PERMINTAAN DAN PENAWARAN UANG
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the critical role of money in the economy, focusing on the concepts of money demand and supply. It explains how demand arises from people's need to hold cash for transactions, precautions, and speculative investments. Theories from Keynes and Ricardo are discussed, emphasizing the inverse relationship between money supply and its value. The video also covers the types of money supply, including M1, M2, and M3, and highlights factors influencing both demand and supply, such as monetary policy, interest rates, and income levels, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential economic concepts.
Takeaways
- 💰 Money plays a crucial role in a country's economic activities, serving as a medium of exchange for society and producers.
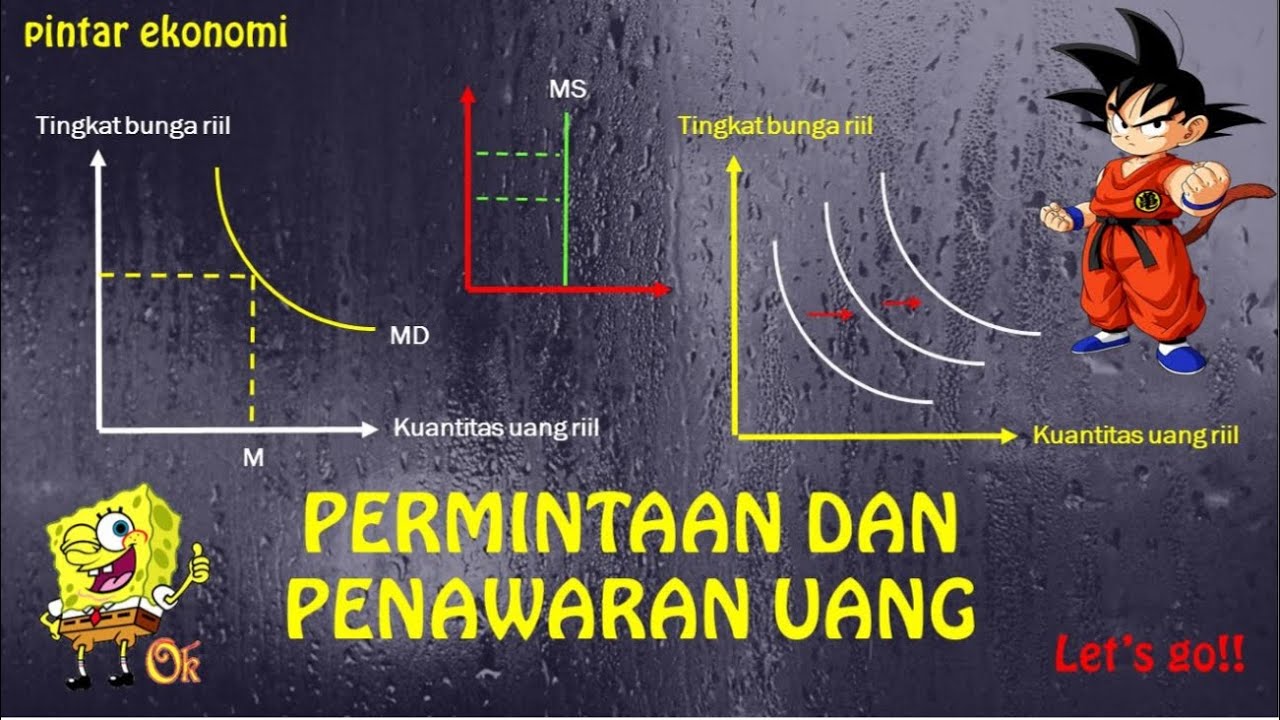
- 📈 Money demand refers to the amount of money people wish to hold as cash, influenced by their desire to meet their needs.
- 🔄 According to Keynesian theory, there are three motives for holding money: transactions, precautionary, and speculative.
- 🛍️ The transaction motive involves holding cash to facilitate daily transactions, such as buying goods or services.
- 🚑 The precautionary motive is about holding cash for unexpected events, like medical emergencies or repairs.
- 📊 The speculative motive refers to holding money to take advantage of price changes in assets, like buying low and selling high.
- 📉 The Quantity Theory of Money suggests that the value of money is inversely related to the amount of money in circulation.
- 💵 The equation MV = PT explains the relationship between the money supply (M), velocity of money (V), price level (P), and number of transactions (T).
- 🔍 Various factors influence money demand, including wealth, price levels, credit availability, payment systems, and income certainty.
- 🏦 Money supply is affected by monetary policy, including open market operations, discount rates, and reserve requirements.
Q & A
What is the role of money in a country's economy?
-Money serves as a medium of exchange, allowing producers and consumers to meet their needs, which creates a demand for money.
What is the definition of money demand?
-Money demand refers to the amount of money that individuals wish to hold as cash, reflecting their desire to convert a portion of their income into cash form.
What are the three motives for holding money according to Keynesian theory?
-The three motives are: 1) Transaction motive - holding money for everyday transactions, 2) Precautionary motive - holding money for unforeseen circumstances, and 3) Speculative motive - holding money to take advantage of investment opportunities.
How does the Quantity Theory of Money relate to the value of money?
-According to the Quantity Theory, the value of money is inversely related to the amount of money in circulation; if the money supply doubles, the value of money is halved.
What is Irving Fisher's contribution to the understanding of money demand?
-Irving Fisher refined the Quantity Theory by incorporating the velocity of money circulation, stating that changes in money supply affect the price level and the value of money.
What formula represents the relationship between money supply, velocity, price level, and transactions?
-The formula is MV = PT, where M is the money supply, V is the velocity of money, P is the price level, and T is the number of transactions.
What factors influence the demand for money?
-Factors include individual wealth, price levels of goods, availability of credit facilities, payment systems, and the certainty of expected income.
What is the definition of money supply?
-Money supply refers to the total amount of money available in the economy for transactions at a specific time.
What are the types of money that circulate in an economy?
-Types of money include M1 (cash and demand deposits), M2 (M1 plus savings accounts and short-term deposits), and M3 (M2 plus long-term deposits).
How do monetary policy decisions affect money supply?
-Monetary policy, through actions such as open market operations, interest rates, and reserve requirements, can either increase or decrease the money supply in the economy.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)