Apa itu Statistika?
Summary
TLDRIn this introductory lecture on statistics, Amanda explains the fundamental concepts of statistical science, including the definition of statistics, data types, and key terms like population and sample. She emphasizes the importance of collecting, processing, and interpreting data for decision-making. The lecture also covers the differences between descriptive and inferential statistics, highlighting their roles in analysis and hypothesis testing. Amanda discusses practical applications of statistics in education, such as measuring student performance and predicting outcomes, while introducing exploratory data analysis techniques and various data visualization methods to enhance understanding and insights.
Takeaways
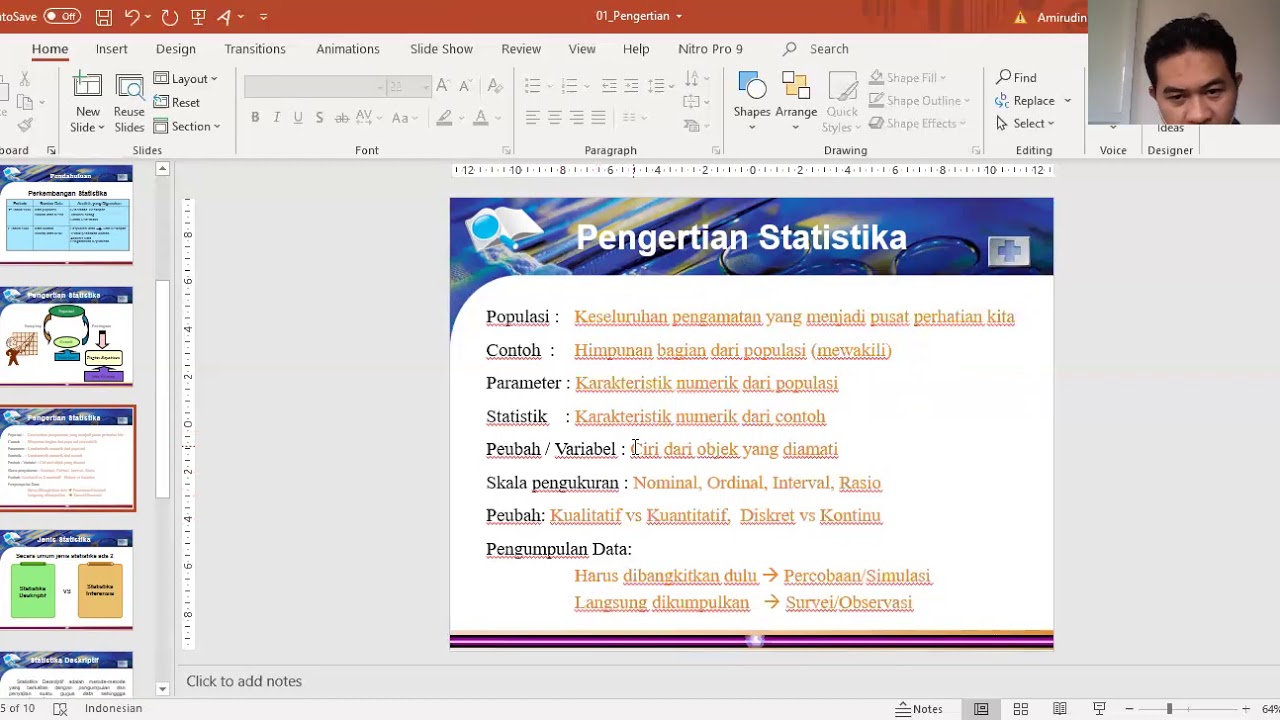
- 😀 Statistics is a branch of mathematics focused on collecting, processing, and interpreting numerical data, especially for analyzing population characteristics through samples.
- 😀 A statistician is responsible for gathering and analyzing data to draw conclusions and make decisions based on statistical designs.
- 📊 Statistics differs from statistics: 'statistics' refers to the field of study, while 'statistic' represents a specific value that describes a characteristic of a sample.
- 📈 Data consists of discrete values that convey information regarding quantity, quality, facts, or other basic meanings.
- 🔍 Data can be classified into primary data, collected directly from sources, and secondary data, obtained from existing records.
- 🌍 A population refers to a complete set of individuals or objects with specific characteristics, while a sample is a smaller subset taken from that population.
- 🧪 Samples are essential when the population is too large or inaccessible, and they must represent the population accurately for valid conclusions.
- 🎓 Understanding basic statistics, like descriptive statistics, helps analyze data such as averages, medians, and modes.
- 📊 The two main branches of statistics are descriptive statistics (data collection and interpretation) and inferential statistics (using data for decision-making).
- 🔍 Exploratory data analysis (EDA) is a key method for summarizing and visualizing data, using simple arithmetic techniques and graphical representations.
Q & A
What is the definition of statistics according to the American Heritage Dictionary?
-Statistics is a branch of mathematics that involves collecting, processing, and interpreting numerical data, particularly to analyze characteristics of populations generalized through samples.
What are the three main aspects of statistics discussed in the transcript?
-The three main aspects of statistics are data collection, data processing, and data interpretation.
How does the term 'statistics' differ from 'statistica'?
-While 'statistica' refers to the field of study concerning data, 'statistics' refers to values that describe characteristics or features of a sample.
What are the two main classifications of data mentioned in the transcript?
-The two main classifications of data are primary data, which is collected directly by the researcher, and secondary data, which is obtained from other sources.
What is the significance of having a representative sample?
-A representative sample is crucial as it allows researchers to generalize findings to the entire population, especially when it is impractical to study the whole population.
What are the two main branches of statistics identified in the script?
-The two main branches of statistics are descriptive statistics, which deals with summarizing and describing data, and inferential statistics, which focuses on making predictions or generalizations about a population based on sample data.
What are some key benefits of studying statistics as mentioned in the transcript?
-Studying statistics helps in understanding basic statistical concepts, making informed decisions based on data, segmenting data for analysis, and forecasting future trends.
What does exploratory data analysis (EDA) entail?
-Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) involves using simple arithmetic techniques and graphical methods to summarize and visualize data, helping to uncover patterns or insights.
What is an outlier in statistical analysis?
-An outlier is a data point that significantly deviates from the rest of the data, which can skew results or indicate variability in measurements.
What types of visualizations are recommended for presenting data?
-Common visualizations include bar charts, pie charts, dot plots, box plots, histograms, and scatter plots, each serving different purposes in data presentation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)