Teori Kemagnetan Bumi Kelas 9 Semester Genap
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Mike explains the fascinating concept of Earth's magnetism and the role of a compass in navigation. He discusses how the Earth's magnetic field causes the compass needle to always point north and south, due to the magnetic poles' attraction. The video covers the importance of declination and inclination angles, and how they vary across the globe. Mike also delves into the origin of Earth's magnetic field, which comes from the movement of molten iron and nickel in the Earth's core, and how this geomagnetic field protects Earth from harmful solar radiation. Lastly, the video touches on auroras and their connection to Earth's magnetic field.
Takeaways
- 😀 A compass is a tool that helps humans navigate by indicating the direction of the magnetic poles of Earth.
- 😀 The magnetic field of Earth causes the compass needle to always point to the Earth's magnetic north and south poles.
- 😀 The north pole of the compass needle is attracted to the south magnetic pole of the Earth, and vice versa, which is why the needle always aligns to north and south.
- 😀 The magnetic north pole of the Earth is near the geographic south pole, while the magnetic south pole is near the geographic north pole.
- 😀 The declination angle is the angle between the compass needle's north direction and the true magnetic north or south of the Earth. This angle varies by location.
- 😀 The inclination angle of the compass needle refers to the tilt between the needle's end and the Earth's horizontal plane. This angle changes with location.
- 😀 At the equator, the inclination angle is zero, while it increases as you approach the poles.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field originates from the Earth's core, which consists of iron and nickel, and is influenced by convection currents due to high temperatures and pressures.
- 😀 The movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, caused by Earth's rotation, generates electric currents, leading to the creation of Earth's magnetic field.
- 😀 The geomagnetic field of Earth extends from the core to the upper limits of the atmosphere and protects Earth from harmful solar and cosmic radiation.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field causes charged particles from the solar wind to be directed toward the poles, where they ionize and form a plasma, producing auroras.
Q & A
What is the function of a compass?
-A compass is a device used to indicate directions, specifically pointing to the Earth's magnetic north and south, which helps with navigation.
Why does the compass needle always point north and south?
-The compass needle is attracted by the Earth's magnetic field, with the north end of the needle pointing to the Earth's magnetic south pole and vice versa, causing the needle to always align with the north-south direction.
What is the relationship between the Earth's geographic poles and its magnetic poles?
-The Earth's magnetic north pole is located near the geographic south pole, and the magnetic south pole is located near the geographic north pole, meaning the magnetic poles are opposite to the geographic poles.
What is declination and how does it affect compass use?
-Declination is the angle between the compass needle's north direction and the true geographic north. It varies by location, being smaller near the equator and increasing as you approach the poles, and must be considered when using a compass.
What is inclination in the context of a compass?
-Inclination refers to the tilt or angle that the compass needle makes relative to the horizontal plane of the Earth's surface. This angle also varies by location, being zero near the equator and increasing towards the poles.
Where does the Earth's magnetic field come from?
-The Earth's magnetic field originates from the movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, driven by convection currents caused by heat and pressure from the Earth's inner core. This movement generates electrical currents, producing the magnetic field.
How does Earth's rotation influence the generation of its magnetic field?
-The Earth's rotation creates differences in the speed between the solid inner core and the liquid outer core, which causes convection currents and electrical currents that generate the Earth's magnetic field.
What is geomagnetism?
-Geomagnetism refers to the Earth's magnetic field, also called the geomagnetic field, which extends from the Earth's interior to the boundary with the solar wind. It protects the Earth from solar and cosmic radiation.
How does Earth's magnetic field protect life on Earth?
-The Earth's magnetic field protects the planet by deflecting charged particles from the solar wind and cosmic radiation, preventing them from reaching the atmosphere and causing ionization or stripping away the atmosphere.
What is the aurora and how is it related to the Earth's magnetic field?
-The aurora, or aurora borealis, is a natural light display in the sky caused by charged particles from the solar wind interacting with the Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere, resulting in ionization and the release of light.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

