Sin Cos Tan
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial simplifies the understanding of the six basic trigonometric functions using the mnemonic 'sohcahtoa'. It breaks down the sine, cosine, and tangent by relating them to the sides of a right-angled triangle, labeling the hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent sides accordingly. The script then calculates these functions for a given angle 'a', and demonstrates how to derive the remaining three functions—cosecant, secant, and cotangent—by inverting the ratios of the initial three, providing a clear and memorable method for students to grasp these mathematical concepts.
Takeaways
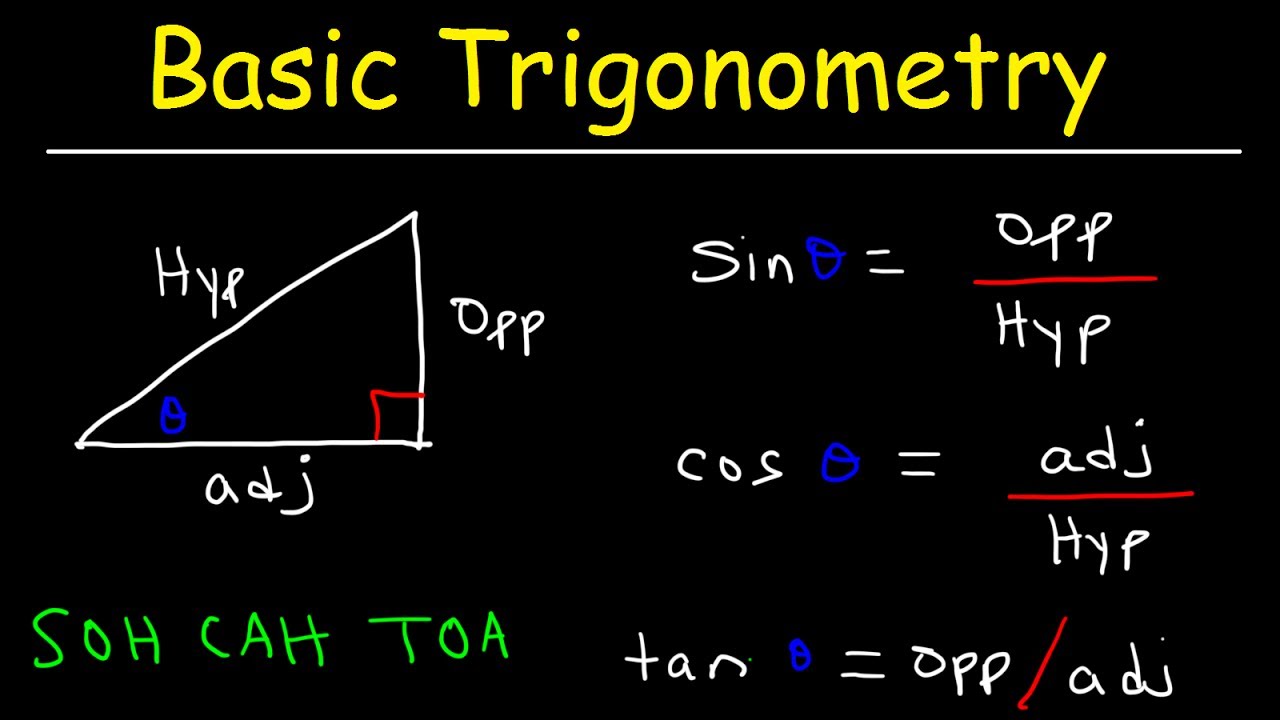
- 📚 The video teaches the six basic trigonometric functions using the mnemonic 'sohcahtoa'.
- 📝 'Soh' stands for sine, which is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse.
- 📝 'Cah' stands for cosine, representing the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse.
- 📝 'Toa' stands for tangent, which is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side.
- 📐 The video demonstrates how to label the sides of a right triangle for trigonometric calculations.
- 📏 The hypotenuse is the longest side and is found opposite the 90-degree angle.
- 📏 The opposite side is the one directly opposite the angle in question.
- 📏 The adjacent side is the one touching the angle but not the hypotenuse.
- 🔢 The sine of angle 'a' is calculated as the opposite side (3) over the hypotenuse (5), resulting in 3/5.
- 🔢 The cosine of angle 'a' is the adjacent side (4) over the hypotenuse (5), resulting in 4/5.
- 🔢 The tangent of angle 'a' is the opposite side (3) over the adjacent side (4), resulting in 3/4.
- 🔄 Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine, so if sine is 3/5, cosecant is 5/3.
- 🔄 Secant is the reciprocal of cosine, so if cosine is 4/5, secant is 5/4.
- 🔄 Cotangent is the reciprocal of tangent, so if tangent is 3/4, cotangent is 4/3.
Q & A
What are the six basic trigonometric functions?
-The six basic trigonometric functions are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot).
What is the mnemonic 'sohcahtoa' used for?
-The mnemonic 'sohcahtoa' is used to help remember the equations for the sine, cosine, and tangent functions, where 'S' stands for sine, 'O' for opposite, 'H' for hypotenuse, 'C' for cosine, 'A' for adjacent, and 'T' for tangent.
How is the sine of an angle calculated in a right triangle?
-The sine of an angle in a right triangle is calculated as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
What is the formula for cosine in the context of the provided script?
-The cosine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
How do you find the tangent of an angle in a right triangle?
-The tangent of an angle is found by dividing the length of the side opposite the angle by the length of the adjacent side.
What is the hypotenuse in a right triangle?
-The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle, which is opposite the right angle.
How do you label the sides of a right triangle when finding trigonometric functions?
-You label the hypotenuse with 'hyp', the opposite side with 'OPP', and the adjacent side with 'adj'.
What is the cosecant of an angle and how is it related to the sine function?
-The cosecant of an angle is the reciprocal of the sine function, meaning if the sine is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, the cosecant is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side.
How do you calculate the secant of an angle?
-The secant of an angle is the reciprocal of the cosine function, which is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the adjacent side.
What is the cotangent of an angle and how is it found?
-The cotangent of an angle is the reciprocal of the tangent function, which is the ratio of the adjacent side to the opposite side.
In the script, what is the length of the hypotenuse when finding the trigonometric functions for angle a?
-In the script, the length of the hypotenuse is given as 5 units.
What are the lengths of the sides opposite and adjacent to angle a in the script's example?
-In the script's example, the length of the side opposite angle a is 3 units, and the length of the adjacent side is 4 units.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Trigonometry For Beginners!

Identitas Trigonometri | Matematika Wajib Kelas X
Trigonometric Functions: Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, and Cotangent

Basic trigonometry II | Basic trigonometry | Trigonometry | Khan Academy
Super Hexagon for Trigonometric Identities | Trigonometry | Infinity Learn
Círculo unitario. Definición de funciones trigonométricas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
