Analisis Node (Simpul)
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into node analysis in electrical circuits, combining Ohm's Law with Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) to analyze and solve for circuit variables. It discusses key steps like choosing a reference node, applying KCL, and transforming equations using Ohm's Law to calculate voltage and current at various points. The script also covers techniques like Cramer's Rule for solving systems of equations, emphasizing the importance of understanding potential differences and currents in the network. Ultimately, the goal is to simplify complex circuit analysis into clear, systematic steps for effective problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the combination of Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is essential for analyzing electrical circuits, specifically in node analysis (nodal analysis).
- 😀 Nodal analysis involves choosing a reference node (ground) and applying KCL to other nodes in the circuit to find unknown voltages.
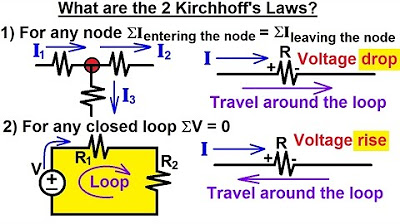
- 😀 In KCL, the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node, which helps to establish equations for solving unknowns in the circuit.
- 😀 Ohm's Law, V = IR, is used to relate the current through resistors to the voltage across them, helping to transform circuit equations into solvable formats.
- 😀 It's crucial to understand the concept of voltage as the difference in potential between two points in a circuit. This helps in calculating the voltages at various nodes.
- 😀 When performing nodal analysis, it’s important to properly assign the correct current directions and voltage polarities for accurate calculations.
- 😀 Using Cramer's Rule or matrix elimination methods allows solving systems of equations that arise from the nodal analysis of circuits with multiple unknowns.
- 😀 Analyzing the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in circuits requires careful attention to signs and direction of flow (e.g., higher potential on one side of a resistor causes current to flow).
- 😀 Practical application of Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) helps in analyzing closed loop circuits, though the script focuses mainly on applying KCL in this scenario.
- 😀 Understanding the behavior of currents and voltages at different points in a circuit, such as the current split at junctions, is key to solving for the unknowns in complex networks.
- 😀 By setting up a matrix from the system of equations obtained from KCL and Ohm’s Law, it becomes possible to calculate the voltages at each node using matrix methods like determinant calculation.
Q & A
What is node analysis in electrical circuits?
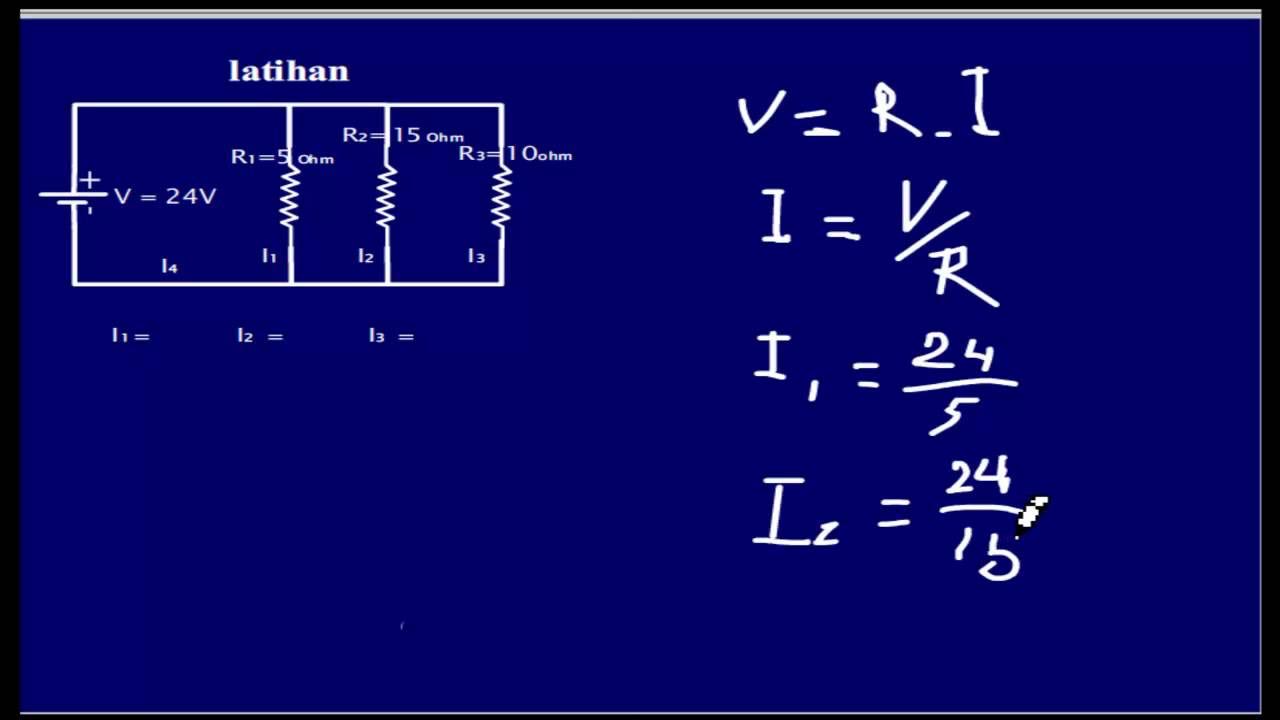
-Node analysis, also known as nodal analysis, is a method used in electrical circuits to determine the voltage at different points (nodes) in the circuit. It involves applying Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Ohm's Law to form a system of equations that can be solved to find the voltages at the nodes.
What is Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and how is it used in node analysis?
-Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node must equal the sum of currents leaving that node. In node analysis, KCL is used to write equations for each node in the circuit, ensuring that current is conserved at each node.
