Summary of Gene Mutations
Summary
TLDRThis video explains gene mutations, focusing on their causes and types. Mutations can occur spontaneously during processes like DNA replication or be induced by mutagens such as UV radiation. The two main categories of mutations are insertion/deletions and point mutations. Insertion/deletions can cause frame shift or non-frame shift mutations, affecting protein structure. Point mutations include silent mutations (no amino acid change), missense mutations (altered amino acid), and nonsense mutations (premature protein termination). The video provides an overview of how these mutations affect genetic information and protein function.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gene mutation refers to a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that is not caused by genetic recombination.
- 😀 Mutations can be caused by errors during natural processes like DNA replication (spontaneous mutations) or by external factors known as mutagens (induced mutations).
- 😀 Spontaneous mutations occur due to errors in processes such as DNA replication, where DNA polymerase might make mistakes.
- 😀 Mutagens are external physical or chemical agents, such as UV radiation, that can induce gene mutations.
- 😀 Insertion and deletion mutations involve adding or removing nucleotides from the DNA sequence.
- 😀 Insertion or deletion mutations that are not multiples of three result in frame-shift mutations, altering the entire reading frame of the mRNA sequence.
- 😀 Frame-shift mutations change the sequence of amino acids produced and often lead to nonfunctional proteins.
- 😀 Insertion or deletion mutations that are multiples of three are called non-frame-shift mutations, which only add or remove amino acids without affecting the reading frame.
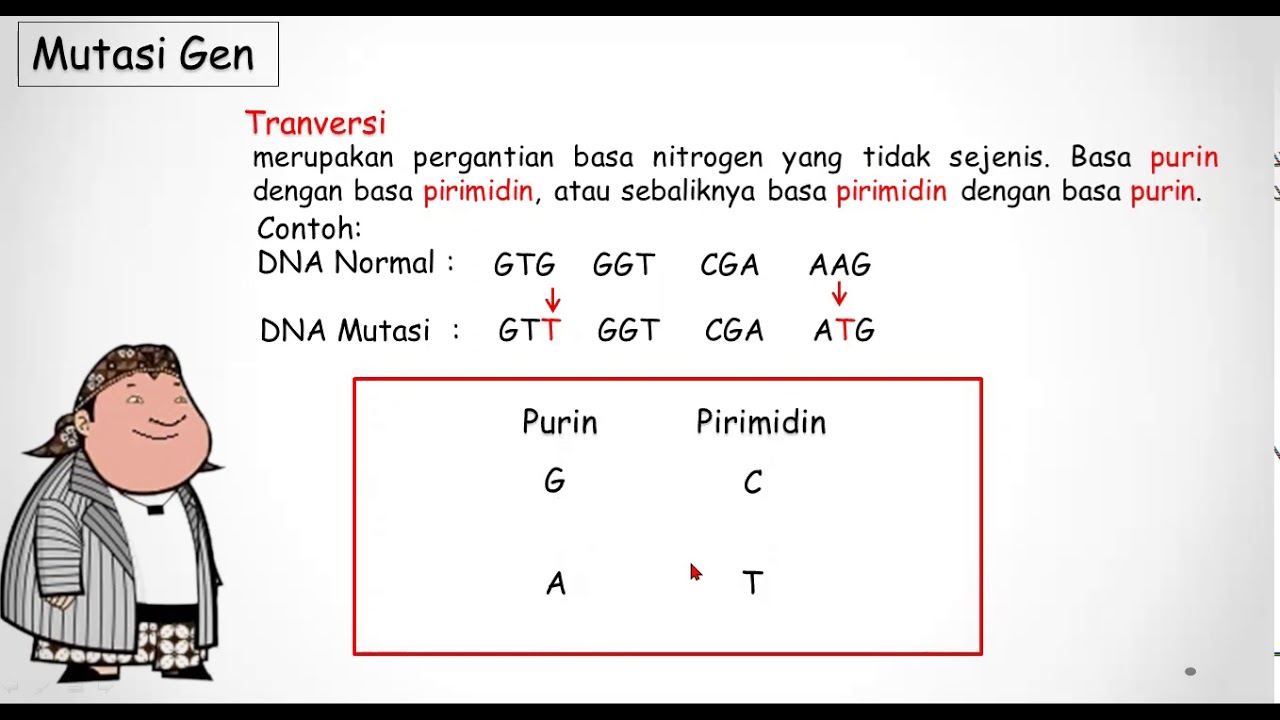
- 😀 Point mutations involve a change in a single nucleotide base pair and can be classified into three types: silent, missense, and nonsense mutations.
- 😀 Silent mutations do not change the amino acid sequence, even though a mutation occurs in the coding region of the DNA, due to the redundancy in the genetic code.
- 😀 Missense mutations result in a different amino acid being produced, altering the protein function.
- 😀 Nonsense mutations occur when a codon is changed to a stop codon, terminating the polypeptide chain prematurely and producing a nonfunctional protein.
- 😀 All point mutations are non-frame-shift mutations, as they only affect one base pair and do not shift the reading frame.
Q & A
What is a gene mutation?
-A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that is not caused by genetic recombination.
What are the two primary causes of gene mutations?
-Gene mutations can arise due to errors in natural cellular processes (spontaneous mutations) or due to external factors such as physical or chemical agents (induced mutations).
How can DNA replication lead to gene mutations?
-During DNA replication, DNA polymerase can make mistakes, incorrectly base-pair nucleotides, which results in a gene mutation.
What is a mutagen, and how does it cause mutations?
-A mutagen is an external physical or chemical agent, like UV radiation, that induces changes in the DNA sequence, leading to gene mutations.
What are insertion and deletion mutations?
-Insertion mutations involve adding nucleotides into the DNA sequence, while deletion mutations involve removing nucleotides. These mutations can affect the protein produced by altering the gene sequence.
What is a frame shift mutation?
-A frame shift mutation occurs when the number of inserted or deleted nucleotides is not a multiple of three, which shifts the reading frame and changes the entire amino acid sequence of the protein.
What is a non-frame shift mutation?
-A non-frame shift mutation occurs when the number of inserted or deleted nucleotides is a multiple of three, causing only a small change in the amino acid sequence without affecting the reading frame.
What is a point mutation?
-A point mutation, also known as a base pair mutation or substitution, is a change in a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence.
What are silent mutations, and why do they occur?
-A silent mutation is a point mutation that does not change the resulting amino acid because the genetic code is degenerate, meaning multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
What is a missense mutation?
-A missense mutation is a point mutation that changes one codon, resulting in the incorporation of a different amino acid into the protein, which can affect the protein's function.
What is a nonsense mutation, and how does it affect the protein?
-A nonsense mutation is when a codon that originally codes for an amino acid is changed to a stop codon, leading to premature termination of the protein and typically resulting in a nonfunctional protein.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)