Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Summary
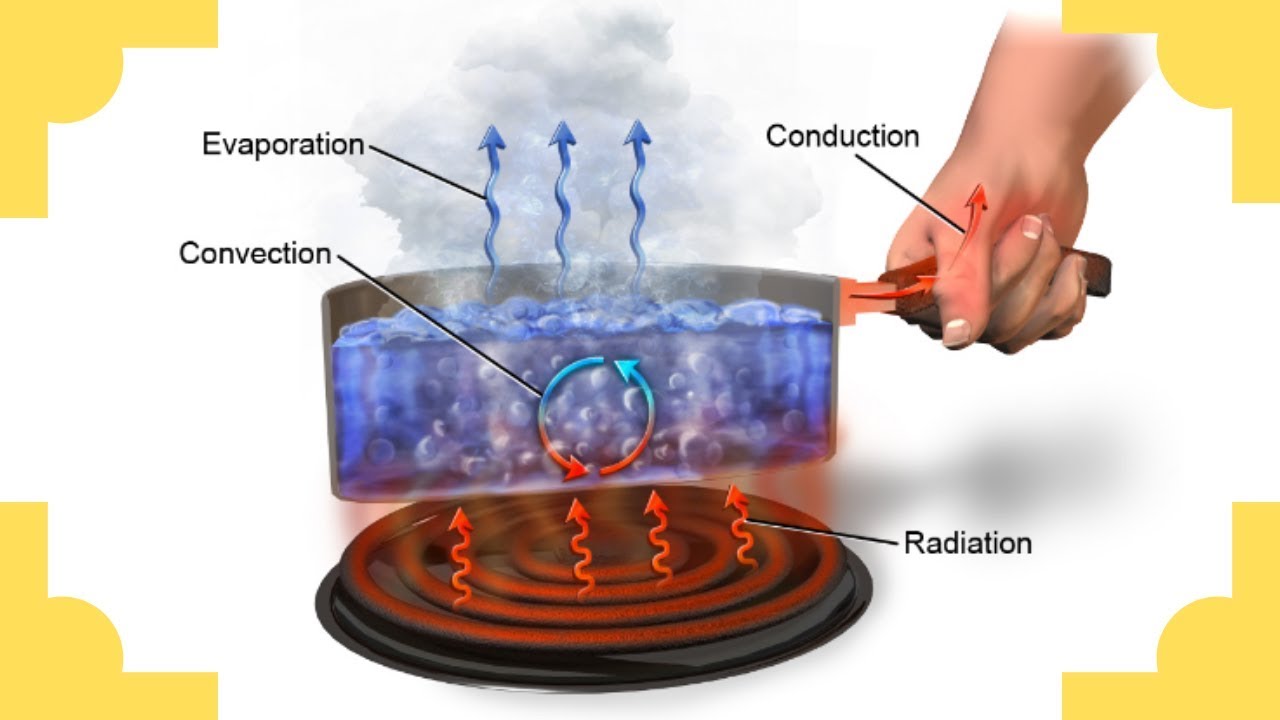
TLDRThis video explores the three mainGenerate summary JSON ways heat energy moves: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs through molecular contact, like a metal spoon heating from a flame. Convection happens as heat rises due to density differences, seen in hot air above a fire. Radiation transfers energy via electromagnetic waves, allowing heat to travel even through empty space, such as from the Sun to Earth. Using the example of a campfire with a pot, the video illustrates all three processes in action, making the concepts easy to understand and visually engaging for learners.
Takeaways
- 😀 Heat transfer refers to the movement of heat energy from one point to another, occurring on Earth, in the atmosphere, and even in space.
- 😀 The three main methods of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation.
- 😀 Conduction is heat transfer through molecular contact and is most effective in solid materials.
- 😀 An example of conduction is when a spoon heats up from a flame, with energy moving through the entire spoon via molecular vibrations.
- 😀 Convection occurs due to density differences in fluids (liquids and gases), causing hot air or liquid to rise and carry heat with it.
- 😀 A common example of convection is the rising heat above a flame, which is why it’s unsafe to hold your hand directly above it.
- 😀 Radiation is heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, and it does not require a material medium to travel through.
- 😀 Radiation allows heat from the Sun to reach Earth through the vacuum of space.
- 😀 In the campfire example, conduction happens as the flame directly heats the pot, convection occurs as hot air rises, and radiation spreads out as waves of energy.
- 😀 The key concepts for each heat transfer type: Contact for conduction, Density differences for convection, and Waves for radiation.
- 😀 Understanding these three methods of heat transfer helps explain everyday phenomena, from cooking to the warmth we feel from the Sun.
Q & A
What is heat transfer?
-Heat transfer is the movement of energy, specifically heat energy, from one place to another, whether on Earth, in the atmosphere, or in space.
What are the three main types of heat transfer?
-The three main types of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does conduction transfer heat?
-Conduction transfers heat through molecular contact, where vibrating molecules pass energy to neighboring molecules, effectively spreading heat through solids.
Can you give an example of conduction?
-An example of conduction is heating a metallic spoon over a flame. The energy from the flame causes the molecules in the spoon to vibrate, warming the entire spoon.
Which materials are best for conduction?
-Solids are most effective for conduction because their tightly packed molecules allow energy to transfer efficiently.
How does convection transfer heat?
-Convection transfers heat through density differences in fluids, where warmer, less dense material rises and cooler, denser material sinks, creating a flow of heat.
Can you give an example of convection?
-An example of convection is heat rising from a flame. The heated air expands, becomes less dense, and rises, carrying heat energy upward.
How does radiation transfer heat?
-Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves, which can travel through empty space without requiring a material medium.
Can you give an example of radiation?
-An example of radiation is the Sun's energy traveling through space to heat the Earth's surface.
What keywords are associated with each type of heat transfer?
-Conduction is associated with 'contact,' convection with 'density differences,' and radiation with 'waves.'
How do all three types of heat transfer occur around a campfire?
-Around a campfire, conduction occurs as the flame transfers heat directly to a pot, convection occurs as heat rises due to density differences, and radiation occurs as energy spreads outward from the flame in waves.
Why is convection less effective in solids than in liquids or gases?
-Convection relies on the movement of fluid caused by density differences, which is limited in solids because their molecules cannot move freely.
Why is radiation important in space?
-Radiation is important in space because it can transfer heat without a medium, allowing energy from the Sun to reach planets.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)