Química Simples #12 - Resumos - Propriedades Coligativas
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker discusses colligative properties, which describe how the presence of solutes affects various properties of solutions. Key concepts include vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. The speaker explains how adding non-volatile solutes lowers vapor pressure, increases boiling points, and decreases freezing points. Additionally, osmotic pressure is explored, emphasizing its relationship with solute concentration. Through simple examples like water and acetone, the video provides insights into the behavior of liquids and the impact of solutes on their physical properties, making it a helpful resource for exam preparation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Properties Colligative refer to how the presence of solutes influences the behavior of solvents in a solution.
- 😀 Vapor Pressure is the pressure exerted by a liquid when it evaporates into a gas, and it varies depending on the substance's volatility.
- 😀 Volatility refers to how easily a liquid transitions into a gas. Acetone has a higher volatility than water due to weaker intermolecular forces.
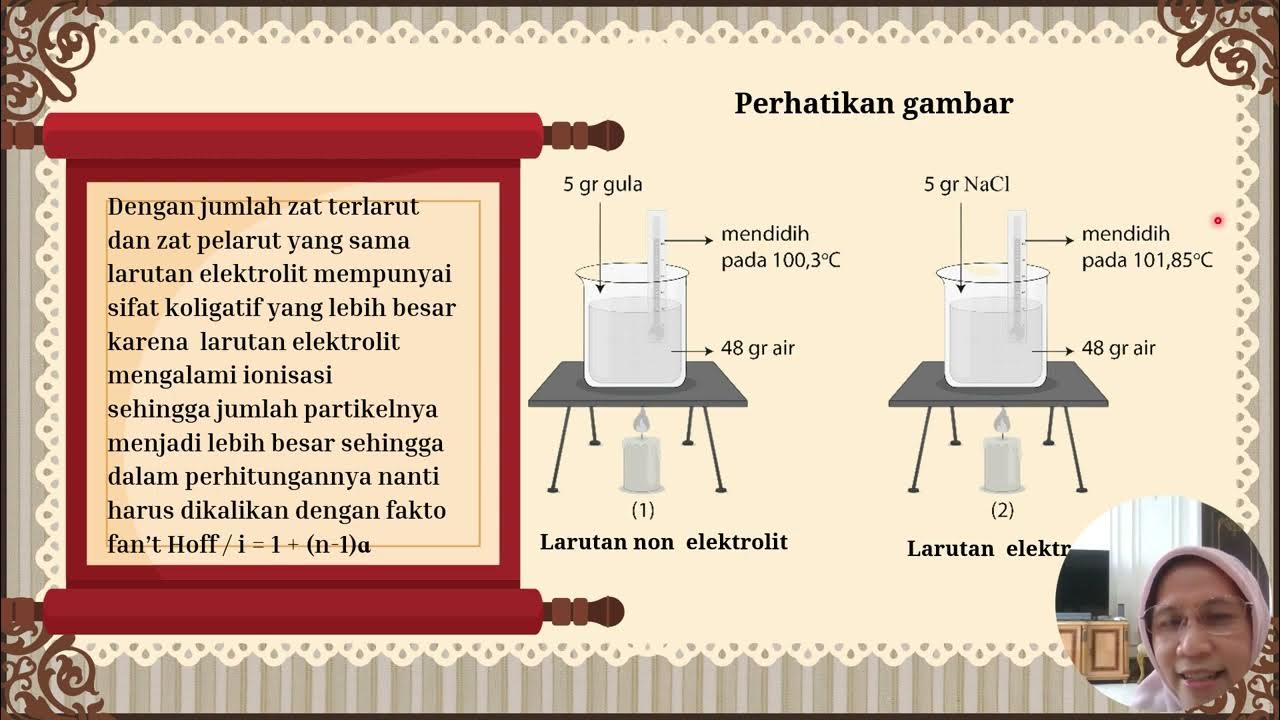
- 😀 Boiling Point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure. Adding solute to a solvent raises the boiling point.
- 😀 Osmosis involves the movement of a solvent from an area of lower solute concentration to one of higher concentration to equalize the concentrations.
- 😀 Solute addition lowers the vapor pressure of a solvent, as solutes interfere with the solvent's ability to evaporate.
- 😀 When solute is added to water, it lowers the vapor pressure, and the temperature required to reach boiling point increases.
- 😀 Osmotic Pressure is the pressure required to prevent osmosis. Adding solute increases osmotic pressure, requiring more pressure to prevent solvent flow.
- 😀 Freezing Point Depression occurs when solute is added to a solvent, making it harder for the solvent molecules to organize into a solid structure.
- 😀 Adding solute decreases the freezing point of a solvent, such as seawater not freezing at 0°C due to dissolved salts.
Q & A
What are colligative properties in solutions?
-Colligative properties are physical properties of a solution that depend on the number of solute particles present, not the identity of the solute. These properties include vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
How does vapor pressure work in solutions?
-Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid phase. It depends on the temperature and the nature of the liquid. A higher vapor pressure indicates higher volatility, meaning the liquid can more easily transition to the gas phase.
What is the relationship between vapor pressure and volatility?
-Volatility refers to how easily a substance can transition from a liquid to a gas. A higher vapor pressure means the substance is more volatile, as it more readily evaporates into the air. For example, acetone has a higher vapor pressure and is more volatile than water.
How does the presence of a non-volatile solute affect the vapor pressure of a solvent?
-When a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent, the vapor pressure of the solvent decreases. This is because the solute particles occupy some of the surface area, preventing the solvent molecules from transitioning to the gas phase.
What is the boiling point elevation and how does solute affect it?
-Boiling point elevation is the increase in the boiling point of a solution when a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent. This happens because the addition of the solute lowers the vapor pressure, requiring more heat (higher temperature) for the vapor pressure to equal the atmospheric pressure and cause boiling.
How does the addition of a solute affect the freezing point of a solution?
-Adding a solute to a solvent lowers the freezing point of the solution, a phenomenon known as freezing point depression. This occurs because the solute particles disrupt the formation of a solid structure, making it harder for the solvent to freeze.
What is osmotic pressure and how does solute affect it?
-Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to prevent the movement of solvent molecules from a lower concentration solution to a higher concentration solution through a semipermeable membrane. Adding more solute increases osmotic pressure because it increases the concentration gradient between the two sides of the membrane.
What does it mean for a solution to be isotonic?
-An isotonic solution is one where the concentration of solute is the same on both sides of a semipermeable membrane, resulting in no net movement of solvent molecules. This means the osmotic pressure on both sides is balanced.
How does temperature affect the boiling and freezing points of a solution?
-Temperature affects both the boiling and freezing points of a solution. For boiling, as the temperature increases, the vapor pressure of the solution rises, and eventually, it reaches the point where it matches the atmospheric pressure, causing the solution to boil. For freezing, the presence of solute lowers the temperature at which the solvent freezes.
What is the effect of adding solute on the properties of water in solutions?
-When a solute is added to water, it decreases the water's vapor pressure, elevates its boiling point, and lowers its freezing point. Additionally, the osmotic pressure increases due to the solute particles. These changes are collectively known as colligative properties.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)