Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the anatomy and function of the four rotator cuff muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. It explains their origins, insertions, and roles in shoulder movement, including abduction, external rotation, and internal rotation. The muscle innervations are detailed, along with specific tests for assessing each muscle's function, such as the Jobes test for supraspinatus and the Belly Press test for subscapularis. Understanding these muscles and their testing is crucial for diagnosing shoulder injuries and dysfunction.
Takeaways
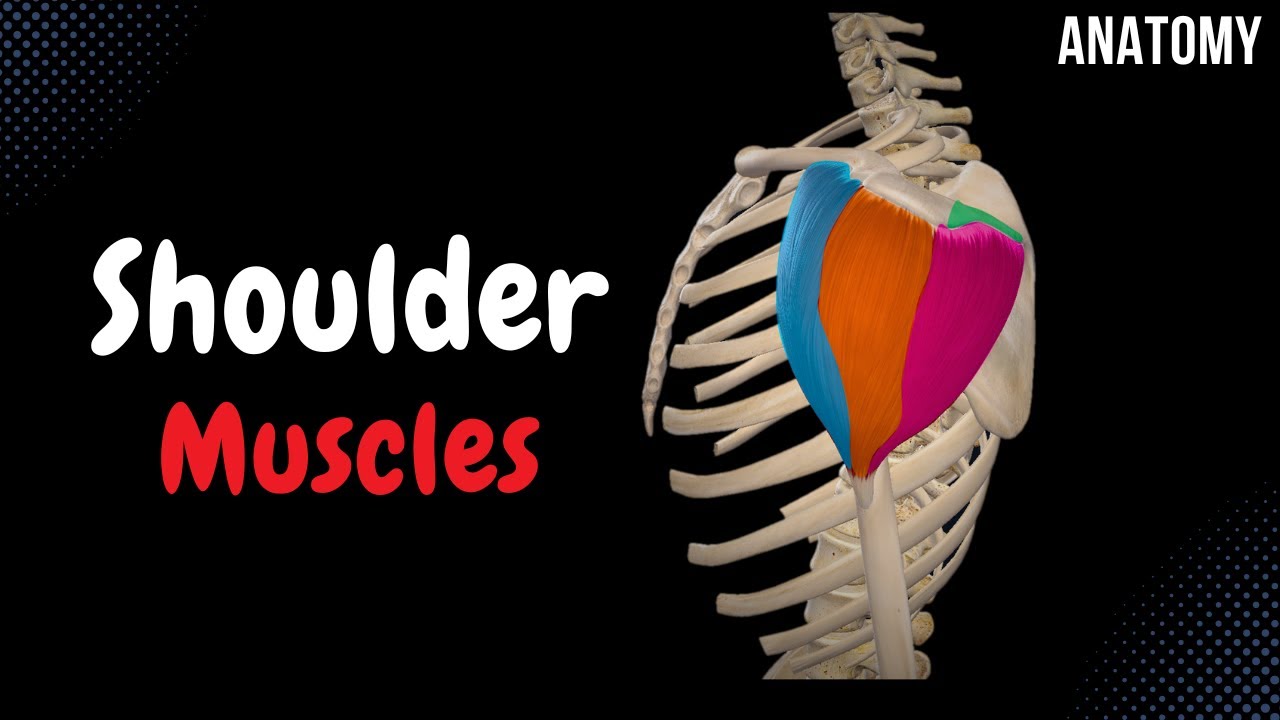
- 😀 The rotator cuff consists of four muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
- 😀 All four muscles of the rotator cuff originate from the scapula and insert into the proximal humerus.
- 😀 The supraspinatus muscle is responsible for abducting the arm and stabilizing the humerus. A tear in this muscle results in difficulty abducting the shoulder.
- 😀 The supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are innervated by the suprascapular nerve (C5, C6), which originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus.
- 😀 Jobe's test is one of the most reliable methods for assessing the supraspinatus muscle, involving shoulder abduction to 90° and flexion to 30° with maximal internal rotation.
- 😀 The infraspinatus muscle is the primary external rotator of the arm and helps stabilize the humerus. It is innervated by the suprascapular nerve (C5, C6).
- 😀 A tear in the infraspinatus results in difficulty with external rotation of the arm. The external rotation lag test is commonly used to assess this muscle.
- 😀 The teres minor muscle also contributes to external rotation of the arm and is innervated by the posterior branch of the axillary nerve (C5, C6).
- 😀 The Hornblower’s test is used to assess the teres minor muscle by testing the arm’s ability to maintain 90° of abduction without falling into internal rotation.
- 😀 The subscapularis muscle is the primary internal rotator of the arm. It originates from the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
- 😀 The Lift-Off, Lag, and Belly Press tests are commonly used to assess the function of the subscapularis muscle, with the Belly Press test focusing on internal rotation and avoiding wrist flexion.
Q & A
What is the function of the supraspinatus muscle in the rotator cuff?
-The supraspinatus muscle abducts the arm and stabilizes the humerus in the shoulder joint.
How can a tear of the supraspinatus muscle affect shoulder function?
-A tear of the supraspinatus muscle will result in an inability to abduct the shoulder.
Which nerve innervates the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles?
-Both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are innervated by the suprascapular nerve, which arises from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus (C5, C6).
What is the Jobes test used to assess?
-The Jobes test (or Empty Can Test) is used to assess the function of the supraspinatus muscle by testing the resistance to downward pressure when the arm is abducted and internally rotated.
Where is the infraspinatus muscle located and what is its primary function?
-The infraspinatus muscle is located on the posterior aspect of the scapula. Its primary function is external rotation of the arm and stabilization of the humerus.
What clinical test is used to assess the infraspinatus muscle?
-The infraspinatus muscle is typically tested by external rotation resistance tests or the external rotation lag test, where the patient is unable to maintain external rotation when the examiner releases the arm.
How is the teres minor muscle involved in shoulder movement?
-The teres minor muscle is involved in the external rotation of the arm, alongside the infraspinatus muscle.
What test is used to evaluate the function of the teres minor muscle?
-The Hornblower’s test is used to assess the teres minor muscle by testing the ability to maintain external rotation of the arm when it is abducted to 90°.
What is the role of the subscapularis muscle in the rotator cuff?
-The subscapularis muscle is the primary internal rotator of the arm and also helps with arm abduction and stabilization of the humerus.
Which tests can be performed to assess the subscapularis muscle?
-Tests for the subscapularis muscle include the Lift-Off test, Bear Hug test, and Belly Press test. These tests assess the muscle's strength and the integrity of its tendon.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)