Rotator cuff muscles
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the intricacies of the shoulder's rotator cuff muscles, crucial for swimmers and athletes. It highlights the role of these muscles in securing the humeral head within the glenoid fossa, enabling a wide range of motion. The video explores the functions of the four rotator cuff muscles—supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis—discussing their attachments, nerve supply, and impact on shoulder stability and movement. It also touches on common injuries and offers exercises to strengthen these muscles, emphasizing the importance of maintaining shoulder health for those with physically demanding activities.
Takeaways
- 🏊♂️ The script discusses the importance of shoulder muscles, especially for swimmers, in providing power and stroke length.
- 🤔 The focus is on the rotator cuff muscles, which are crucial for securing the humeral head within the glenoid fossa and preventing shoulder injuries.
- 💪 There are six scapular humeral muscles, including the deltoid and teres major, which are not part of the rotator cuff but play a role in shoulder movement.
- 🔍 The rotator cuff muscles include supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis, which are essential for supporting the shoulder joint.
- 🏋️♀️ The supraspinatus muscle initiates the abduction of the upper limb, followed by the deltoid and trapezius muscles.
- 🔄 The rotator cuff muscles are responsible for both medial and lateral rotation of the humerus, with specific muscles contributing to each movement.
- 🚫 The rotator cuff muscles do not contribute to the adduction of the humerus, which is handled by other muscles like latissimus dorsi.
- 🤕 Overuse injuries are common in the rotator cuff muscles due to their small size and the large range of motion they support.
- 🏥 The supraspinatus tendon can become inflamed, leading to issues like tendonitis, especially when passing through the narrow space under the acromion.
- 💡 Strengthening the rotator cuff muscles is essential for those who use their shoulders extensively, such as swimmers, and can be done using light resistance like elastic bands.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the rotator cuff muscles in the shoulder?
-The primary function of the rotator cuff muscles is to support the humeral head within the glenoid fossa, maintaining the shoulder joint's integrity and stability.
How many muscles form the rotator cuff, and what are their names?
-There are four muscles that form the rotator cuff: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
Why are the rotator cuff muscles prone to overuse injuries?
-The rotator cuff muscles are prone to overuse injuries because they have to pass across a small space, which can lead to inflammation and tendonitis, especially due to their critical role in stabilizing the shoulder joint.
What is the role of the deltoid muscle in the shoulder joint?
-The deltoid muscle plays a significant role in holding the humerus into the joint, aiding in abduction, flexion, extension, medial rotation, and lateral rotation of the humerus.
How does the supraspinatus muscle contribute to the movement of the arm?
-The supraspinatus muscle initiates the abduction of the upper limb, allowing the arm to move away from the body.
What is the difference between the teres major and teres minor muscles in terms of their function and innervation?
-Teres major is a medial rotator of the humerus and is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve, while teres minor is a lateral rotator and is innervated by the axillary nerve.
Which nerve innervates the infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscles?
-Both the infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscles are innervated by the suprascapular nerve.
What is the function of the subscapularis muscle in the shoulder joint?
-The subscapularis muscle, located anteriorly, contributes to medial rotation of the humerus, and its main function is to hold the humeral head in place within the glenoid fossa.
How can one strengthen the rotator cuff muscles?
-Strengthening the rotator cuff muscles can be achieved through exercises using elastic bands, focusing on medial and lateral rotation movements to engage the respective muscles effectively.
What is the significance of the brachial plexus in relation to the shoulder muscles discussed in the script?
-The brachial plexus is significant as it provides the nerves that innervate the shoulder muscles discussed, including the suprascapular, axillary, and subscapular nerves.
Why is it important to maintain good shoulder posture and muscle strength for individuals who use their shoulders frequently?
-Maintaining good shoulder posture and muscle strength is crucial for individuals who frequently use their shoulders to prevent joint and muscle damage, ensuring effective use of the rotator cuff muscles and overall shoulder joint health.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
FULL VIDEO: Main muscles of the upper limb - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
Muscles of the Shoulder (Division, Origin, Insertion, Function)

Shoulder Pain and Popping (SHORT & LONG TERM FIX!)
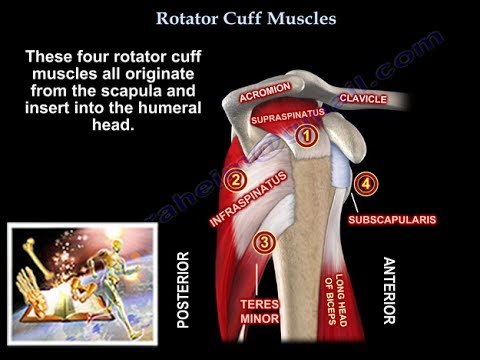
Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Building Bulletproof Shoulders: For Strength, Mobility, Resilience, & Stability

Regio Pectoralis, Deltoidea, Dorsalis (Video 15)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)