Introduction to Perfect Competition | Economics Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video explores perfectly competitive markets, characterized by numerous sellers and buyers, identical products, and easy market entry and exit. Using the wheat market as a prime example, it illustrates how businesses have no power over pricing, as consumers will always opt for the lowest price available. Sellers produce where their marginal cost meets the market price, leading to minimal advertising and straightforward operational decisions. Although true perfect competition is rare, understanding this concept helps clarify market dynamics and the importance of product differentiation in most industries.
Takeaways
- 🏆 Competition can be understood in various contexts, including sports, markets, and businesses.
- 📊 The Market Structure Continuum ranges from Perfect Competition to Monopoly, with Perfectly Competitive markets being a focal point.
- 🌾 The wheat market is an example of a perfectly competitive market with many buyers and sellers.
- 👥 In a perfectly competitive market, each seller holds a small share of the overall market.
- 💡 Characteristics of perfect competition include identical goods, ease of entry and exit for businesses, and many market participants.
- 💰 In perfectly competitive markets, price is determined by the market, and individual sellers have little control over it.
- 📈 The demand curve faced by individual sellers in a perfectly competitive market is flat, meaning they cannot charge more than the market price.
- 🔍 Sellers can sell as much as they produce at the market price but have no incentive to charge less.
- 📉 Businesses in perfect competition produce where marginal cost equals market price, influencing their output decisions.
- ✨ While perfect competition is rare in reality, it serves as a useful model for understanding economic concepts and market dynamics.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video primarily focuses on perfectly competitive markets within the broader context of market structures.
What are the four types of market structures mentioned in the video?
-The four types of market structures mentioned are Perfect Competition, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Monopoly.
What characteristics define a perfectly competitive market?
-A perfectly competitive market is characterized by many sellers and buyers, identical products, and easy entry and exit for businesses.
Why is the wheat market considered an example of perfect competition?
-The wheat market is considered an example of perfect competition due to its large number of sellers and buyers, as well as the identical nature of the product being sold.
How do buyers behave in a perfectly competitive market?
-In a perfectly competitive market, buyers primarily focus on price and will purchase from the seller offering the lowest price.
What happens if a seller tries to charge more than the market price?
-If a seller tries to charge more than the market price, they will not sell any product, as buyers will choose to buy from sellers offering the lower market price.
What does the demand curve look like for a seller in a perfectly competitive market?
-The demand curve for a seller in a perfectly competitive market is flat, indicating that the seller can sell any amount of product at the market price.
What is the relationship between marginal cost and market price for businesses in a perfectly competitive environment?
-Businesses in a perfectly competitive environment choose to produce at a level where their marginal cost equals the market price.
Why do businesses in perfectly competitive markets typically not engage in advertising?
-Businesses do not engage in advertising in perfectly competitive markets because it offers no advantage; the market price is determined by overall supply and demand, not individual seller efforts.
Is perfect competition realistic for most goods and services? Why or why not?
-No, perfect competition is not realistic for most goods and services because variety and product differentiation are essential for consumer choice, leading to many businesses making unique decisions about what to produce.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

pasar persaingan sempurna
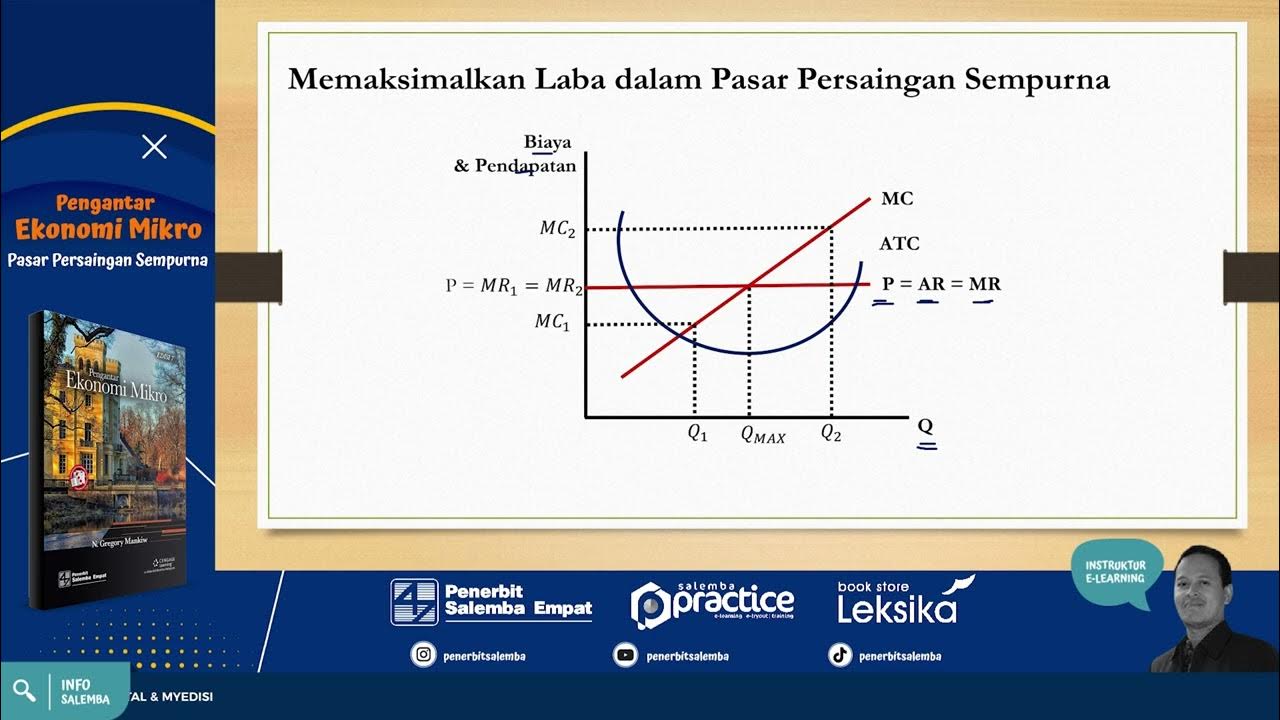
Pasar Persaingan Sempurna -Pengantar Ekonomi Mikro- #soaldanpembahasan #elearningplatform

"PASAR PERSAINGAN SEMPURNA" Kelompok 4

Market Structure Part 1: Introduction

CFA® Level I Economics - Characteristics of Market Structure

Perfect competition | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
