USB ports, cables and colours explained
Summary
TLDRIn this tech tutorial, Daniel from TwinBytes explains the evolution of USB ports, covering types, speeds, and colors. Starting with USB 1.0 in 1996, the video progresses through each version, highlighting the increase in data transfer rates and changes in port colors and designs. USB 3.2 and beyond are discussed, with a focus on the universal Type-C connector and speeds reaching 40 Gigabits per second. The tutorial also touches on 'always-on' ports, which provide power even when the computer is off.
Takeaways
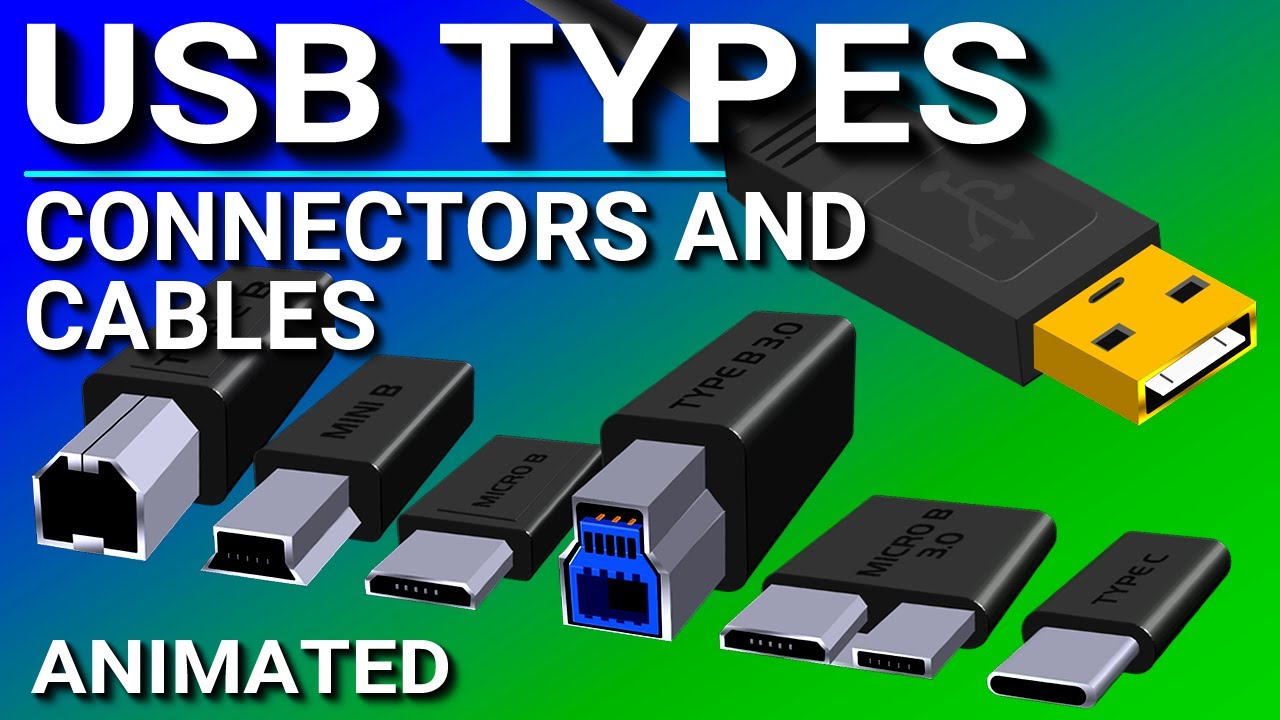
- 🔌 USB ports come in various types, each designed for specific devices, such as Type A for computers, Type B for printers, Mini and Micro series for phones, and Type C for a wide range of devices.
- 🌈 USB port colors often indicate their version: white for USB 1.0/1.1, black for USB 2.0, blue for USB 3.0, teal blue for USB 3.1, and red for USB 3.2.
- 🚀 USB 1.0, introduced in 1996, had speeds from 1.5 to 12 megabits per second, with a maximum cable length of 3 to 5 meters.
- 🌟 USB 2.0, released in 2000, increased speeds up to 480 megabits per second and introduced the ability to charge batteries through USB ports.
- 🎯 USB 3.0, launched in 2008, boasted speeds of up to 5 gigabits per second but was limited by physical symbol encoding, reducing effective speed to about 3.2 gigabits.
- 💡 USB 3.1, introduced in 2013, doubled the speed to 10 gigabits per second and slightly reduced the maximum cable length to 3 meters.
- 🔝 USB 3.2, released in 2017, further doubled the speed to 20 gigabits per second, maintaining the 3-meter maximum cable length.
- 🔄 USB4, announced in 2019, doubled the speed again to 40 gigabits per second, with a continued maximum cable length of 5 meters.
- 🔑 USB Type C connectors are reversible, allowing for plug-and-play without worrying about orientation, and are becoming standard for new devices.
- ⚡ Some USB ports may be yellow or orange, indicating they provide 'always-on' power, useful for charging devices even when the computer is off.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video by Daniel from TwinBytes?
-The main topic of the video is an explanation of different USB port types, their speeds, colors, history, and the future of USB technology.
What is the purpose of the Type A USB connector?
-The Type A USB connector is typically used to plug into a computer.
Which USB type is commonly used for printers?
-Type B USB connectors are commonly used for printers.
What was the primary use of Mini series USB connectors?
-The Mini series USB connectors were primarily used for old phones, with Mini A and B being the specific types, where B was more commonly used.
What is unique about the USB Type C connector?
-USB Type C connectors are unique because they are reversible, meaning they can be plugged in either way without being upside down.
What is the significance of a black USB port on a computer?
-A black USB port on a computer typically indicates that it is a USB 2.0 port.
What was the original speed range of USB 1.0?
-The original speed range of USB 1.0 was from 1.5 megabit per second up to 12 megabit per second.
When was USB 3.0 introduced and what was its maximum speed?
-USB 3.0 was introduced in November 2008, and its maximum speed was up to five Gigabit per second.
What color typically identifies a USB 3.2 port on a computer?
-A red port on a computer typically identifies it as a USB 3.2 port.
What is the maximum speed of USB 4.0 as introduced in August 2019?
-The maximum speed of USB 4.0, introduced in August 2019, is 40 Gigabit per second.
What does a yellow USB port indicate?
-A yellow USB port indicates that it is always on, allowing devices to be charged even when the computer is turned off.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
USB Ports, Cables, Types, & Connectors

Motherboard I/O Ports Explained: What Every Port Does and How to Use Them!
Serial transmission vs parallel transmission
¿Qué y cuáles son los conectores de la computadora?

KVM 101 - Starter Kit | What you need to know and why it matters

Lo que nadie te cuenta del Motor 2 Tiempos, 🤯 Distintos tipos, Escapes, Funcionamiento.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)