GRADE 11 - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE (Quarter 1-Module 14) : GEOLOGIC TIMELINE
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Teacher Maya G. Espinoza from Compostela National High School introduces the topic of the Geologic Time Scale to Grade 11 students. She explains how Earth’s history is recorded using eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages, emphasizing the importance of fossils in building the scale. The lesson covers the types of fossils, fossilization, and the work of paleontologists. The script also includes a pre-test, interactive activities, and a review of key vocabulary, ensuring an engaging learning experience on Earth’s geological history.
Takeaways
- 😀 The geologic time scale is a timeline used to describe Earth's history, including the age of rocks and fossils.
- 😀 The Earth’s history is divided into eons, which are the broadest categories of geological time, and these are further divided into eras, periods, and epochs.
- 😀 Eons are divided into four main categories: Hadean, Archaean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic.
- 😀 The Phanerozoic eon is subdivided into three major eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic.
- 😀 Fossils are remains or evidence of ancient life and are essential in building the geologic time scale.
- 😀 Fossils are typically found in sedimentary rocks, which are formed from layers of sand and clay.
- 😀 The process by which remains of ancient living things are turned into rock is called fossilization.
- 😀 Paleontologists are scientists who study fossils and ancient life forms to understand Earth's history.
- 😀 The Paleozoic era includes periods such as Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian.
- 😀 The Cenozoic era, which is the most recent, includes the Paleogene, Neogene, and Quaternary periods.
- 😀 Fossils can be classified into body fossils, which are actual parts of plants or animals, and trace fossils, which are signs like footprints or dung left by organisms.
Q & A
What is the geologic time scale?
-The geologic time scale is a calendar for events in Earth's history. It serves as a standard timeline used to describe the age of rocks, fossils, and the events that form them.
What are eons, and how many eons are there in Earth's history?
-Eons are the broadest category of geological time. There are four eons in Earth's history: Hadean, Archaean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic.
What is the significance of the Phanerozoic eon?
-The Phanerozoic eon is significant because it is divided into three eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. It is the eon where most of the fossil evidence of life, such as plants, animals, and dinosaurs, can be found.
What is the main difference between the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras?
-The main difference lies in the types of life forms present and the geological changes during each era. The Paleozoic era includes the emergence of early life like fish and amphibians. The Mesozoic era is famous for the rise of dinosaurs, and the Cenozoic era is characterized by the dominance of mammals and the formation of modern ecosystems.
Why do most eons and eras end in 'zoic'?
-Most eons and eras end in 'zoic' because these time periods were recognized by the animal life present at that time.
What type of rocks are fossils most commonly found in?
-Fossils are most commonly found in sedimentary rocks, which are formed by the deposition and compaction of sediments over time.
What is the process called by which ancient remains are turned into fossils?
-The process is called fossilization. It occurs when the remains of ancient living things are gradually turned into rock over long periods.
What is the role of paleontologists in studying fossils?
-Paleontologists are scientists who study fossils and ancient life. They analyze fossils to understand the history of life on Earth and the evolution of species.
What is the difference between body fossils and trace fossils?
-Body fossils are actual parts of plants and animals that have been fossilized, such as bones, shells, and leaves. Trace fossils, on the other hand, are fossilized signs of animal or plant activity, such as footprints or coprolite (fossilized dung).
What are the primary uses of fossils in geology?
-Fossils are used as markers to build up the geologic time scale. They help geologists and paleontologists determine the age of rocks and understand the environmental conditions and life forms that existed at different points in Earth's history.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
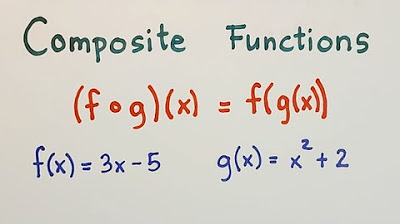
Composition of Functions - Grade 11 - General Mathematics
Composite Function | General Mathematics @MathTeacherGon

Operation of Functions
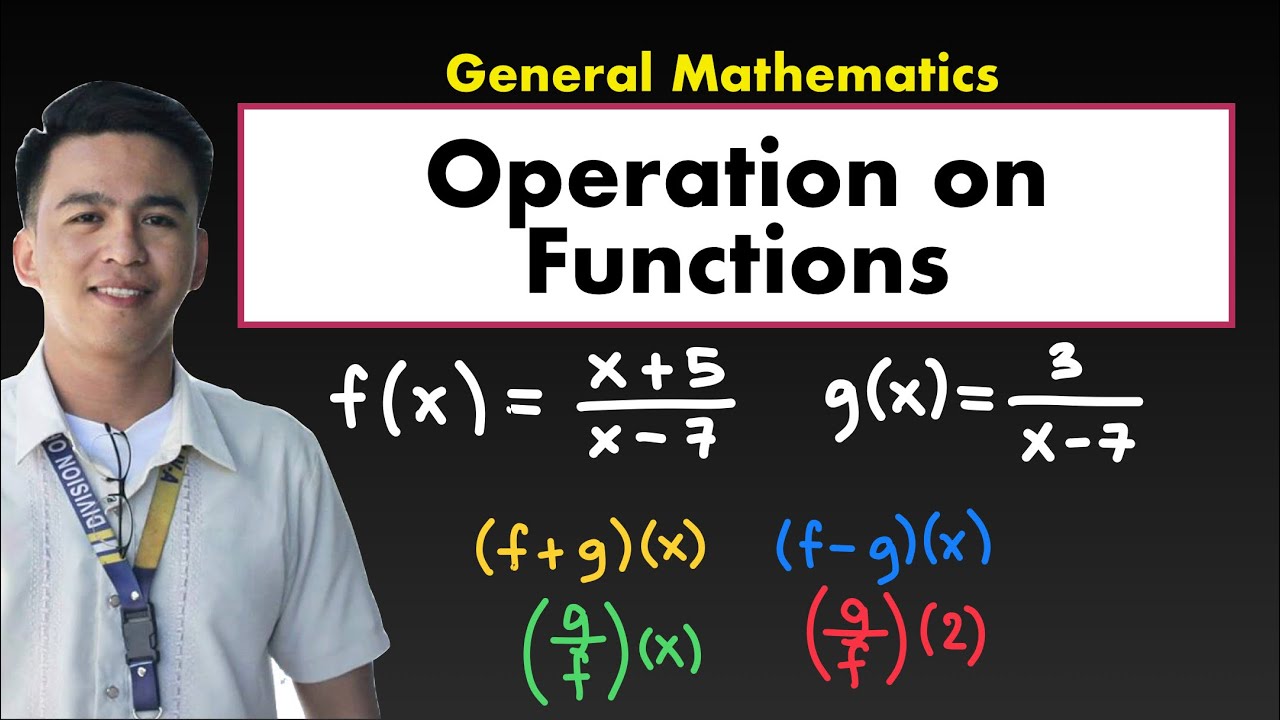
Operation on Functions | Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division of Functions

How to Solve Quadratic Inequality - Part 2

Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction (Introduction) #grade12 #deped #seniorhigh #shs #disaster
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
