#7 Karir dan Profesi : Perancangan Proses Produksi (S1 T.Industri, Kelas 1) - SEG 2
Summary
TLDRThis video script discusses the concept of waste in industrial engineering, highlighting different types of waste such as transportation, inventory, labor, and overproduction. Experts emphasize strategies to minimize waste through lean manufacturing and Six Sigma techniques, alongside the importance of effective production planning and employee training. The conversation also compares conventional methods with automation, showcasing the efficiency benefits of automation in reducing waste. The focus is on how reducing waste leads to added value and improved profitability, especially during challenging times like a pandemic, and the role of investments in technology to optimize processes.
Takeaways
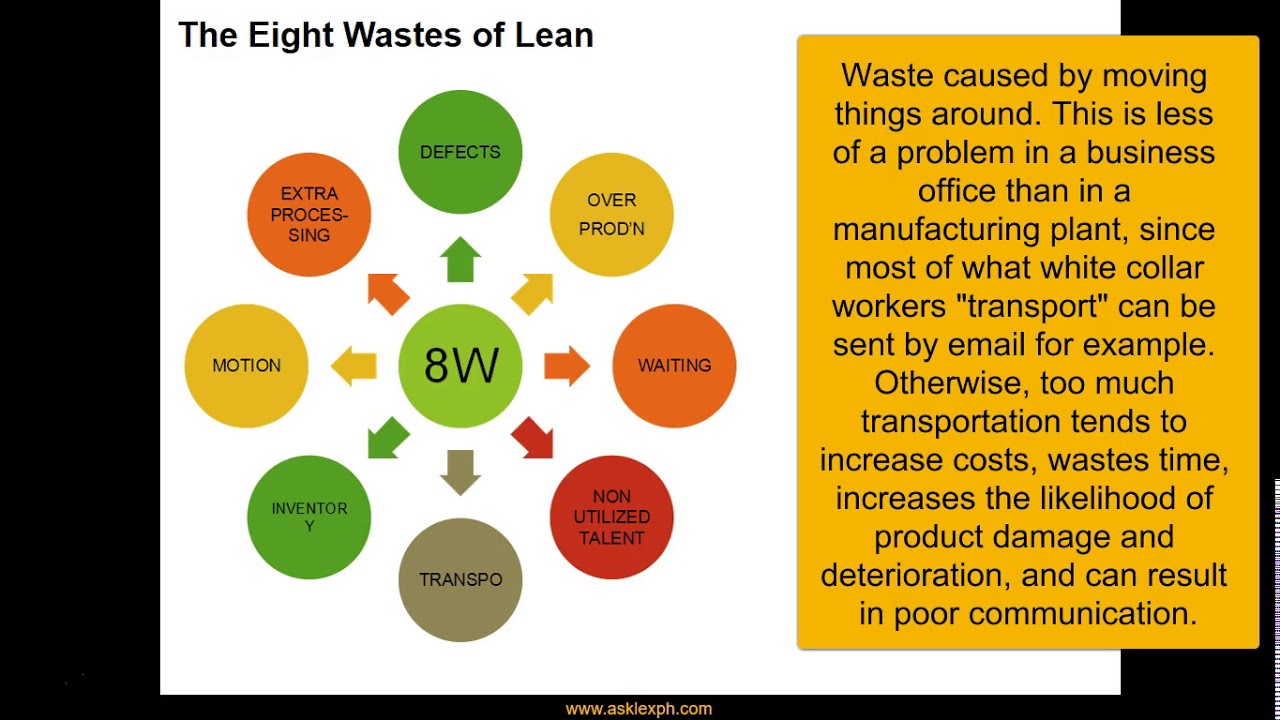
- 😀 Waste in industrial engineering refers to all activities that do not add value during the process of converting raw materials into finished products.
- 😀 There are seven common types of waste in the industry, including transportation, inventory, labor, motion, waiting time, over-processing, and overproduction.
- 😀 Effective production planning can minimize waste, which is essential for optimizing operations and improving profitability.
- 😀 Understanding the root causes of waste, such as poor factory layout, inadequate training, and inefficient work methods, is key to addressing inefficiencies.
- 😀 Mapping the value stream using tools like the 'VSM' (Value Stream Mapping) technique can help identify and eliminate waste sources.
- 😀 Six Sigma methodology, with its emphasis on process optimization and reducing defects, is a key approach for achieving world-class operational standards.
- 😀 Companies can reduce waste by implementing structured training programs in quality control, production planning, and inventory management.
- 😀 Automation can significantly reduce waste compared to conventional machines, though companies often face high upfront costs for automation systems.
- 😀 The shift from conventional machines to automated systems leads to improved efficiency, reduced waste, and higher process capability, but requires substantial investment.
- 😀 Financial assessments, such as benefit-cost analysis, are crucial for making informed decisions about machine investments and process upgrades.
- 😀 Even during challenging times like a pandemic, companies can create added value by optimizing the use of limited resources, such as materials and time, through efficient planning.
Q & A
What is waste in the context of industrial engineering?
-In industrial engineering, waste refers to all activities that do not add value to the production process, specifically the transformation of raw materials into finished goods. This includes inefficiencies in transportation, inventory, labor, motion, waiting times, over-processing, overproduction, and defects.
What are the seven types of waste in industrial engineering according to Taiichi Ohno?
-The seven types of waste in industrial engineering, as defined by Taiichi Ohno, include transportation waste, inventory waste (excessive stock), waste of labor, waste of motion, waste of waiting time, waste of over-processing, waste of overproduction, and waste due to defects.
What are the primary causes of waste in the production process?
-The primary causes of waste in the production process include poor factory and office layout, inappropriate training, non-standard work methods, low process capability, poor planning, and issues with the quality of materials from suppliers.
How can companies reduce waste in their production processes?
-Companies can reduce waste by mapping their value stream to identify sources of waste, analyzing processes, and implementing improvements such as better training, process optimization, and more efficient use of resources. Additionally, adopting systems like Six Sigma can help reduce waste by improving the quality of processes.
What is the relationship between production planning and waste reduction?
-Production planning plays a critical role in waste reduction because proper planning helps avoid inefficiencies in the production process. It involves forecasting demand, managing inventory, and ensuring resources are allocated effectively, which can minimize waste.
What role does human resources play in waste management?
-Human resources are crucial in waste management as employees need to be trained in efficient work methods and problem-solving techniques. Training programs on quality control tools and process optimization can help workers understand how to minimize waste and improve the overall production process.
How does the implementation of automation affect waste in production?
-Automation can significantly reduce waste in production by improving precision, reducing human error, and increasing efficiency. Automated systems can also optimize the flow of materials and reduce excessive waiting times, which can lower waste levels compared to traditional, manual systems.
What is the difference between conventional machines and automated processes in waste management?
-Conventional machines typically operate at a lower Sigma level (3 Sigma), meaning they have a higher rate of waste. Automated processes, on the other hand, can operate at higher Sigma levels (4-6 Sigma), reducing waste by increasing process consistency, precision, and speed. Automation generally leads to more optimized resource use.
What is Six Sigma, and how does it help in waste reduction?
-Six Sigma is a methodology that focuses on improving process quality by identifying and eliminating sources of waste and defects. It uses data-driven techniques to improve the consistency and capability of production processes, reducing waste and enhancing overall efficiency.
How can a company calculate the return on investment (ROI) for automating production processes?
-A company can calculate the ROI for automating production processes by performing a benefit-cost ratio analysis. This involves evaluating the initial investment costs (e.g., for machinery, training) against the long-term benefits, such as reduced waste, improved efficiency, and lower production costs.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)