Peripheral Cables - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.1
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the evolution of USB standards from USB 1.1 to USB 3.2, highlighting the speed and cable length advancements, and the introduction of USB-C connectors. It also covers the Thunderbolt technology, detailing its high-speed data and power capabilities, and the transition to USB-C. The script briefly touches on older serial connections like RS-232 and their current uses.
Takeaways
- 🔌 USB is a standard method for connecting peripherals to computers, with various versions offering different speeds and cable lengths.
- 🚀 USB 1.1 had two speeds: low speed at 1.5 Mbps with a 3m cable and full speed at 12 Mbps with a 5m cable.
- ⏫ USB 2.0 increased the speed to 480 Mbps over a 5m cable, improving upon USB 1.1.
- 🔄 USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, supports 5 Gbps over a typically 3m cable, with a different connector design to accommodate higher speeds.
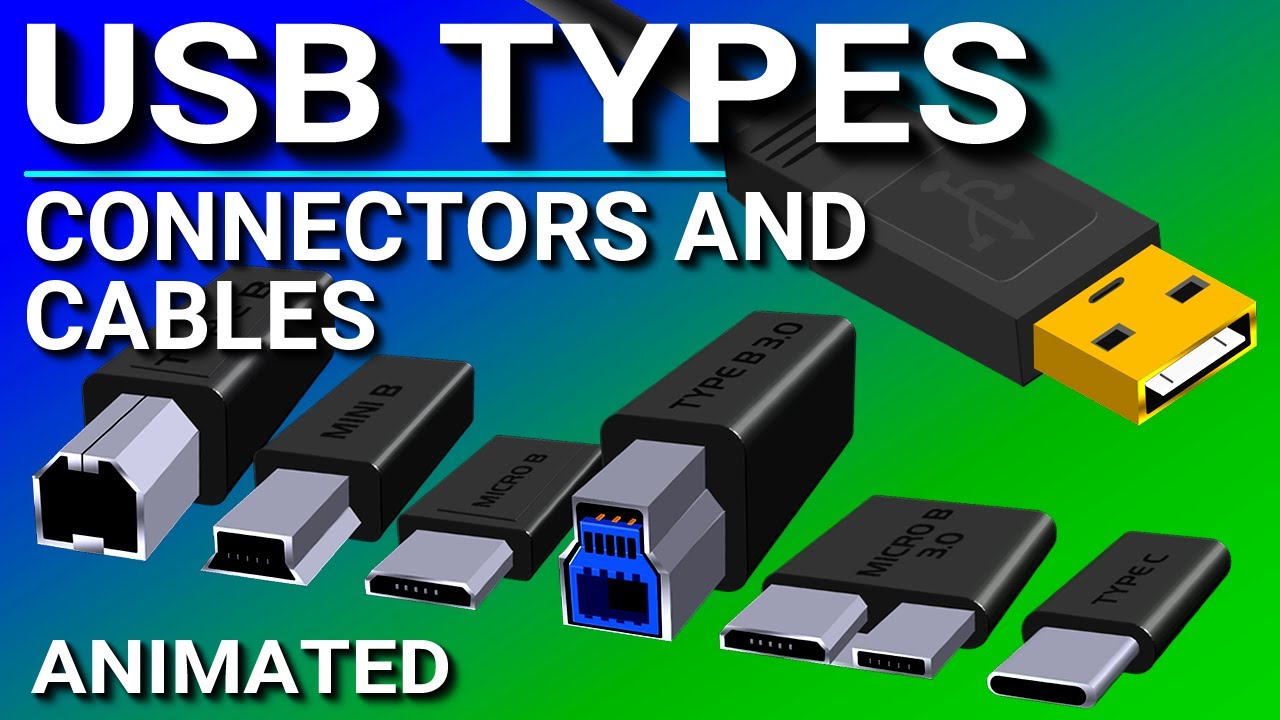
- 🔌 USB connectors have evolved from Standard-A, Standard-B, Mini-B, and Micro-B to the newer USB-C, which is reversible and can handle various signal types including data and video.
- 🔄 USB-C is a significant change, being a symmetric connector that works in any orientation and supports higher data rates.
