What is Remote Sensing and GIS?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Mikey, a PhD student at UC Berkeley, introduces remote sensing and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) in an accessible way. He explains the concept of remote sensing as measuring or obtaining information without physical contact, using examples like satellites, drones, and LiDAR. The video also covers the different types of remote sensing, including active and passive, and discusses GIS as a framework for collecting, managing, and analyzing spatial data. With engaging examples and a clear breakdown of key terms like vector, raster data, shapefiles, and 3D models, Mikey aims to make these complex topics easier to understand and apply.
Takeaways
- 😀 Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about an object without physical contact, using technologies like satellites, drones, and even lasers in autonomous cars.
- 😀 Remote sensing can be classified into two categories: active (using its own energy source) and passive (relying on external energy like sunlight).
- 😀 Active remote sensing is often more reliable, but more expensive, and may be harder to use for large-scale or recurring studies.
- 😀 Remote sensing technologies like optical, lidar, thermal, and microwave sensors are all based on the electromagnetic spectrum and have various applications in fields like agriculture and urban design.
- 😀 GIS (Geographic Information Systems) helps to collect, manage, and analyze spatial data, making it easier to visualize data as maps for decision-making.
- 😀 GIS data can be collected using GPS devices, surveying tools, or digitizing existing maps. The data is typically stored in vector or raster formats.
- 😀 Vector data in GIS uses points, lines, and polygons, whereas raster data is represented as a grid of cells, often used for satellite and aerial imagery.
- 😀 Shapefiles are a common format used in GIS for managing vector data, and are an essential part of GIS workflows.
- 😀 GIS software like ArcMap (from ESRI) and open-source alternatives like QGIS help users create, analyze, and visualize geospatial data.
- 😀 A geographic coordinate system provides a reference framework for spatial data, helping ensure accurate positioning when working with multiple datasets.
- 😀 Geodatabases store large volumes of spatial data efficiently, optimized for querying and analysis, often using simple geometric objects like points, lines, or polygons.
Q & A
What is remote sensing?
-Remote sensing is the science of measuring or obtaining information about an object without making any physical contact with it. It involves extracting data through sensors mounted on platforms such as satellites, drones, or even cars.
How is remote sensing applied in everyday life?
-Remote sensing can be observed in everyday life through examples like using satellite imagery for weather forecasting, drones for surveying, or even the laser scanning technology (LiDAR) used in autonomous cars.
What are the two types of remote sensing based on how energy is provided?
-Remote sensing is classified into active and passive types. Active remote sensing uses its own energy source to illuminate objects (e.g., LiDAR), while passive remote sensing depends on external sources like sunlight to capture reflected data (e.g., drones or satellite imagery).
What makes active remote sensing more dependable than passive remote sensing?
-Active remote sensing is more dependable because it provides its own source of energy for illumination, meaning it can operate during the night or in cloudy conditions, unlike passive remote sensing that depends on sunlight and can be affected by weather conditions.
What are some types of remote sensing technologies?
-Some common types of remote sensing technologies include optical remote sensing (using visible and infrared light), LiDAR (using laser light for 3D object detection), thermal remote sensing (measuring emitted thermal energy), and microwave remote sensing (using microwave energy).
What is GIS, and what is its main function?
-GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, and its main function is to collect, manage, and analyze spatial data to make decisions based on the location of objects or phenomena. It helps in understanding what has happened, what is happening, and what might happen in the future.
How does GIS help in decision-making?
-GIS helps in decision-making by organizing data into layers that can be analyzed for various purposes. For example, it can help determine how far a new house is from key locations like the airport, identify nearby rivers, or assess population density in an area.
What are the two main types of spatial data in GIS?
-In GIS, spatial data is classified into two main types: vector and raster data. Vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to represent objects, while raster data uses grid cells to represent continuous data, like temperature or satellite imagery.
What is a shapefile in GIS?
-A shapefile is a geospatial vector data format used in GIS to store spatial data. It represents objects as points, lines, or polygons and is widely used for analyzing and visualizing spatial information.
Why is it important to consider the projection and coordinate systems in GIS?
