Probabilitas dan Statistik: 8.2 Populasi
Summary
TLDRIn this video on probability and statistics, the presenter explains key terms like population and sample, emphasizing their importance in statistical analysis. A population refers to the entire set of observations we wish to understand, while a sample is a subset of that population, which is often the only data we can feasibly collect. The video uses analogies, such as comparing a sample to a beam of light entering a cave, to illustrate the difficulty of studying a whole population. The video also covers the challenges of gathering complete data, using examples like measuring video streaming speeds and voice call overloads.
Takeaways
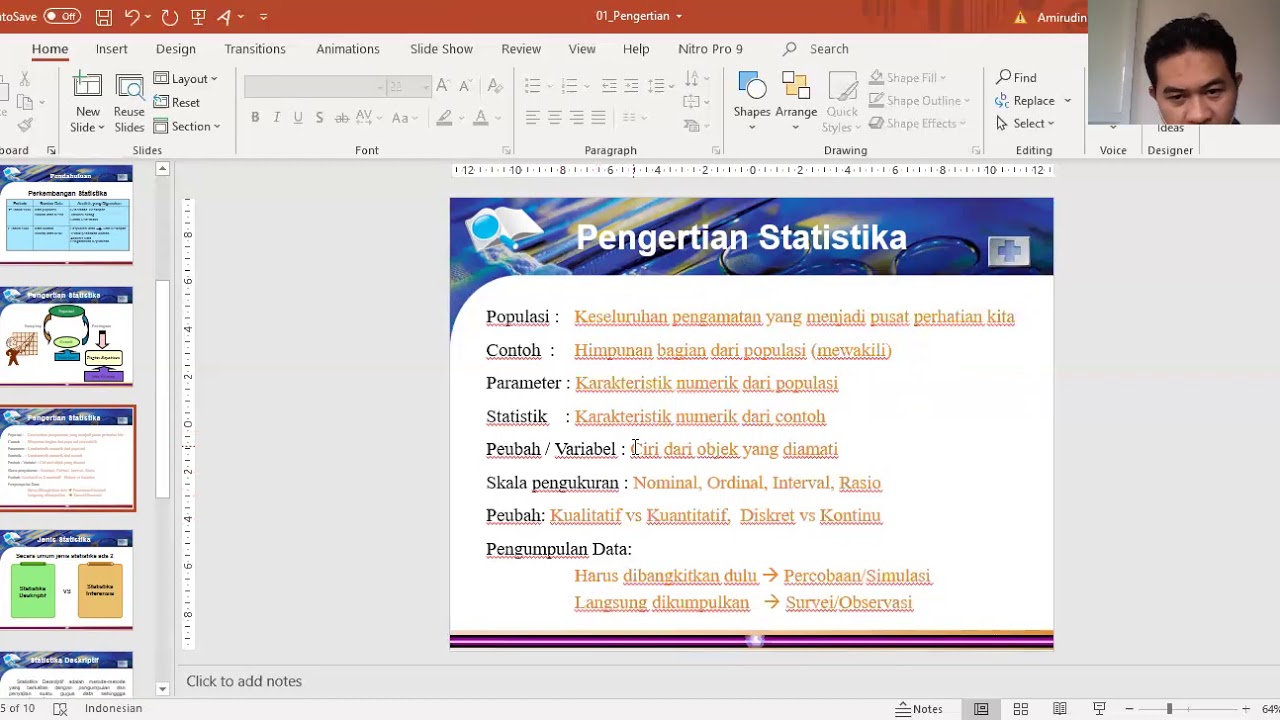
- 😀 A population in statistics refers to the entire set of observations or data that is being studied, which can be finite or infinite.
- 😀 A sample is a subset of the population, and it is used when it is impractical or impossible to study the entire population.
- 😀 In statistics, random variables are used to represent population data, and these are fundamental in making statistical inferences.
- 😀 Statistical inference is the process of drawing conclusions about a population based on data collected from a sample.
- 😀 The concept of a population is often abstract and inaccessible, making it difficult to collect all data from it directly.
- 😀 A common analogy is that the population is like the outside world (reality), and the sample is like a beam of light representing a small part of that reality.
- 😀 Populations must be quantifiable (represented by numbers) in order to apply statistical methods like random variables and probability distributions.
- 😀 The population may be subjective depending on the researcher's perspective and the scope of the study.
- 😀 In real-world scenarios, gathering data from the entire population is often too time-consuming or expensive, which makes sampling essential for efficiency.
- 😀 Real-world examples include measuring video streaming speeds or customer surveys for large companies, where it is impossible to measure every individual.
- 😀 The choice of how to measure and analyze data (like using averages or specific metrics) depends on the research goals and the specific context of the study.
Q & A
What is the difference between a population and a sample in statistics?
-A population in statistics refers to the entire set of observations or data that we are interested in studying, whether it is finite or infinite. A sample, on the other hand, is a subset of the population, which is used for analysis when it's impractical or impossible to study the entire population.
Why is it difficult to observe an entire population?
-It is often difficult to observe an entire population because it may be too large or even infinite. Collecting data from every member of the population can be time-consuming, expensive, and sometimes impractical.
How does the concept of probability relate to statistics?
-In statistics, probability plays a crucial role when analyzing populations and samples. When observations are taken from a population, they are assumed to follow a random distribution, which allows statisticians to make inferences and predictions about the population based on the sample data.
What is the role of statistical inference?
-Statistical inference involves making conclusions about a population based on a sample. Since it's often not feasible to study the entire population, we use statistical methods to estimate population parameters and draw conclusions from sample data.
Why can't we always collect data from the entire population?
-It's often impossible to collect data from the entire population due to factors like time, cost, accessibility, or the sheer size of the population. For example, surveying every customer of a multinational company is impractical.
How do we define a population mathematically?
-Mathematically, a population is a set of all possible observations or outcomes that are relevant to a particular study. These observations must be measurable and represented by numbers, such as real numbers in most cases.
What is the nature of a population in statistics?
-The nature of a population in statistics is that it is often unknown, subjective, and inaccessible. The data is typically difficult to collect in its entirety, and the definition of the population may vary depending on the researcher's perspective and the specific research question.
Can we apply statistical methods like sampling in all cases?
-Statistical methods, including sampling, are typically applied when it's impractical to collect data from the entire population. For instance, in large-scale studies involving millions of individuals, taking a representative sample can yield meaningful insights without the need to survey every individual.
What is an example where statistical sampling is necessary?
-An example is when measuring the average speed of video streaming access across a large customer base. It would be impossible to measure the streaming speeds of every individual user, so a sample is taken to estimate the overall performance.
How do subjective decisions influence statistical studies?
-Subjective decisions in statistics can influence how a study is designed, including the selection of parameters and variables. For example, when measuring video streaming performance, the choice of whether to focus on the minimum, maximum, or average speed can depend on the specific goals of the study and what data is most relevant for the analysis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Pertemuan 1 Statistika sosial

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?

Apa itu Statistika?

STATISTIKA PENDIDIKAN PERTEMUAN 1-PENGANTAR STATISTIKA DAN STATISTIK

Probabilitas dan Statistik: 8.6 Central Limit Theorem

Statistical Inference: Introduction and Terminology (in Hindi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
