Ciclo Biogeoquimico do Carbono Ju
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the carbon cycle, explaining how carbon moves through the Earth's ecosystems, from atmospheric CO2 to organic molecules in plants and animals. It explores the role of photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition in this process, as well as how human activities, like burning fossil fuels, disrupt the cycle and contribute to global warming. The video also touches on the importance of tropical forests in carbon sequestration and the impact of oceanic absorption of CO2. It concludes with a reflection on the necessity of understanding and addressing the carbon cycle to combat climate change.
Takeaways
- 😀 Global warming is increasing the likelihood of diseases, such as smallpox, returning due to the thawing of permafrost in Siberia, which may release preserved viruses.
- 😀 The carbon atom is essential to life and is found in all organic molecules, like glucose, collagen, and keratin.
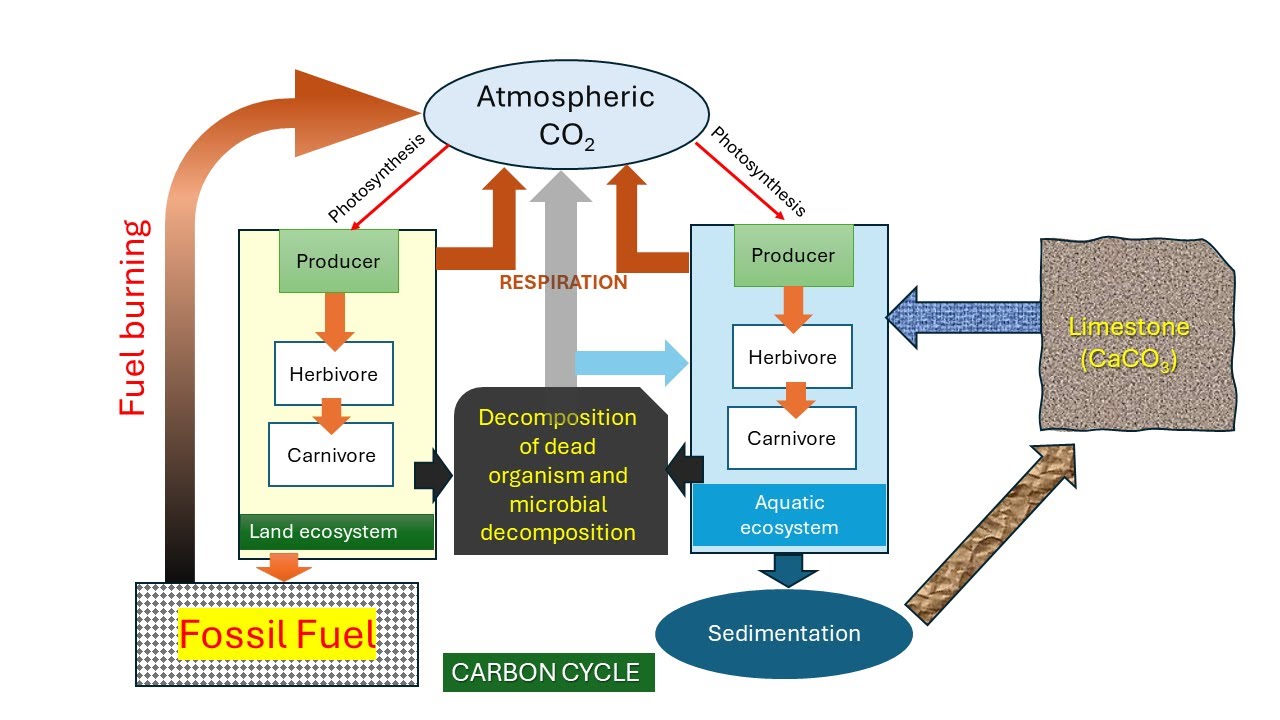
- 😀 The primary source of carbon for living organisms comes from atmospheric CO2, which plants and algae absorb through photosynthesis.
- 😀 Through photosynthesis, plants convert atmospheric CO2 into organic carbon, which is used to form molecules like cellulose and glucose.
- 😀 Carbon moves through the food chain as herbivores consume plants and carnivores eat herbivores, transferring carbon from one organism to another.
- 😀 Decomposers break down dead organisms and waste, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2.
- 😀 Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) are formed from the burial of organic matter without oxygen, trapping carbon underground for millions of years.
- 😀 The burning of fossil fuels by humans releases previously trapped carbon into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to global warming.
- 😀 Since the Industrial Revolution, CO2 levels in the atmosphere have risen by 40%, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels.
- 😀 Oceans play a crucial role in the carbon cycle by absorbing CO2 and storing it in marine life forms, such as shells made of calcium carbonate.
- 😀 Deforestation and land-use changes contribute to increased CO2 emissions, as the carbon stored in trees is released into the atmosphere when they are burned or cleared.
Q & A
What is the relationship between global warming and the resurgence of smallpox?
-Global warming is accelerating the thawing of permafrost in Siberia, where smallpox virus-infected bodies were buried in 1890. As the ice melts, the virus could potentially be re-exposed and cause a new smallpox outbreak.
What is the importance of carbon in life forms?
-Carbon is an essential element for all living organisms. It forms the backbone of organic molecules like glucose, collagen, and keratin, which are fundamental to the structure and function of living beings.
How do plants capture carbon from the atmosphere?
-Plants capture carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis, where they use sunlight to convert CO2 into organic carbon compounds, such as glucose.
What happens to the carbon that plants capture from the atmosphere?
-Once plants capture carbon, some of it is used to form organic molecules like glucose and cellulose, while the rest is stored in their biomass. A portion of the carbon is also released back into the atmosphere during cellular respiration.
How do herbivores contribute to the carbon cycle?
-Herbivores consume plants, absorbing the carbon stored in plant biomass. They release some of this carbon back into the atmosphere through respiration, while the rest remains in their bodies, which may later decompose.
What role do decomposers play in the carbon cycle?
-Decomposers break down dead organic matter, returning carbon to the atmosphere in the form of CO2. This process occurs when plants, animals, and their waste products decompose in the soil.
How do fossil fuels relate to the carbon cycle?
-Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, store carbon that was once part of living organisms. When burned, these fuels release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
What impact does burning fossil fuels have on the environment?
-Burning fossil fuels releases carbon that has been stored underground for millions of years, significantly increasing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and contributing to global warming and climate change.
How do oceans help regulate the carbon cycle?
-Oceans absorb a significant portion of atmospheric CO2, where it is used by marine organisms to form calcium carbonate shells. This helps reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
What is the effect of increased CO2 on ocean acidity?
-As more CO2 is absorbed by the oceans, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, leading to increased ocean acidity. This phenomenon, known as ocean acidification, can harm marine life, particularly organisms that rely on calcium carbonate to form shells.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)