- 📈 With the advent of USB 3.2, the naming conventions were updated, with USB 3.1 Gen 1 becoming USB 3.2 Gen 1 and USB 3.1 Gen 2 becoming USB 3.2 Gen 2, offering higher throughputs.
- 🔗 Thunderbolt is a high-speed connection technology that can carry both data and power, with versions 1-3 offering increasing speeds and using different physical connectors, including mini DisplayPort and USB-C.
- 🌐 Thunderbolt 3 provides a 40 Gbps throughput using USB-C connectors and supports daisy-chaining up to six devices.
- 🔌 Before USB, serial connections such as DB-9 and DB-25 were common for peripherals like modems, using RS-232 for serial communication.
- 🔄 USB standards have continually evolved to accommodate higher speeds and new types of signals, reflecting the changing needs of technology and peripherals.
Q & A
What is USB and what is its primary use?
-USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, and it is primarily used for connecting peripherals such as mice, keyboards, printers, and other devices to computers.
What were the two different speeds of USB 1.1?
-USB 1.1 had two speeds: low speed at 1.5 megabits per second and full speed at 12 megabits per second.
What is the maximum cable length for USB 1.1 low speed and full speed versions?
-The maximum cable length for USB 1.1 low speed is around 3 meters, while for the full speed version, it is 5 meters.
How does USB 2.0 differ from USB 1.1 in terms of speed and cable length?
-USB 2.0 increased the maximum speed to 480 megabits per second and maintained the maximum cable length of 5 meters.
What is the term used to refer to the upgraded version of USB 2.0?
-The upgraded version of USB 2.0 is referred to as USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB.
What is the maximum data transfer speed supported by USB 3.0 over a typical cable length?
-USB 3.0 supports a maximum data transfer speed of 5 gigabits per second over a typical cable length of about 3 meters.
What are the common connectors used in USB 1.1 and 2.0 versions?
-Common connectors in USB 1.1 and 2.0 versions include the Standard-A plug, Standard-B plug, Mini-B plug, and Micro-B plug.
How did USB 3.0 change the connectors to support higher speeds?
-USB 3.0 introduced new connector designs, such as the USB 3.0 Standard-B and Micro-B plugs, which are different from their USB 2.0 counterparts to support higher speeds.
What is the main advantage of the USB-C connector over previous USB connectors?
-The main advantage of the USB-C connector is its symmetric design, allowing it to be plugged in any orientation without worrying about top or bottom.
What does USB-C allow in addition to data transfer?
-In addition to data transfer, USB-C allows the transmission of video and other signals.
How have the names of USB standards evolved with the introduction of USB 3.1 and USB 3.2?
-With the introduction of USB 3.1, USB 3.0 was renamed to USB 3.1 Gen 1, and USB 3.1 Gen 2 became USB 3.2 Gen 2. USB 3.2 also introduced USB 3.2 Gen 1x2, which doubles the throughput of Gen 1 to 10 gigabits per second.
What is Thunderbolt and how does it differ from USB in terms of data transfer capabilities?
-Thunderbolt is a high-speed serial connection capable of combining data and power on the same cable. Thunderbolt 3, for example, provides a total aggregated throughput of 40 gigabits per second, which is higher than USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 standards.
What are the physical connection types used by Thunderbolt in its early versions?
-Early versions of Thunderbolt used mini DisplayPort as the physical connection type.
What is the maximum cable length for Thunderbolt connections over copper and fiber?
-For copper connections, the maximum cable length is 3 meters, and for fiber connections, it is 60 meters.
How many devices can be daisy-chained together using Thunderbolt?
-Up to six different devices can be daisy-chained together using Thunderbolt.
What were the common serial connections used before the advent of USB?
-Before USB, nine-pin and 25-pin serial connections, such as DB-9 and DB-25 connectors, were commonly used for RS-232 serial communication, often for connecting modems.
What is the current common use of DB-9 and DB-25 connectors?
-DB-9 and DB-25 connectors are currently commonly used to connect to serial consoles on peripheral devices like switches, routers, or firewalls for command-line configuration.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)