Two-sample t test for difference of means | AP Statistics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, the audience is guided through a two-sample T-test to determine if there's a significant difference in the sizes of tomato plants grown in two separate fields. The instructor assumes all conditions for inference are met, including random sampling, normality, and independence. With a significance level of 0.05, the T-test is conducted, resulting in a T-statistic of -2.44. A P-value of approximately 0.024 is calculated, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis, thus suggesting a difference in plant sizes between the fields.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The scenario involves Kaito growing tomatoes in two fields and wanting to know if there's a difference in plant sizes.
- 🔍 Kaito takes random samples from each field and measures the heights to compare them.
- 📊 A two-sample T-test is suggested to determine if there's a significant difference in plant sizes between the fields.
- 📚 The conditions for inference, including randomness, normality, and independence, are assumed to be met.
- 🔑 The significance level for the test is set at 0.05, which is the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis.
- ❓ The null hypothesis states that there is no difference in mean sizes between the two fields.
- 🚫 The alternative hypothesis posits that there is a difference in the mean sizes of the tomato plants in the two fields.
- 📐 The T statistic is calculated using the difference in sample means over an estimate of the standard deviation of the sampling distribution.
- 📈 The formula for the T statistic includes the sum of squared sample standard deviations divided by their respective sample sizes.
- 🔢 The calculated T statistic for the given data is approximately -2.44.
- 📉 The probability of obtaining a T value with an absolute value of 2.44 or more is found to be approximately 0.024.
- 🚫 The P-value (0.024) is less than the significance level (0.05), leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis.
- 🌟 The conclusion suggests that there is evidence of a difference in the sizes of tomato plants between the two fields.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the video script?
-The main objective of the video script is to guide the viewer through conducting a two-sample T-test to determine if there is a significant difference in the sizes of tomato plants grown in two separate fields.
What are the assumptions made before conducting the two-sample T-test?
-The assumptions made before conducting the two-sample T-test are that the random condition, normal condition, and independent condition for inference are met.
What is the significance level used in the T-test?
-The significance level used in the T-test is 0.05.
What is the null hypothesis in this context?
-The null hypothesis is that there is no difference between the mean sizes of tomato plants in field A and field B, meaning the mean size in field A is equal to the mean size in field B.
What is the alternative hypothesis in this scenario?
-The alternative hypothesis is that the mean sizes of tomato plants in field A are not equal to the mean sizes in field B, indicating a difference between the two fields.
How is the T statistic calculated in a two-sample T-test?
-The T statistic is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the estimated standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the difference of the sample means, which is the square root of the sum of the squared sample standard deviations divided by their respective sample sizes.
What sample data is used to calculate the T statistic in the script?
-The sample data used includes the mean heights of plants in both fields (1.3 for field A and 1.6 for field B), the sample standard deviations (0.5 for field A and 0.3 for field B), and the sample sizes (22 for field A and 24 for field B).
What is the calculated T statistic value in the script?
-The calculated T statistic value is approximately -2.44.
How is the probability associated with the T statistic determined?
-The probability is determined by using a calculator to find the cumulative distribution function for the T distribution and then multiplying the result by two to account for both tails of the distribution.
What is the degrees of freedom used in the T-test?
-The degrees of freedom used in the T-test is the smaller of the two sample sizes minus one, which in this case is 21 (22 - 1).
What conclusion is drawn from the P-value compared to the significance level?
-Since the P-value (approximately 0.024) is less than the significance level (0.05), the null hypothesis is rejected, suggesting that there is indeed a difference between the sizes of tomato plants in the two fields.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

T-Tests: A Matched Pair Made in Heaven: Crash Course Statistics #27

Independent-Samples T Test - Pertemuan 7

How to Perform and Interpret Independent Sample T-Test in SPSS
STATISTIKA - Uji T Sampel Bebas (Independent Samples T Test) Perhitungan Manual

UJi - T Menggunakan Excel || T-Test Two Sample
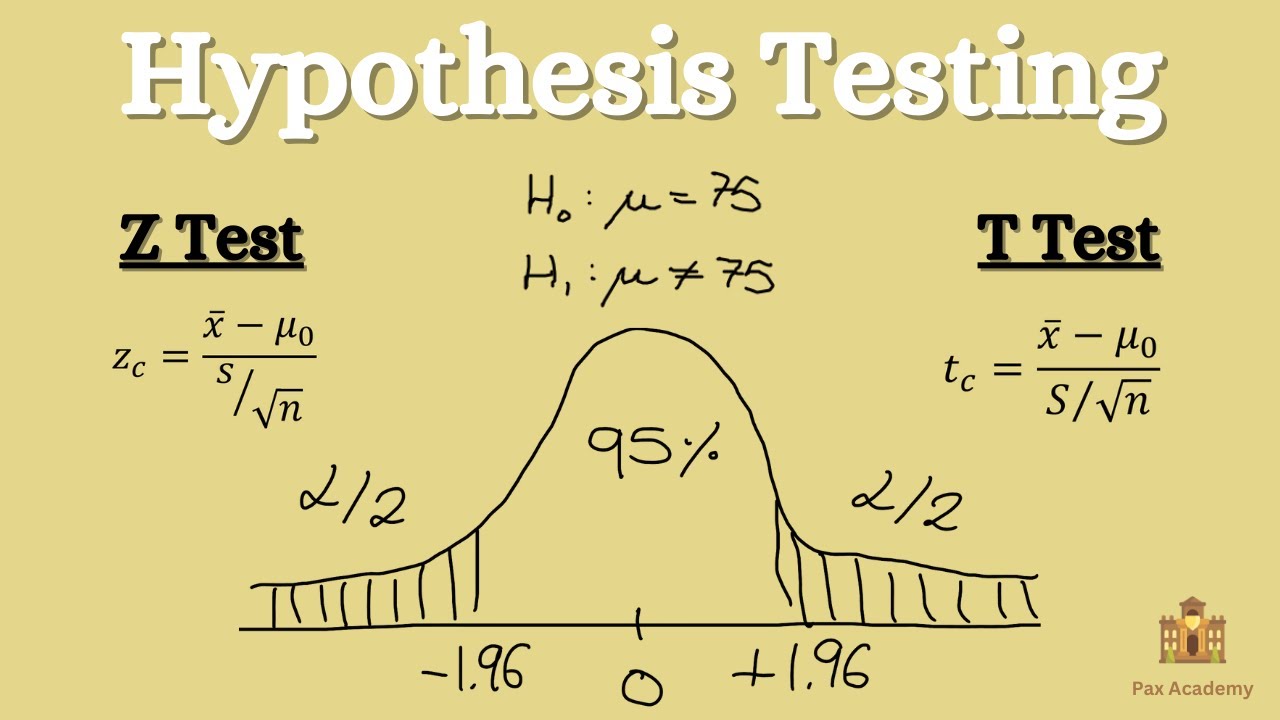
Hypothesis Testing - Z test & T test
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