KEMAGNETAN KELAS 9 part 2 - MEDAN MAGNET DAN MAGNET BUMI

Basic Theory of Magnetism | Magnetic Force Concept | Earth Magnetism Theory - Magnetism | IPA Class9
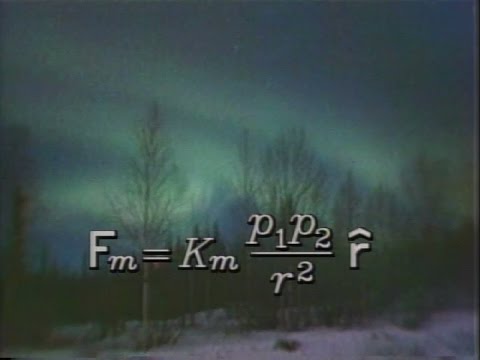
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe

Física - Magnetismo: imãs e campo magnético

Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-2) Kemagnetan Bumi, Migrasi Hewan dan Pemanfaatan Elektromagnet
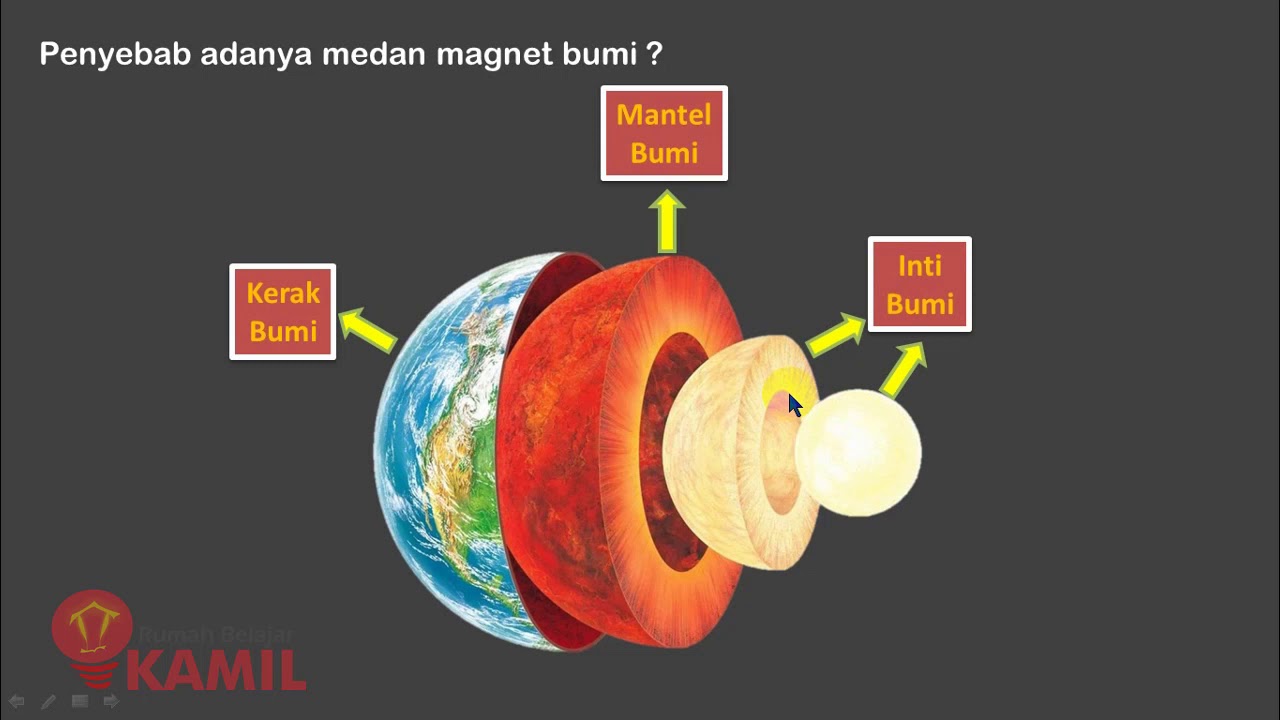
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
