Bioenergetics: The transformation of free energy in living systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate processes of energy transformation in living organisms, focusing on photosynthesis and cellular respiration. It begins with the importance of the heart's continuous function and traces energy back to the sun, which plants harness through photosynthesis to create glucose. This glucose is then utilized by animals through cellular respiration to produce ATP, the energy currency of cells. The video highlights the cyclical nature of these processes, demonstrating how the products of one serve as the reactants of the other, ultimately illustrating the vital relationship between sunlight, plants, and animal life.
Takeaways
- 😀 The heart beats continuously, requiring a significant amount of energy throughout life.
- 🌞 Energy for the body originates from the sun, but humans cannot directly absorb it.
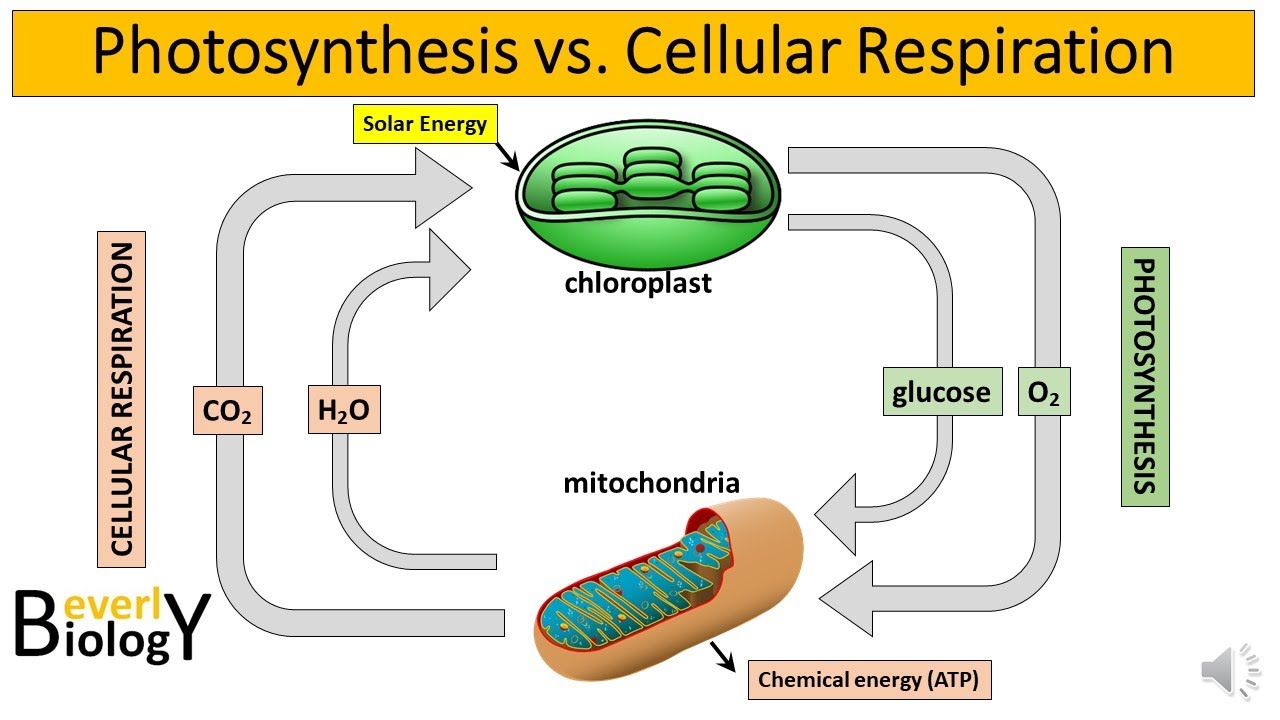
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert sunlight into glucose using inorganic compounds.
- 🔄 Cellular respiration is the process that breaks down glucose in animals to release usable energy (ATP).
- 🧪 The light reactions in photosynthesis occur in the chloroplasts, generating NADPH and ATP from sunlight.
- 🔬 The Calvin Cycle uses NADPH and ATP to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide.
- ⚗️ Glucose breakdown begins with its conversion to pyruvate, releasing a small amount of ATP.
- 🍃 The TCA cycle (Krebs cycle) further processes pyruvate, producing NADH and FADH2, which are vital for energy production.
- 💧 The electron transport chain uses high-energy carriers to produce ATP and water, illustrating the connection between photosynthesis and respiration.
- 🔁 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected; the products of one are the reactants of the other, creating a continuous cycle of energy transformation.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the heart?
-The heart's primary function is to pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
Where does the energy that our body uses originate from?
-The energy our body uses originates from the sun, which is transformed into usable energy through the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
How do plants convert sunlight into energy?
-Plants convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, where they transform inorganic compounds into glucose using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
What is ATP, and why is it important?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the usable form of energy for cells. It powers various cellular processes, including muscle contraction and biochemical reactions.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
-The two main stages of photosynthesis are the light reactions and the Calvin Cycle.
What is produced during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
-The light reactions produce NADPH and ATP as energy carriers and release oxygen as a byproduct.
What happens to glucose during cellular respiration?
-During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, which is then further processed to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
What is the TCA cycle, and what is its significance?
-The TCA cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that generate high-energy electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) and carbon dioxide from acetyl-CoA.
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration connected?
-Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected; the products of one process serve as the reactants for the other, maintaining the cycle of energy flow in ecosystems.
What role do NADPH and NADH play in these processes?
-NADPH is produced during photosynthesis and acts as a high-energy electron carrier, while NADH is produced during cellular respiration, serving a similar role in transferring energy to produce ATP.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration | Week 8 | SCIENCE 9 - QUARTER 1 (MELC 5)
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration

Grade 9 Science Q1 Ep 8 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Part 2

Transformasi Energi dan Metabolisme di dalam Sel - Energi dalam Sistem Kehidupan

Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Comparison

مسابقة موهوب - (علوم الأحياء): الطاقة الخلوية
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
