51. Mutations
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of gene mutations, including their types (substitution, insertion, deletion), consequences, and causes. Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur naturally or be triggered by external factors like mutagens. Point mutations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), can alter proteins, while frame shift mutations (insertions or deletions) change the protein structure significantly. The video also explores the role of mutations in evolution, explaining how beneficial mutations contribute to natural selection. Mutations can occur in germ cells, affecting offspring, or somatic cells, which don't pass on the changes. Ultimately, mutations contribute to genetic variation, driving evolution.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mutations are any changes to the DNA or RNA base sequence of a cell or virus.
- 😀 Gene mutations are structural changes at the molecular level in genes, leading to changes in the nucleotide sequence.
- 😀 Point mutations include substitutions, insertions, and deletions that alter DNA sequences.
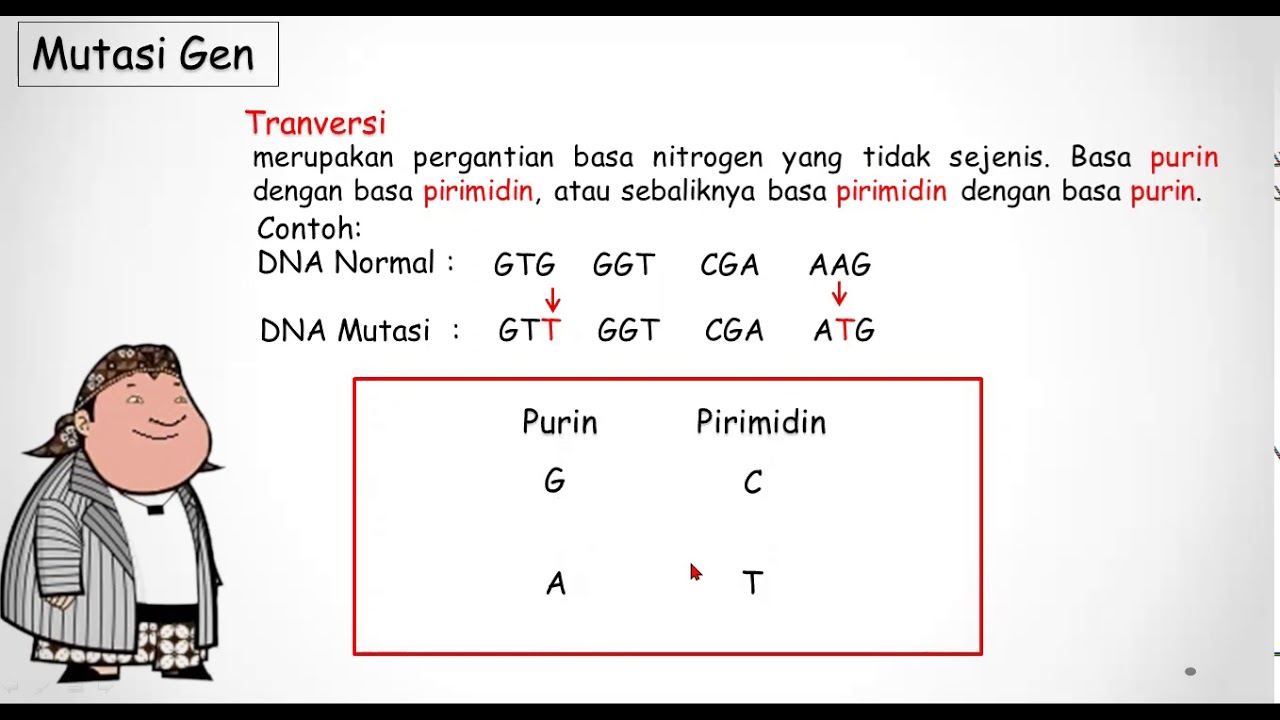
- 😀 Substitution mutations occur when one nucleotide is replaced by another, potentially leading to different amino acids in proteins.
- 😀 Insertion mutations add nucleotides to a DNA sequence, which can alter multiple codons and lead to significant changes in protein structure.
- 😀 Deletion mutations remove nucleotides from a gene, also altering codons and potentially resulting in a non-functional protein.
- 😀 Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur when one nucleotide is replaced, which can change the amino acid sequence and the protein function.
- 😀 Frame shift mutations result from insertions or deletions, which disrupt the reading frame of codons and can lead to dysfunctional proteins.
- 😀 Mutations can be neutral, beneficial, or harmful depending on their effects on the organism's traits, such as in genetic diseases or adaptation.
- 😀 Mutagens are agents like UV light, X-rays, and chemicals that can cause mutations in DNA, leading to genetic disorders or cancer.
Q & A
What are mutations?
-Mutations are changes to the DNA or RNA base sequence of a cell or virus, which can occur naturally or be induced by external factors.
What is the difference between gene mutations and other mutations?
-Gene mutations are structural changes at the molecular level of a gene, whereas other mutations may affect larger segments of DNA or the entire genome.
What are the three types of point mutations?
-The three types of point mutations are substitutions, insertions, and deletions. Each affects the DNA sequence in different ways, leading to changes in the protein produced.
What is a substitution mutation?
-A substitution mutation occurs when one nucleotide in the DNA sequence is replaced by another, which can change the protein produced if it alters the amino acid sequence.
What is the concept of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)?
-Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur when a single nucleotide is changed in a gene, potentially leading to different proteins and resulting in variations in traits or phenotypes.
What are insertion and deletion mutations, and how do they differ from substitutions?
-Insertion mutations add one or more nucleotides to the DNA sequence, while deletion mutations remove nucleotides. Both can cause frame shifts, altering the reading frame of codons and leading to significant changes in the resulting protein.
What is the difference between point mutations and frame shift mutations?
-Point mutations affect a single codon in a gene, often changing only one amino acid in the protein, while frame shift mutations involve insertions or deletions that shift the entire reading frame, altering the protein significantly.
Why are insertion and deletion mutations considered more dangerous than substitution mutations?
-Insertion and deletion mutations are more dangerous because they change the entire reading frame of the gene, affecting all subsequent codons and potentially producing a completely nonfunctional protein.
What are mutagens, and how do they cause mutations?
-Mutagens are agents, either physical (e.g., radiation) or chemical (e.g., tobacco smoke), that cause permanent changes to DNA. They can trigger mutations by directly damaging the DNA sequence.
How do mutations contribute to evolution and natural selection?
-Mutations provide genetic variation, which is essential for natural selection. The beneficial mutations improve an organism's chances of survival and reproduction, contributing to evolution over time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)