pasar persaingan sempurna
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the concept of perfect competition in economic markets, highlighting its definition, characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. Perfect competition is characterized by many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and free entry and exit. It leads to efficient resource allocation and optimal production levels, benefiting consumers with lower prices. However, it also lacks incentives for innovation and may result in negative social costs. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these dynamics in analyzing market behaviors and economic efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 Perfect competition is defined as a market structure with many buyers and sellers, where no single entity can influence market prices.
- 😀 Characteristics of perfect competition include price-taking firms, easy entry and exit from the market, and the production of identical goods.
- 😀 In a perfectly competitive market, all buyers have perfect knowledge about prices, preventing producers from charging above-market rates.
- 😀 Firms in perfect competition cannot maintain long-term profits due to the inability to differentiate their products.
- 😀 The efficiency of resource allocation in perfect competition is achieved when price equals marginal cost.
- 😀 Long-term, firms in perfect competition achieve productive efficiency, producing at the lowest possible cost.
- 😀 Perfect competition does not incentivize innovation, as firms cannot secure long-lasting advantages from new technologies.
- 😀 The model of perfect competition may lead to social costs, such as environmental pollution, despite being economically efficient.
- 😀 Consumer choice is limited in perfect competition due to the uniformity of products, contrasting with monopolistic and oligopoly markets that offer more variety.
- 😀 Income distribution in a perfectly competitive market can be uneven, leading to inefficiencies in resource allocation that favor wealthier groups.
Q & A
What defines a perfectly competitive market?
-A perfectly competitive market is defined by the presence of many buyers and sellers, identical products, and prices that are determined by market forces rather than individual firms.
What is the significance of firms being price takers in perfect competition?
-Being price takers means that individual firms cannot influence the market price; they must accept the price determined by the overall market supply and demand.
Why is easy entry and exit into a market important in perfect competition?
-Easy entry and exit allow firms to respond quickly to market conditions, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. Firms can leave if they incur losses, maintaining overall market health.
How do homogeneous products affect competition among firms?
-Homogeneous products mean that goods offered by different firms are identical, leading to competition primarily on price rather than product differentiation.
What role does consumer knowledge play in a perfectly competitive market?
-Consumers possess perfect knowledge about market prices and products, which prevents firms from charging higher prices than those prevailing in the market.
How do firms maximize profits in a perfectly competitive market?
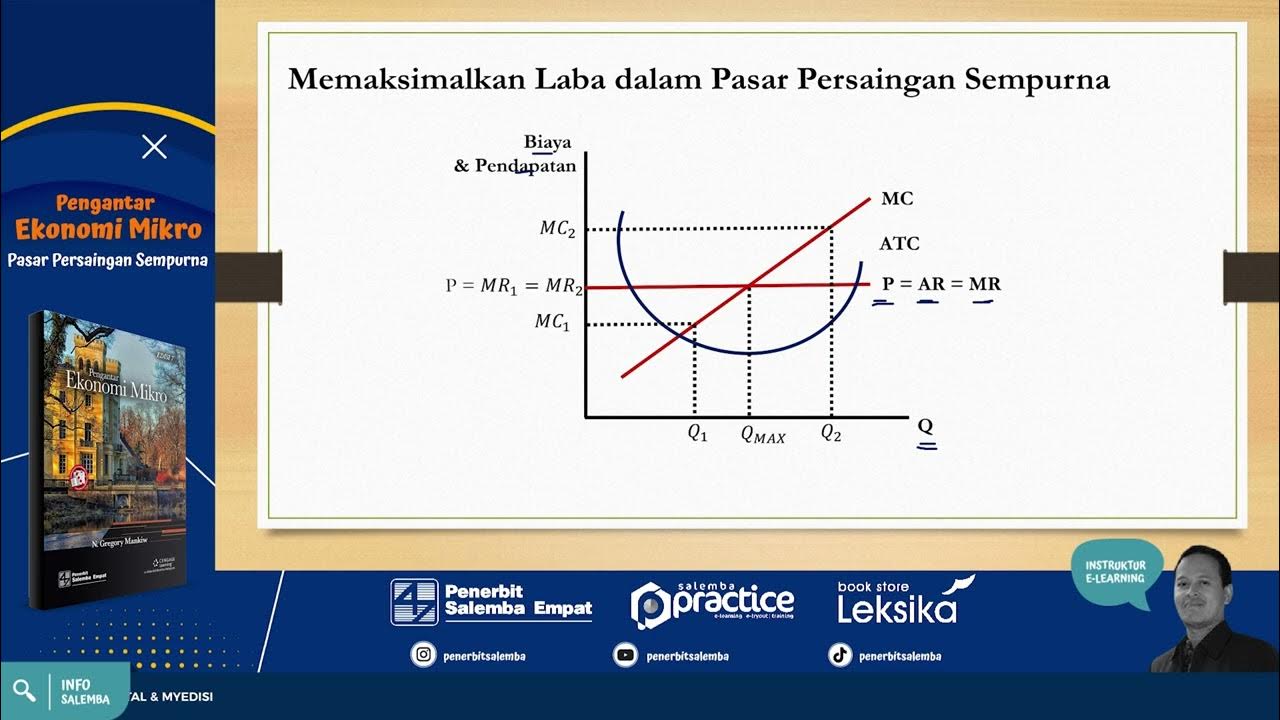
-Firms maximize profits by producing at a level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR = MC), ensuring the highest possible profit margin.
What are the two types of efficiency discussed in perfect competition?
-The two types of efficiency are productive efficiency, which occurs when production costs are minimized, and allocative efficiency, which happens when the price equals marginal cost.
What are the advantages of perfect competition for consumers?
-Consumers benefit from lower prices, greater efficiency, and a wider range of choices, as firms strive to meet the demands of well-informed buyers.
What are the drawbacks of perfect competition regarding innovation?
-The lack of sustained profits discourages firms from investing in innovation and technological advancements, leading to stagnation in product development.
How does income distribution in a perfectly competitive market affect resource allocation?
-Inequalities in income distribution can result in resources being allocated inefficiently, as wealthier consumers may drive production towards luxury goods rather than essential items needed by lower-income groups.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Globalization - an overview - Englisch Abitur, Oberstufe - Abiturthemen

Perfect Competition- Microeconomics 3.7
Pasar Persaingan Sempurna -Pengantar Ekonomi Mikro- #soaldanpembahasan #elearningplatform

¿Qué es el CAPITALISMO y cuáles son sus características? Representantes, ventajas y desventajas💰

Pasar dan Jenis Pasar | Ekonomi Kelas 10 - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR

"PASAR PERSAINGAN SEMPURNA" Kelompok 4
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)