The Carbon Cycle
Summary
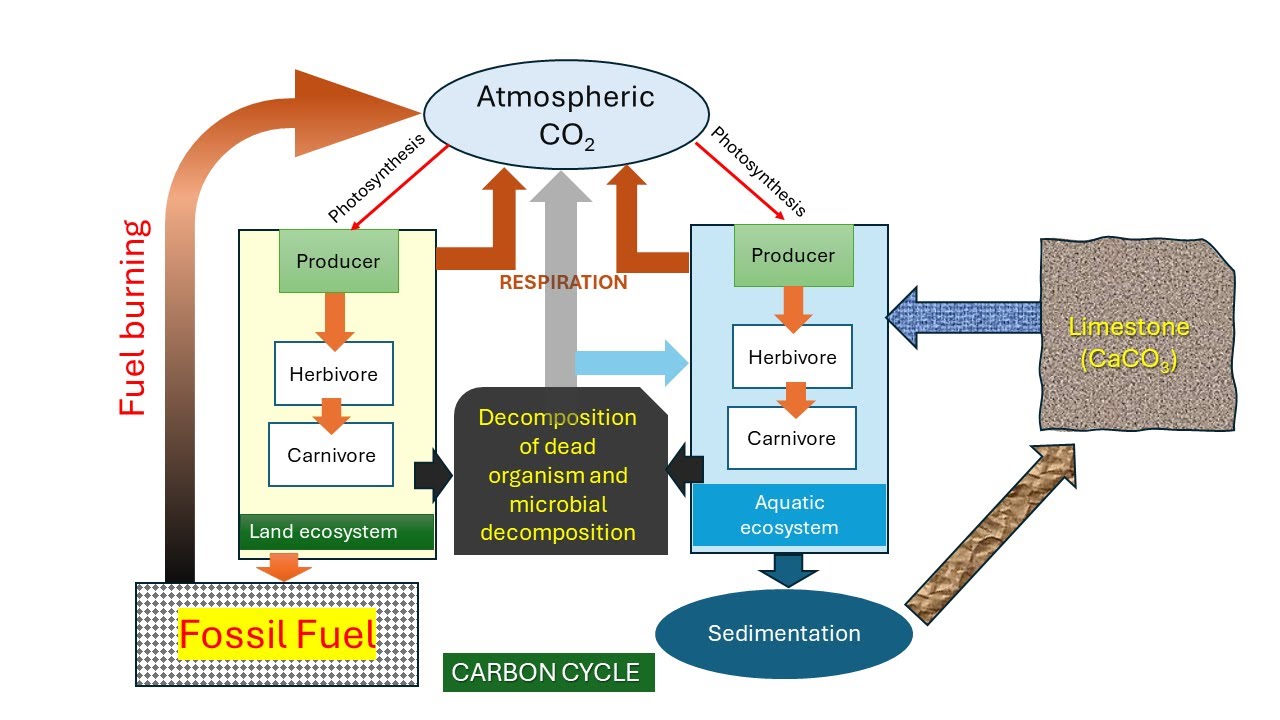
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricacies of the carbon cycle, highlighting its critical components and processes. It begins with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and follows its transformation through photosynthesis in plants, respiration in animals, and decay facilitated by decomposers. The script also addresses the role of fossil fuels and their combustion, contributing to atmospheric carbon dioxide. Additionally, it touches on the exchange of carbon with the oceans, including the formation and dissolution of calcium carbonate. The video aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how carbon circulates through Earth's systems.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The atmosphere is a major reservoir of carbon on Earth, primarily in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is a key process where plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds like glucose and starch.
- 🐦 Primary consumers, such as herbivores, obtain carbon by consuming plants, and secondary consumers get it by eating other animals.
- 💨 Respiration in plants and animals releases carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2.
- 🍃 Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, break down dead organic matter and respire, contributing to atmospheric CO2.
- 🔥 Combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and gas, releases carbon stored over millions of years back into the atmosphere as CO2.
- 🔥 Forest fires also contribute to the carbon cycle by burning organic matter and releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
- 🌊 The ocean plays a significant role in the carbon cycle by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in the form of calcium carbonate in marine organisms.
- 🐚 Shells of marine organisms, like mollusks, incorporate calcium carbonate, which eventually forms limestone and can release carbon back into the atmosphere.
- ♻️ The carbon cycle is a continuous process involving multiple reservoirs and pathways, including the atmosphere, oceans, and fossil fuels.
Q & A
What is the primary form of carbon in the Earth's atmosphere?
-The primary form of carbon in the Earth's atmosphere is carbon dioxide (CO2).
How does carbon dioxide enter the biosphere from the atmosphere?
-Carbon dioxide enters the biosphere from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis, where plants fix carbon into organic compounds.
What are the organic compounds created by plants during photosynthesis?
-Plants create organic compounds such as sugars, glucose, starch, and cellulose during photosynthesis.
How does carbon return to the atmosphere from living organisms?
-Carbon returns to the atmosphere through respiration, a process where living organisms convert organic compounds back into carbon dioxide.
What is the role of primary consumers in the carbon cycle?
-Primary consumers, such as herbivores, consume plants, and through respiration, they return carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
What happens to the carbon in plants when they are consumed by animals?
-When plants are consumed by animals, the carbon is transferred to the primary consumers, and it continues through the food chain to secondary consumers.
How does the carbon from dead animals re-enter the carbon cycle?
-When animals die, their organic matter decays and is broken down by decomposers, which through respiration, return carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
What are fossil fuels and how are they formed?
-Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are formed from the decayed remains of ancient organisms that have been subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years.
What is the role of combustion in the carbon cycle?
-Combustion is a process that releases carbon stored in fossil fuels, converting it into carbon dioxide and other products, which then re-enter the atmosphere.
How does carbon dioxide get into the ocean?
-Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere can dissolve into water bodies, where it can combine with calcium to form calcium carbonate, which is used by marine organisms to build shells.
What is the significance of the ocean in the carbon cycle?
-The ocean is a significant reservoir in the carbon cycle, as it can absorb and store carbon dioxide, and through processes like shell formation and decay, it can also release carbon back into the atmosphere.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KELAS 10 : MATERI EKOSISTEM BAG. 2 (Daur Biogeokimia)

S9Q1W7: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration (Part 1)
Carbon cycle | gaseous cycle | CARBON FIXATION | RESPIRATION| COMBUSTION | Decomposition

Systems and the Water Cycle (ESS 4.1.1 & 1.2)

Importance of Carbon and Global Carbon Cycle - Stores and Flows (A-Level Geography)

The Earth's Atmosphere
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)