How does Ohm's Law apply in node analysis?
-Ohm's Law, V = IR, is used in node analysis to relate the voltage, current, and resistance in the circuit. It is applied to each component (like resistors) to express the current in terms of voltage and resistance, which helps in forming the equations for each node.
What is the importance of choosing a reference node in node analysis?
-Choosing a reference node (often referred to as ground) is crucial in node analysis because it provides a point of zero potential. All other node voltages are measured relative to this reference node, simplifying the calculation of voltages at other nodes in the circuit.
What is the role of Cramer's Rule in solving node analysis equations?
-Cramer's Rule is a mathematical method used to solve systems of linear equations. In node analysis, it is applied to solve the system of equations derived from KCL and Ohm's Law. It involves calculating the determinant of matrices to find the voltages at the nodes.
What is a 'node' in the context of electrical circuits?
-A node in an electrical circuit is a point where two or more components (such as resistors, capacitors, or voltage sources) are connected. The voltage at each node is determined during node analysis.
How do you determine the voltage at a node using node analysis?
-The voltage at a node is determined by solving the system of equations formed by applying Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Ohm’s Law. The solution gives the voltage differences between nodes, which can then be used to calculate the voltage at each individual node.
What is the relationship between current and voltage in a resistor, and how is it used in node analysis?
-In a resistor, the current is related to the voltage across it by Ohm’s Law: I = V/R. In node analysis, this relationship is used to express the current flowing through each resistor in terms of the node voltages, which are then used to form equations for each node.
Can you explain the concept of 'potential difference' in relation to node analysis?
-The potential difference, or voltage, is the difference in electric potential between two points (nodes) in a circuit. In node analysis, the voltage at each node is the potential difference relative to the reference node (ground). The voltage difference drives the current flow through the circuit.
What is the purpose of solving for voltages V1 and V2 in a circuit analysis example?
-The purpose of solving for voltages V1 and V2 in a circuit analysis example is to determine the voltage at specific nodes in the circuit. These voltages are essential for understanding the behavior of the circuit, including the distribution of electrical potential and the operation of circuit components.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (8 of 31) What Are Kirchhoff's Laws?

Kirchhoff's current law | Circuit analysis | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Elektronika Dasar 002 Resistor 02 Universitas Jember

Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) - How to Solve Complicated Circuits

KVL and KCL (Circuits for Beginners #11)

Node Voltage Analysis (Circuits for Beginners #15)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
