Mutasi Gen | Transisi dan Transversi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore gene mutations, focusing on substitution mutations. Substitution mutations involve changes in the nitrogenous bases of DNA, leading to two types: transition and transversion. Transition mutations replace purines with purines or pyrimidines with pyrimidines, while transversions involve swapping purines and pyrimidines. These mutations can result in silent mutations, where the protein remains unchanged, or missense mutations, causing a change in the protein's amino acid sequence. The video also teases upcoming lessons on frame-shift mutations, providing a comprehensive introduction to genetic mutation concepts in biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mutations in genes are changes in the genetic information of living organisms, affecting the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
- 😀 There are two main types of gene mutations: base substitution and frame shift mutations.
- 😀 Base substitution mutations involve replacing one nitrogen base with another, whereas frame shift mutations involve the insertion or deletion of bases.
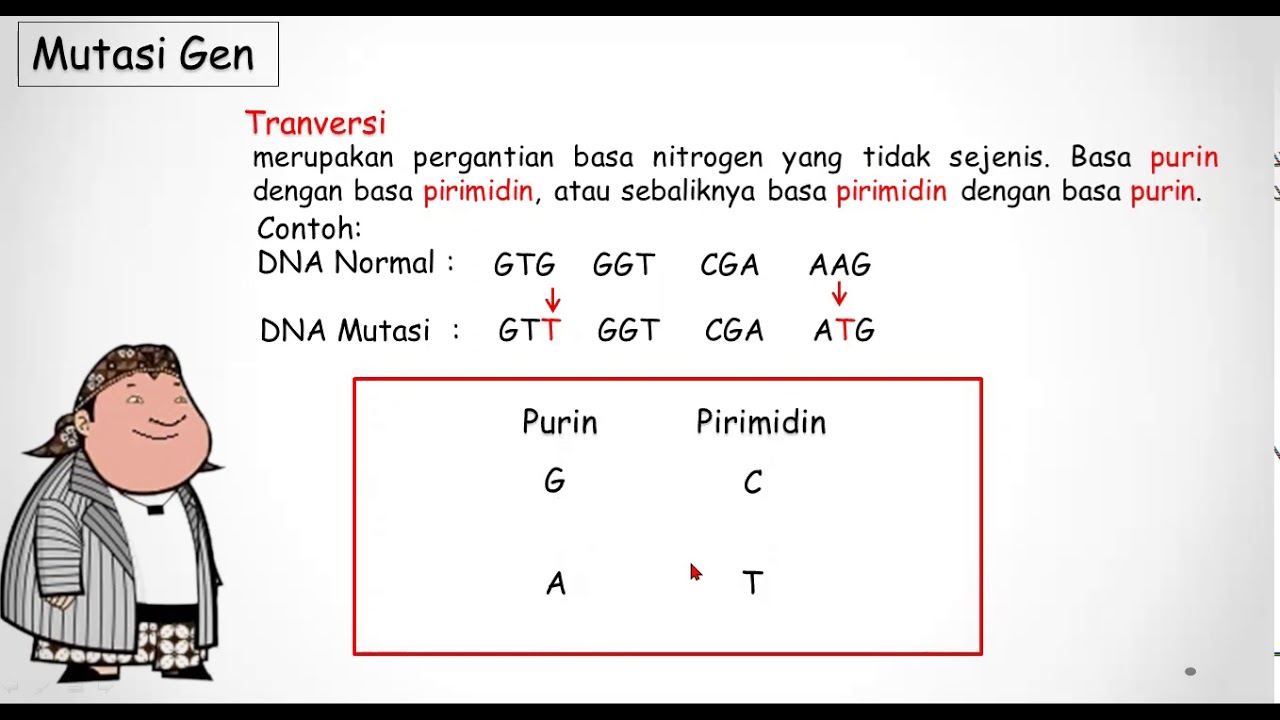
- 😀 Substitution mutations can be further categorized into transitions and transversions. Transition mutations involve swapping bases of the same type (purine for purine or pyrimidine for pyrimidine).
- 😀 Transversion mutations involve replacing a purine with a pyrimidine or vice versa.
- 😀 Purine bases include adenine (A) and guanine (G), while pyrimidine bases include cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
- 😀 In a transition mutation, purine bases (adenine or guanine) can be swapped, and pyrimidine bases (cytosine or thymine) can also be exchanged.
- 😀 In the case of a transversion mutation, a purine base (e.g., adenine or guanine) is replaced by a pyrimidine base (e.g., thymine or cytosine), or vice versa.
- 😀 A silent mutation occurs when a mutation does not alter the resulting amino acid, meaning the protein produced remains unchanged, despite the change in the DNA sequence.
- 😀 A missense mutation leads to a change in the amino acid sequence, which can affect the protein's structure and function. This happens when a base substitution causes an amino acid change.
Q & A
What is gene mutation?
-Gene mutation is a change in the genetic information of an organism. It involves alterations in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, which may affect the proteins that are produced.
What are the two main categories of gene mutations?
-The two main categories of gene mutations are base substitution and frameshift mutations.
What is the difference between a transition and a transversion mutation?
-A transition mutation occurs when one purine base is replaced by another purine, or one pyrimidine is replaced by another pyrimidine. A transversion mutation happens when a purine is replaced by a pyrimidine, or vice versa.
Can you explain what a silent mutation is?
-A silent mutation is a type of mutation that occurs when a change in the DNA sequence does not result in a change in the encoded protein. This can happen if the mutation leads to the same amino acid being produced.
What is a missense mutation?
-A missense mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that results in a different amino acid being produced, which can alter the function of the protein.
What happens in a transition mutation?
-In a transition mutation, a purine base is replaced by another purine (e.g., adenine is replaced by guanine) or a pyrimidine base is replaced by another pyrimidine (e.g., cytosine is replaced by thymine).
How does a transversion mutation affect the protein?
-A transversion mutation replaces a purine with a pyrimidine, or vice versa, which can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence of the protein, potentially altering its structure or function.
What does the term 'codon' refer to in the context of mRNA?
-A codon is a sequence of three nitrogen bases in mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis.
How does a transversion mutation involving guanine and thymine lead to a silent mutation?
-When guanine (a purine) is replaced by thymine (a pyrimidine) in a transversion mutation, the corresponding codon on mRNA may still code for the same amino acid, leading to no change in the resulting protein. This is an example of a silent mutation.
What are the three types of frameshift mutations mentioned in the video?
-The three types of frameshift mutations mentioned are insertion, addition, and deletion, which all result in a shift in the reading frame of the DNA sequence.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)