Muscles of the Shoulder (Division, Origin, Insertion, Function)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the key muscles of the shoulder, focusing on their anatomy, function, and clinical importance. The shoulder muscles are categorized into four groups, with the rotator cuff (subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor) being essential for shoulder stability and movement. The deltoid muscle, divided into three parts, is responsible for a range of motions, including arm abduction and rotation. Understanding these muscles is crucial for diagnosing common shoulder injuries, such as rotator cuff tears and tendinitis, which can cause significant pain and limit mobility.
Takeaways
- 😀 The muscles of the shoulder joint are crucial for arm movement and stability.
- 😀 The shoulder muscles are divided into four anatomical parts: shoulder joint muscles, arm muscles, forearm muscles, and hand muscles.
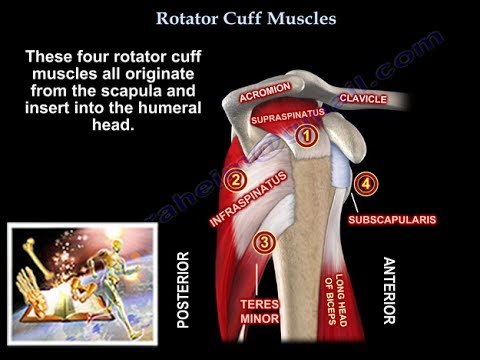
- 😀 The rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis) are essential for shoulder rotation and stability.
- 😀 Rotator cuff injuries can cause dull shoulder pain and worsen when raising the arm in certain ways.
- 😀 The deltoid muscle, located on the shoulder, is divided into three parts: spinal, acromial, and clavicular.
- 😀 The deltoid muscle allows for various movements: abduction, internal and external rotation, adduction, flexion, and extension of the arm, depending on which part contracts.
- 😀 The subscapularis muscle, located on the anterior scapula, adducts and internally rotates the arm.
- 😀 The supraspinatus muscle, located above the spine of the scapula, helps with arm abduction.
- 😀 The infraspinatus muscle, located below the spine of the scapula, externally rotates the arm.
- 😀 The teres minor muscle externally rotates and extends the arm, while the teres major muscle adducts, extends, and internally rotates the arm.
- 😀 The rotator cuff muscles are critical for stabilizing the shoulder joint, which is under constant stress from daily activities like lifting and moving arms.
- 😀 Rotator cuff injuries, such as tears, tendinitis, and bursitis, are common causes of shoulder pain.
Q & A
What are the four main groups of muscles in the upper limb?
-The muscles of the upper limb are categorized into four groups: muscles of the shoulder joint, muscles of the arm, muscles of the forearm, and muscles of the hand.
What muscles make up the rotator cuff in the shoulder?
-The rotator cuff consists of the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles.
What is the primary function of the deltoid muscle?
-The deltoid muscle is responsible for moving the shoulder. Its functions include abducting, flexing, and extending the arm, depending on which part of the muscle contracts.
How is the deltoid muscle divided anatomically?
-The deltoid muscle is divided into three parts: the spinal part (originating from the spine of the scapula), the acromial part (originating from the acromion of the scapula), and the clavicular part (originating from the clavicle).
What actions does the deltoid muscle perform when different parts contract?
-The deltoid performs various actions depending on the part that contracts: the acromial part abducts the arm, the clavicular part internally rotates the arm, and the spinal part externally rotates the arm. Combinations of these parts can flex, extend, or adduct the arm.
Where does the subscapularis muscle originate and what is its function?
-The subscapularis originates from the subscapular fossa on the scapula and inserts at the lesser tubercle of the humerus. Its function is to adduct and internally rotate the arm.
What is the role of the supraspinatus muscle in shoulder movement?
-The supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and helps abduct the arm by pulling it upwards.
How does the infraspinatus muscle contribute to shoulder motion?
-The infraspinatus muscle, which originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula, is responsible for externally rotating the arm.
What is the function of the teres minor muscle?
-The teres minor originates from the lateral margin of the scapula and externally rotates the arm. It also assists in extending the arm backwards.
What are the actions of the teres major muscle?
-The teres major muscle adducts, extends, and internally rotates the arm. It originates from the angle of the scapula and inserts at the crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus.
Why are rotator cuff injuries clinically significant?
-Rotator cuff injuries, such as tears, tendinitis, and bursitis, are clinically significant because they can cause persistent shoulder pain and limited mobility, particularly during arm elevation or certain movements.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)