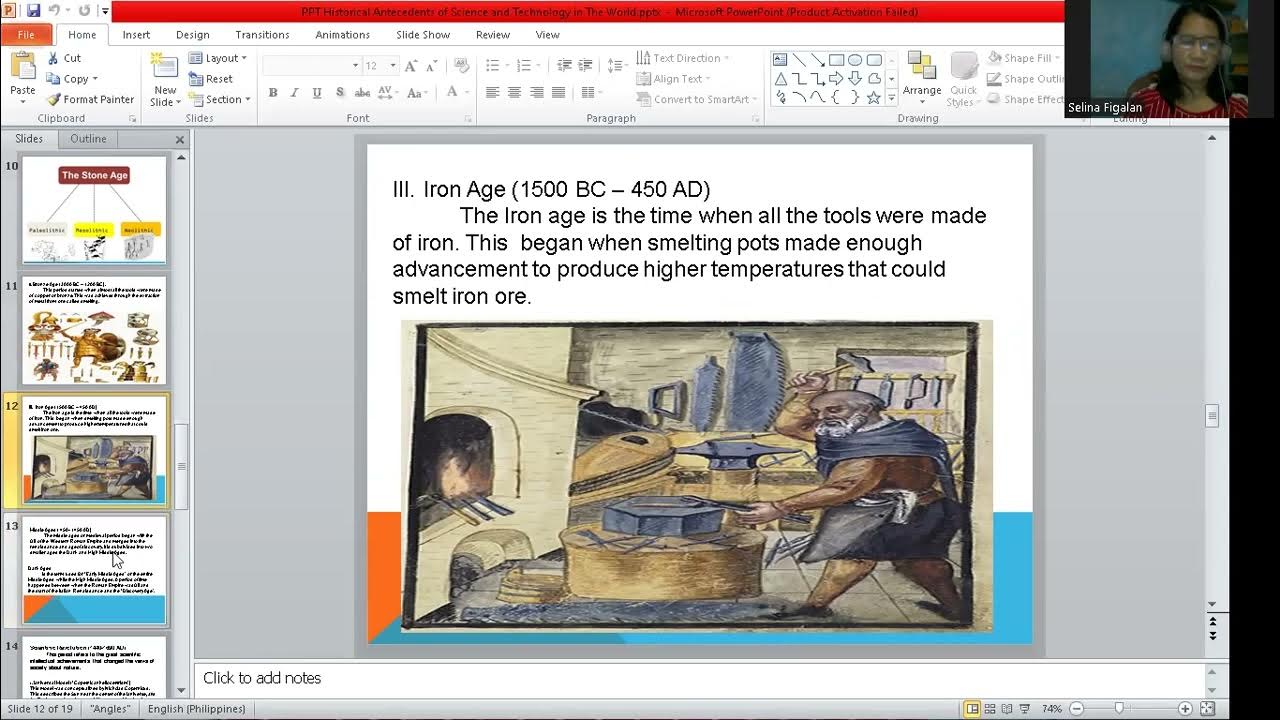
Historical Antecedents of Science and Technology in the World

arte prehistorico

Cultural and Sociopolitical Evolution - Understanding Culture, Society and Politics | Galaxy

#1 The origin of botany | Pioneering Botanists and Their Times

Chapter 1: First Peoples, First Farmers
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
