motore asincrono trifase - 01 - principio di funzionamento
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the workings of a three-phase asynchronous motor, detailing its core components: the stator and rotor. The stator, made from laminated ferromagnetic sheets, features slots for windings that create a rotating magnetic field. The arrangement of these windings, spaced at 120-degree intervals, enables the generation of balanced currents essential for motor operation. The rotor, typically designed as a squirrel cage, rotates within the stator, driven by this magnetic field. Additionally, the video discusses how changing the phase connections can reverse the motor's rotation direction, illustrating the intricate relationship between structure, current, and motion.
Takeaways
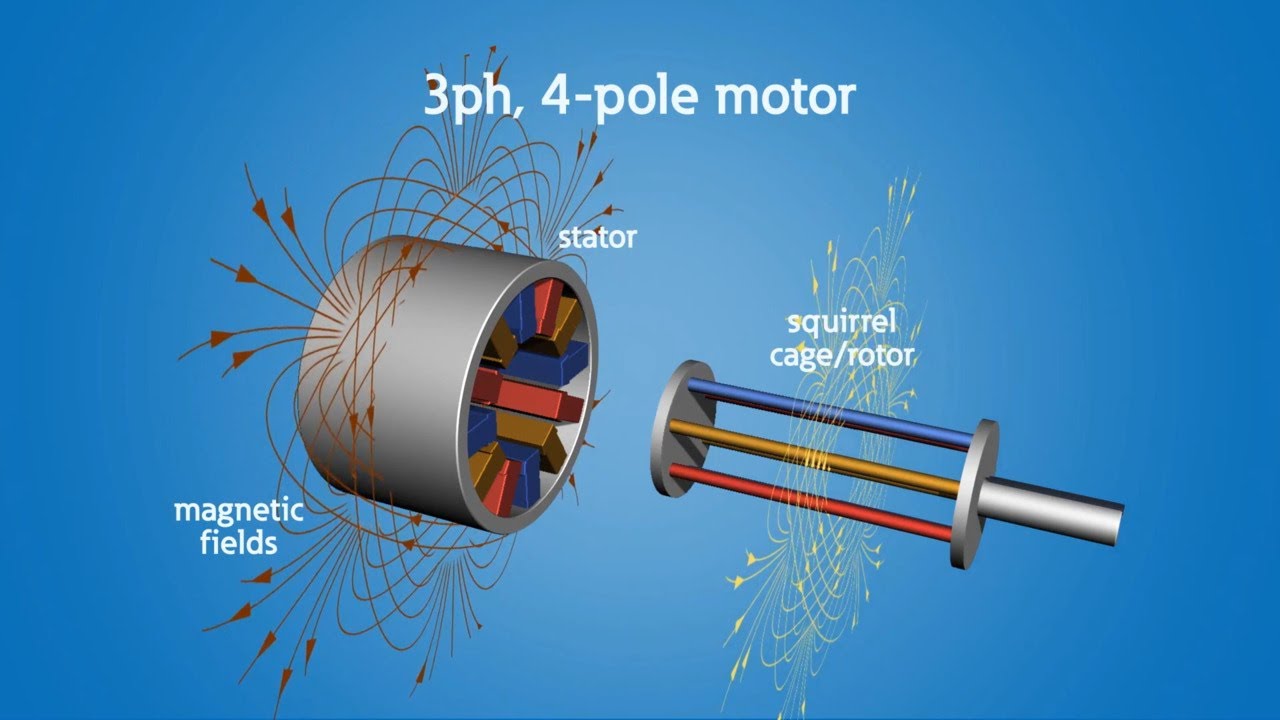
- 🔧 The three-phase asynchronous motor consists of two main components: the stator and rotor.
- 🧲 The stator is made of insulated ferromagnetic laminations, creating a cylindrical shape with 24 slots for windings.
- 📏 Each phase of the motor has 8 slots, and the total number of slots is always a multiple of 3.
- ⚡ The stator windings are arranged in pairs across the slots to produce a magnetic field with north and south polarities.
- 🔄 The rotor is typically designed as a squirrel cage, with conductive bars connected by short-circuiting rings.
- 📐 Windings in the stator are spaced 120 degrees apart to ensure a balanced three-phase current.
- 🌪️ This arrangement generates a rotating magnetic field essential for the motor's operation.
- 🚀 The angular velocity of the rotating magnetic field (ω₀) is related to the supply frequency and the number of pole pairs.
- 🔁 The direction of the magnetic field—and thus the rotor's rotation—can be reversed by swapping two of the supply phases.
- 🛠️ Understanding the structure and function of both the stator and rotor is crucial for the efficient operation of the motor.
Q & A
What is the primary component of a three-phase asynchronous motor described in the transcript?
-The primary component is the stator, which is made of a laminated ferromagnetic material.
How is the stator constructed?
-The stator is constructed using a stack of laminated sheets, insulated from each other, to form a cylindrical shape.
What are the cavities in the stator used for?
-The cavities in the stator are used to house the stator windings, which are arranged in a specific configuration.
Why is the number of cavities along the stator's circumference always a multiple of three?
-The number of cavities is a multiple of three because there are three primary windings that make up the stator windings.
How many cavities are mentioned in the transcript for the discussed motor?
-The motor has 24 cavities, which means there are 8 cavities per phase.
What is the significance of the arrangement of the windings in the stator?
-The arrangement of the windings determines the number of poles in the magnetic field generated by the motor.
What is a 'squirrel cage' rotor?
-A 'squirrel cage' rotor is a type of rotor commonly used in these motors, characterized by conductive bars and short-circuiting rings.
How are the stator windings spaced in relation to each other?
-The stator windings are spaced at an angle of 120 degrees from each other.
What condition is necessary to achieve a rotating magnetic field?
-A balanced set of currents with equal effective values and a phase shift of 120 degrees between them is necessary to achieve a rotating magnetic field.
What relationship exists between the angular velocity of the rotating magnetic field and the motor's characteristics?
-The angular velocity of the rotating magnetic field is related to the frequency of the supply currents and the number of pole pairs in the magnetic field.
How can the direction of rotation of the motor be changed?
-The direction of rotation can be changed by swapping two of the supply phases.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Motors 101

Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor | Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Single Phase Induction Motor (Capacitor Induction Motor or AC Motor) explained

penjelasan dan pengenalan bagian - bagian dari motor listrik 3 phase || motor induksi 3 fase

MOTORE ASINCRONO TRIFASE o MOTORE A INDUZIONE - smontaggio e spiegazione del suo funzionamento
Construction and Working of a Single phase Induction Motor | Skill-Lync
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)