Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) - How to Solve Complicated Circuits
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL), a foundational tool for circuit analysis. It explains the conservation of charge principle, where the total current entering a node must equal the total current leaving it. The script outlines a five-step process for applying KCL to solve complex circuits, including establishing reference flows, identifying a ground point, writing equations for each node, combining them using KCL, and solving the equations. The video also provides practical examples to demonstrate these steps, emphasizing the importance of correct sign assignments and the use of tools like LT Spice for verification.
Takeaways
- 📘 The video introduces Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) as a fundamental tool for circuit analysis, emphasizing its importance in solving complex circuits.
- 👨🔬 Kirchhoff's law is based on the principle of conservation of charge, stating that the total current entering a node must equal the total current leaving the node.
- 🔄 The concept of nodal analysis is derived from KCL, allowing for the determination of currents at each node within a circuit by setting up mathematical equations.
- 🤔 The process of nodal analysis involves making arbitrary assumptions about the direction of current flow, which can later be adjusted based on the calculated results.
- 🔢 The video outlines a five-step method for solving circuits using KCL, which includes taking time to understand the circuit, establishing reference flows, writing equations for each node or branch, combining equations for each node, and solving the equations.
- 🧭 It's important to ensure that the direction of assumed current flow aligns with the mathematical signs used in the equations to avoid confusion and errors.
- 📚 The script mentions that the steps are conceptually similar to other methods but includes additional 'psychological steps' to address common challenges faced during circuit analysis.
- 📉 The video provides practical examples to illustrate the application of the five-step method, demonstrating how to work through a circuit analysis problem step by step.
- 🔍 The importance of checking solutions using multiple methods, such as algebraic solutions, simulation software like LT Spice, or matrix calculators, is highlighted to ensure accuracy.
- 💡 The video encourages developing an intuitive sense of circuit behavior and the importance of understanding why certain currents and voltages are expected in a circuit.
- 🔗 Additional resources and examples are available on circuitbred.com for further learning and clarification on concepts like supernodes and other aspects of circuit analysis.
Q & A
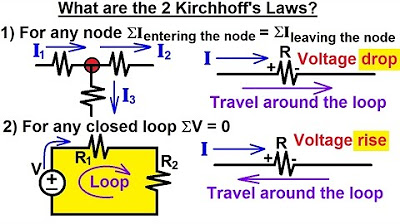
What is Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)?
-Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is a fundamental principle in circuit analysis that states the conservation of charge at a node, meaning the total current entering a node is equal to the total current leaving the node.
How does KCL relate to nodal analysis?
-Nodal analysis is a method that utilizes KCL to solve for unknown currents at various nodes in a circuit by setting up and solving a system of equations based on the currents flowing into and out of each node.
What is the significance of the term 'node' in circuit analysis?
-In circuit analysis, a 'node' is a point where two or more electrical components meet. The concept of a node is crucial for applying KCL, as it is the point where the law ensures the conservation of charge.
Why is it important to assign current directions when using KCL?
-Assigning current directions is important because it helps in setting up the correct equations for KCL. The direction of current flow determines whether the current is considered positive (entering a node) or negative (leaving a node) in the equations.
What is the mathematical representation of KCL at a node?
-The mathematical representation of KCL at a node is the equation ∑I_in - ∑I_out = 0, where I_in represents the currents entering the node and I_out represents the currents leaving the node.
What are the five steps mentioned in the script for solving circuits with KCL?
-The five steps are: 1) Take your time to understand the circuit and establish reference flows, 2) Identify the reference ground, 3) Write equations for each branch or element in the circuit, 4) Combine these equations for each node according to KCL, and 5) Solve the resulting system of equations.
Why is it recommended to check solutions with multiple tools or methods?
-Checking solutions with multiple tools or methods helps to ensure accuracy and provides a deeper understanding of the circuit behavior. It also helps to identify any potential mistakes made during the algebraic process.
