GCSE Physics - How the Electric Motor Works #80
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the workings of an electric motor are explained through the concept of the motor effect, where a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experiences force. Using Fleming's left-hand rule, the video illustrates how the direction of current and magnetic fields determine the motion of a coil, which spins due to alternating forces. To maintain continuous rotation, a split ring commutator is introduced, allowing the current direction to swap with each half turn. The video concludes by noting that while the example is simplified, these principles are foundational in various applications, from fans to vehicles.
Takeaways
- ⚡ The motor effect occurs when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, causing it to experience a force.
- 🖐️ Fleming's Left Hand Rule helps determine the direction of the force based on the current and magnetic field directions.
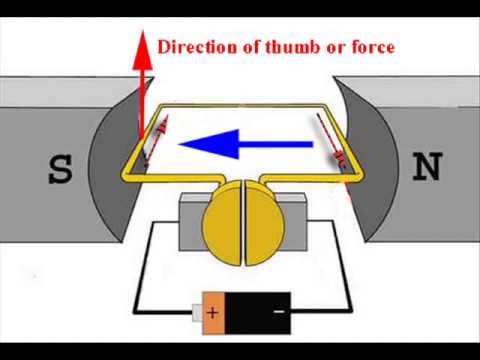
- 🔄 A coil with current flowing through it experiences different forces on each side, causing it to spin.
- 🔁 Upon rotating 180 degrees, the current direction in the coil reverses, which also reverses the forces acting on it.
- ↔️ Without current direction reversal, the coil would oscillate instead of achieving continuous rotation.
- 🔄 A split ring commutator is used to reverse the current direction every half turn, allowing for consistent spinning motion.
- 🔗 The commutator keeps the current flowing in the same direction relative to the coil's position, facilitating uninterrupted rotation.
- 🛠️ Electric motors are widely used in various applications, including fans, vehicles, and hard drives.
- 📈 The rotation speed of a motor can be increased by boosting the current, adding more coil turns, or using stronger magnets.
- ⚙️ Understanding the principles behind electric motors is essential for grasping broader concepts in engineering and physics.
Q & A
What is the motor effect?
-The motor effect occurs when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, causing the wire to experience a force.
How does the direction of the force on the wire depend on the magnetic field and current?
-The direction of the force is determined by the orientations of both the magnetic field and the current, which can be predicted using Fleming's left-hand rule.
What happens to the forces acting on a coil of wire as it rotates 180 degrees?
-As the coil rotates 180 degrees, the direction of the current changes, which swaps the forces acting on each side of the coil, causing the direction of rotation to reverse.
Why would a coil not turn continuously in one direction without modification?
-Without modifications, the coil would just flip back and forth between two positions instead of completing a full 360-degree rotation.
What is the purpose of a split ring commutator in a motor?
-The split ring commutator changes the direction of the current every half turn, ensuring that the forces acting on the coil continue to rotate it in the same direction.
How does the split ring commutator affect the rotation of the coil?
-The commutator maintains a consistent flow of current direction, allowing the coil to rotate continuously in one direction, rather than reversing.
What are some methods to increase the speed of rotation in an electric motor?
-The speed of rotation can be increased by raising the current, adding more turns to the coil, or using stronger magnets to enhance the magnetic flux density.
In what types of devices are electric motors commonly found?
-Electric motors are used in various devices, including fans, vehicles, and hard drives.
What is the relationship between the direction of the current and the forces on the coil?
-The direction of the current determines the direction of the forces acting on the coil; when the current reverses, the forces do as well.
Why is understanding the operation of electric motors important in engineering?
-Understanding how electric motors work is crucial for designing and improving devices that rely on electric power for movement and functionality.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)