-It is important to consider the projection and coordinate systems in GIS because they ensure that spatial data is accurately aligned and mapped, preventing distortions and ensuring the accuracy of analysis and decision-making.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Pengetahuan Peta, Pengindraan Jauh, dan Sistem Informasi Geografi (SIG) X SMA/MA
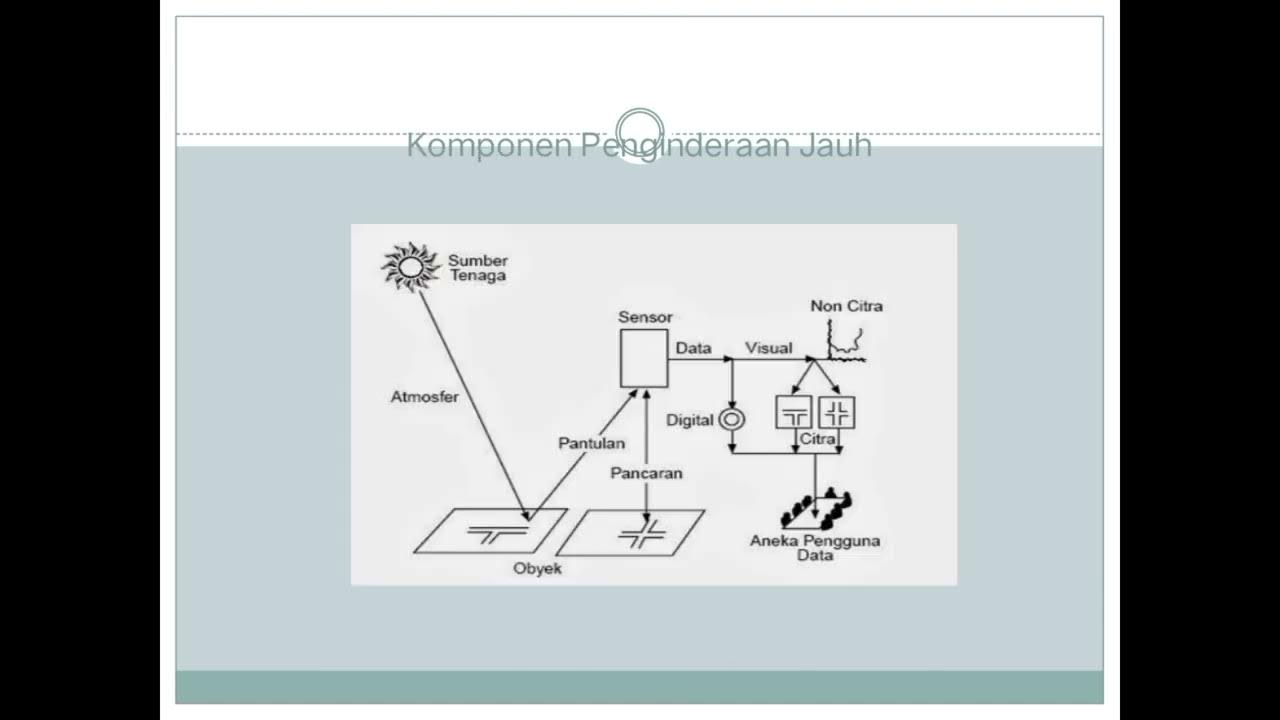
Popy X 1 Dasar Pemetaan Indera SIG Geo X Regulasi Diri

Penginderaan Jauh | Geografi | Alternatifa
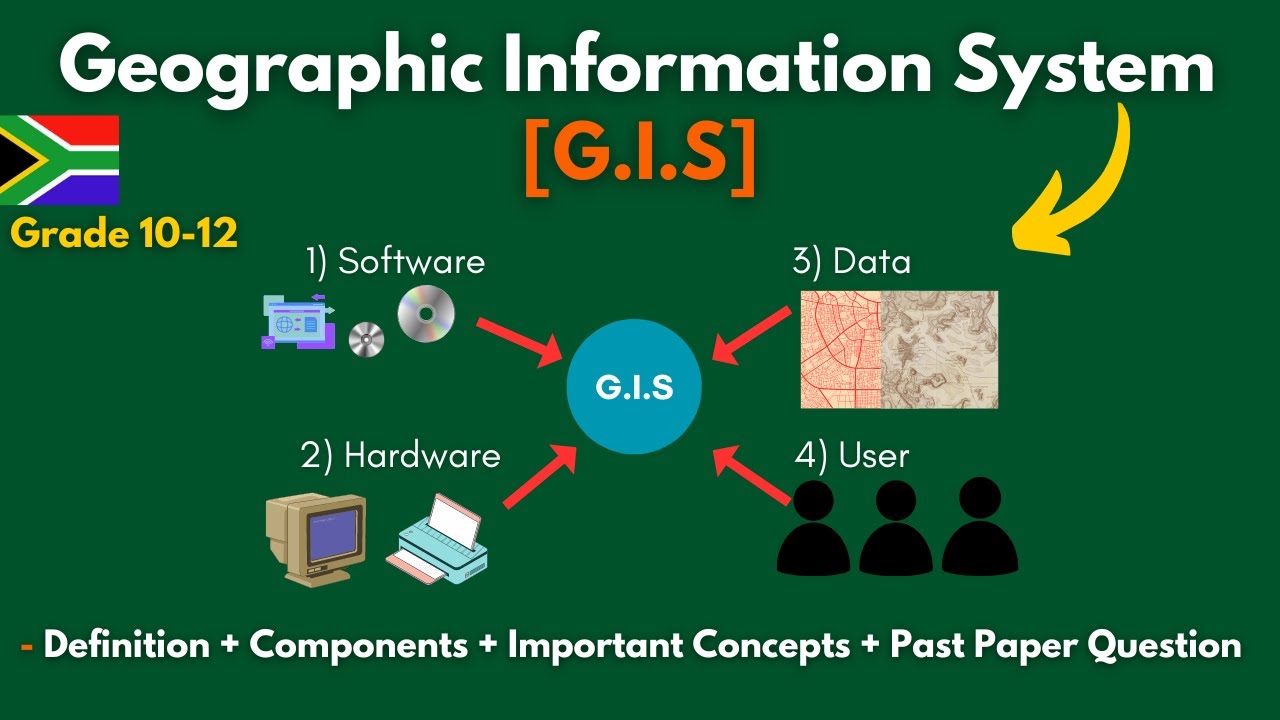
G.I.S (Geographic Information Systems)- Concepts, Components, Advantages + Past Paper | Grade 10-12.

Pengolahan Citra Penginderaan Jauh untuk jaringan transportasi
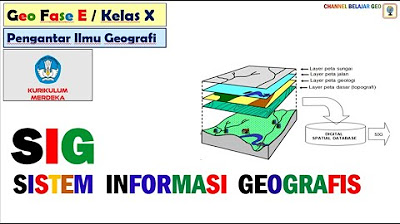
Sistem Informasi Geografis # kurikulum merdeka.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