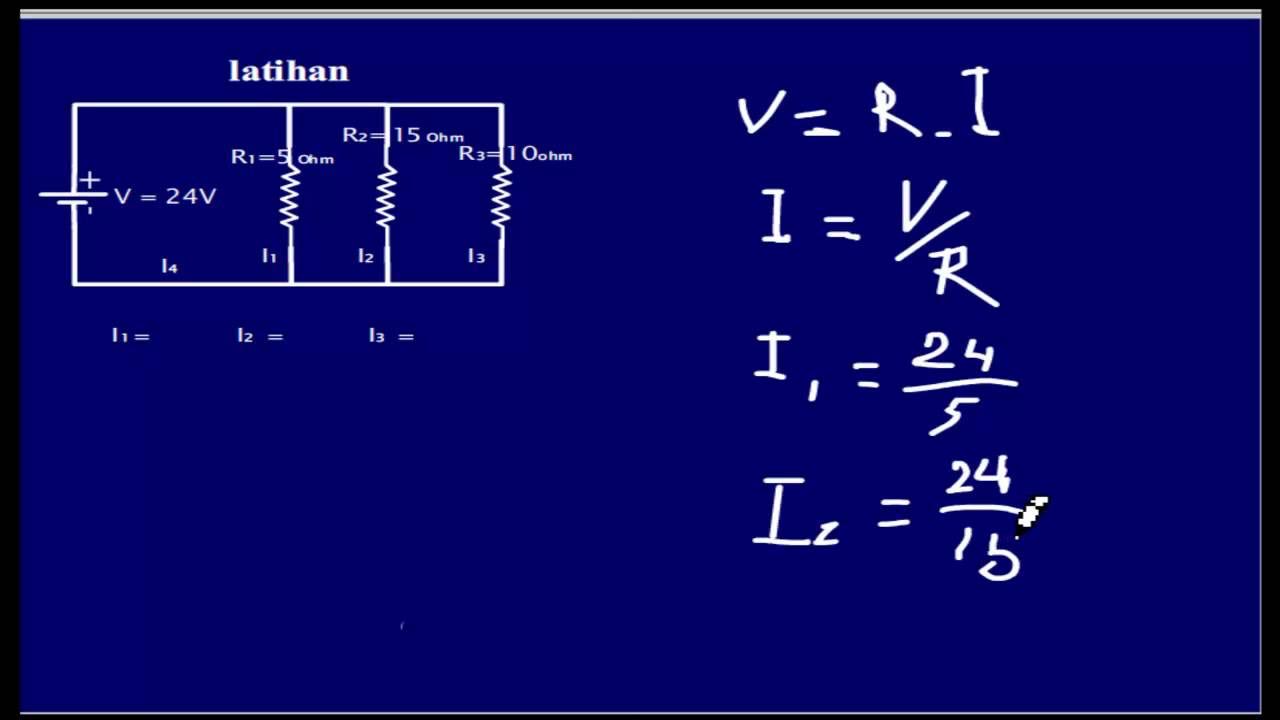
What is the role of Ohm's Law in nodal analysis?
-Ohm's Law (V = IR) is used in nodal analysis to relate the voltage across a resistor to the current flowing through it, which is essential for setting up the equations needed to solve for unknown currents at nodes.
How can one intuitively determine the current flow in a circuit?
-One can intuitively determine the current flow by observing the circuit components and their connections, assuming the direction of current flow that makes the most sense based on the circuit's configuration and the direction of known current sources.
What is a supernode and why is it treated differently in KCL?
-A supernode is a group of nodes that are all at the same potential due to a voltage source that isn't tied to the reference ground. It is treated differently because the voltage across the nodes is not zero, and special considerations must be made when applying KCL in such scenarios.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Analisis Node (Simpul)

Kirchhoff's current law | Circuit analysis | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Elektronika Dasar 002 Resistor 02 Universitas Jember
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (8 of 31) What Are Kirchhoff's Laws?

KVL and KCL (Circuits for Beginners #11)
Chapter 2 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)