How does a Refrigerator work? 3D Animation
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate workings of a refrigerator, detailing its structure, insulation, and refrigeration cycle. It explains how the outer cabinet is crafted from coated sheet metal, while the inner components are designed for maximum insulation. The refrigeration cycle is examined, highlighting the roles of the compressor, condenser, and evaporator in keeping food fresh by transferring heat away from the interior. Additionally, the video outlines the electrical system that controls the fridge's temperature, showcasing the various components involved in its efficient operation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Refrigerators use coated sheet metal and thermoplastic for their outer structure to protect against external elements.
- 🧊 The inner liner and door lining are made of high-impact polystyrene, insulated with rigid polyurethane foam to keep the cold air in.
- 🔒 A rubber gasket seals the refrigerator, ensuring cold air stays inside.
- 📦 Shelves and drawers made of acrylic plastic provide convenient storage for food items.
- 🔄 The refrigeration cycle is a closed compression process involving five main components: compressor, condenser, expansion device, evaporator, and refrigerant.
- 💨 The refrigerant is a fluid that has a low boiling point, allowing it to cycle between vapor and liquid while transferring heat.
- ⚙️ The cycle starts with the refrigerant entering the compressor as a low-pressure vapor, which is then pressurized and turned into a high-pressure vapor.
- 🌬️ In the condenser, the refrigerant condenses into a liquid while releasing heat to the environment, aided by aluminum fins for better heat transfer.
- 🚰 After passing through a filter dryer, the refrigerant enters the expansion device, where it experiences a significant pressure drop before entering the evaporator.
- ❄️ Inside the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, cooling the interior of the fridge and evaporating back into vapor to restart the cycle.
Q & A
What materials are used for the outer cabinet and door of a refrigerator?
-The outer cabinet and door are made from coated sheet metal and thermoplastic materials that protect the fridge from the elements.
What is the purpose of the rigid polyurethane foam in a refrigerator?
-Rigid polyurethane foam provides insulation, keeping the cold air inside the fridge and preventing heat from entering, which helps to keep food fresh.
How does the refrigeration cycle begin?
-The refrigeration cycle begins with the refrigerant entering the compressor as a low-pressure, low-temperature vapor.
What role does the compressor play in the refrigeration cycle?
-The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure, high-temperature vapor before it moves to the condenser.
What happens to the refrigerant in the condenser?
-In the condenser, the refrigerant condenses into a liquid while releasing heat to the environment, aided by copper coils and aluminum fins to enhance heat transfer.
What function does the expansion device serve in the refrigeration cycle?
-The expansion device, often a thin capillary tube, reduces the pressure of the refrigerant as it flows into the evaporator, allowing it to expand and cool.
How does the evaporator contribute to cooling the refrigerator?
-The evaporator absorbs heat from the air inside the fridge, causing the refrigerant to evaporate, which cools the air within the refrigerator.
What triggers the compressor to turn on in the electrical system?
-The thermostat monitors the internal temperature of the refrigerator; if it rises above a set threshold, it activates the compressor via a relay.
What materials are the shelves and drawers of a refrigerator typically made from?
-The shelves and drawers are usually made of acrylic plastic, providing durability and storage space.
Why is refrigerant chosen for use in refrigerators?
-Refrigerant is selected for its low boiling point, which allows it to efficiently absorb heat and transition between liquid and vapor states during the refrigeration cycle.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

The History of Refrigeration
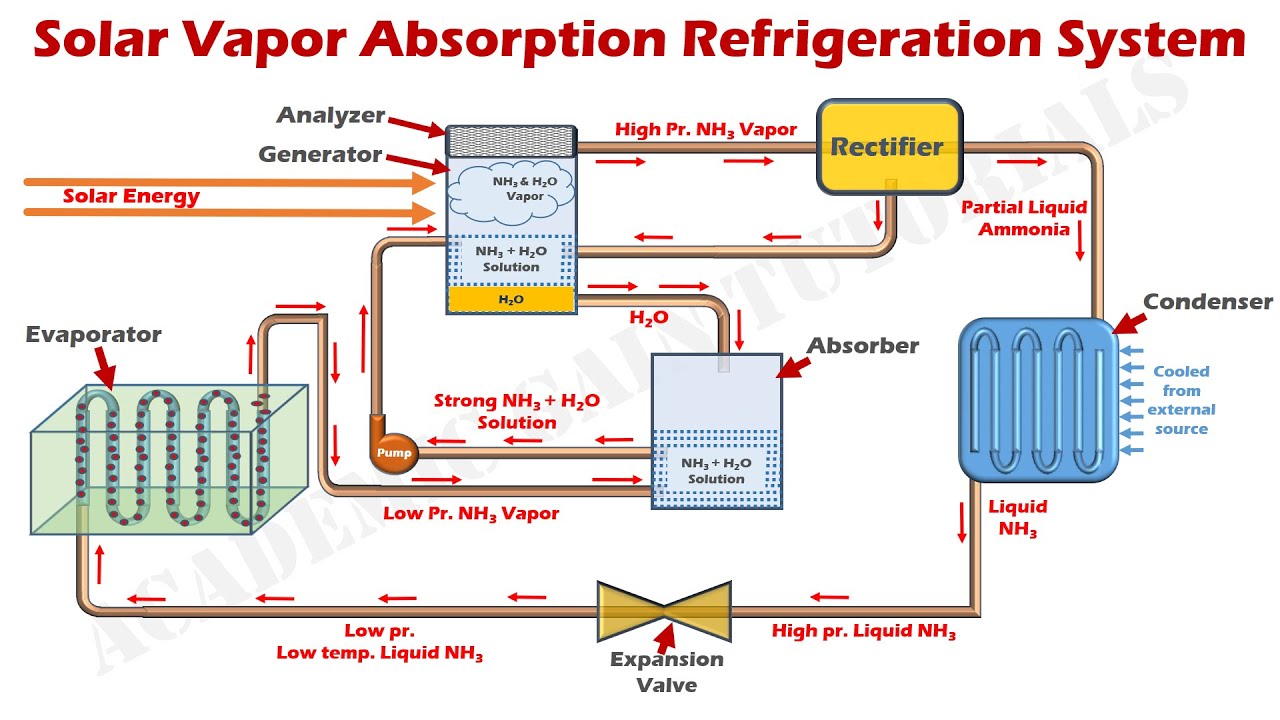
Solar Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (Ammonia-Water Solar Cooling System) Explained.

DIY Vapor Compression Refrigeration System

Sistem Saraf: Otak Manusia | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda

motore asincrono trifase - 01 - principio di funzionamento

IPA kelas 9 Bab 2 kurikulum merdeka sistem saraf Alat Indera Manusia #kurikulummerdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
