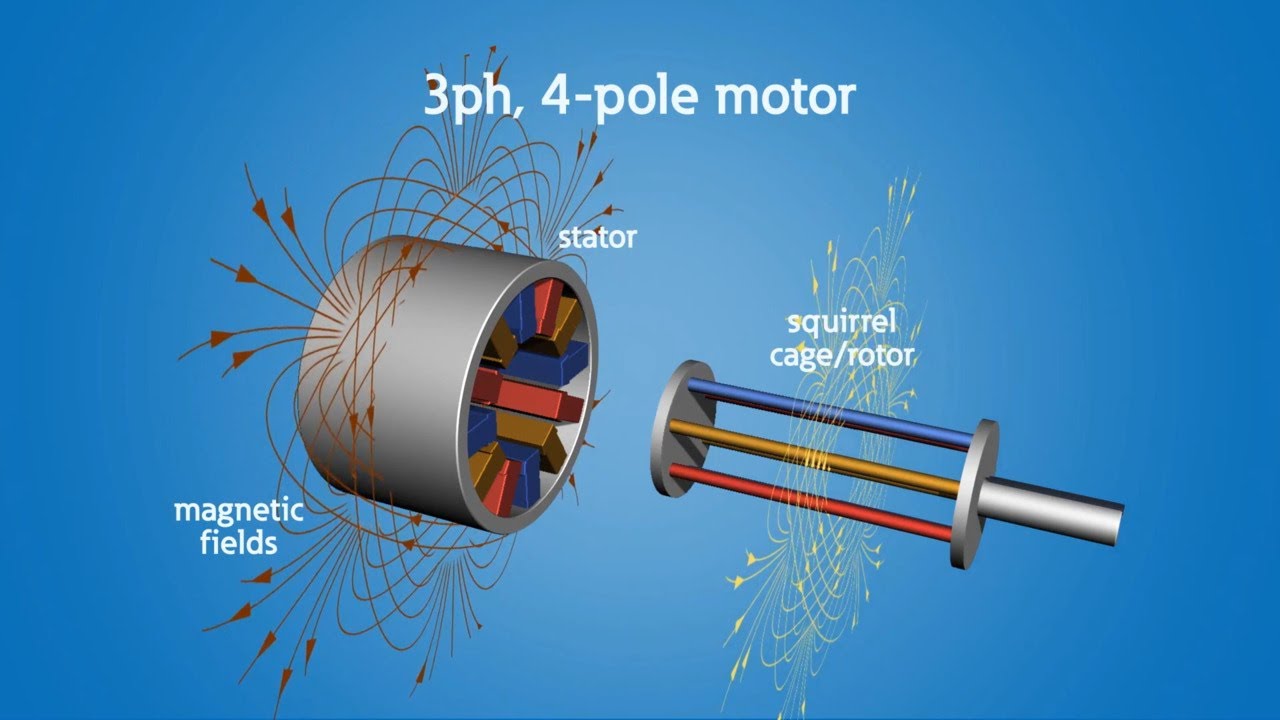
Induction Motor animation I: The Rotating Magnetic Field RMF
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamentals of three-phase AC motors, highlighting their robust design for high power and widespread use. It explores how the rotating magnetic field (RMF) is generated in these motors through a three-phase current, comparing it to a DC-powered wire's magnetic field. The video demonstrates how variations in the arrangement of wires can influence the speed of the RMF and explains the concept of synchronous speed. Additionally, the technical design of the motor’s stator is discussed, showcasing the use of laminated cores to minimize electric eddy currents.
Takeaways
- 😀 Three-phase AC motors, whether synchronous or induction, are robust and commonly used for high power applications.
- 😀 The operation of three-phase motors is based on the concept of a rotating magnetic field (RMF).
- 😀 A rotating magnetic field is generated by the motor winding and is essential to how these motors function.
- 😀 A single wire connected to DC generates a concentric magnetic field, which can be determined using the right-hand rule.
- 😀 When connected to AC, the magnetic field alternates in strength and direction but does not rotate.
- 😀 To create a rotating magnetic field, three wires are used, spaced 120 degrees apart and connected to three-phase current.
- 😀 Magnetic fields of the same direction combine to create the rotating magnetic field that powers the motor.
- 😀 The speed of the RMF can be controlled by adjusting the pole configuration in the motor's stator.
- 😀 A magnetic field with two poles rotates through a complete 360-degree cycle within one period of the input signal.
- 😀 The synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field can be adjusted based on the arrangement of the stator poles.
- 😀 The stator is made of a hollow cylindrical core with evenly spaced slots for the stator winding, and it's built from stacked laminations to prevent eddy currents.
Q & A
What makes three-phase AC motors one of the most commonly used electric motors?
-Three-phase AC motors are known for being robust and designed for high power, which makes them reliable and efficient for various industrial and commercial applications.
What is the basic principle behind the operation of three-phase motors?
-The basic principle behind three-phase motors is the rotating magnetic field (RMF) generated by the motor windings, which is essential for their operation.
How can the direction of the magnetic field in a DC circuit be determined?
-The direction of the magnetic field in a DC circuit can be determined using the right-hand rule, where the direction of the current flow dictates the orientation of the magnetic field.
What happens when a DC circuit is connected to an AC source?
-When a DC circuit is connected to an AC source, the magnetic field alternates in strength and direction but does not rotate, which differs from the behavior in a three-phase motor.
Why are three wires necessary to generate a rotating magnetic field (RMF)?
-Three wires are necessary to generate an RMF because they are spaced 120 degrees apart and connected to a three-phase current, allowing the magnetic fields to combine and create a rotating effect.
How does the arrangement of the three-phase wires affect the magnetic field?
-The arrangement of the three-phase wires creates a combined magnetic field that rotates around the stator, allowing the motor to produce rotational motion.
How does the magnetic field speed change when the number of poles is altered?
-When the number of poles is increased, the speed of the rotating magnetic field decreases. For example, doubling the number of poles halves the speed of the RMF.
What is the synchronous speed of a three-phase motor?
-The synchronous speed of a three-phase motor refers to the speed at which the magnetic field rotates. It is determined by the number of poles and the frequency of the input signal.
How is the synchronous speed calculated?
-The synchronous speed is calculated using a specific equation that involves the number of poles and the frequency of the input signal, providing the speed at which the motor's magnetic field rotates.
What is the purpose of the laminations in the stator core?
-The laminations in the stator core are used to interrupt the path of electric eddy currents, which helps to reduce energy losses and improve the efficiency of the motor.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)