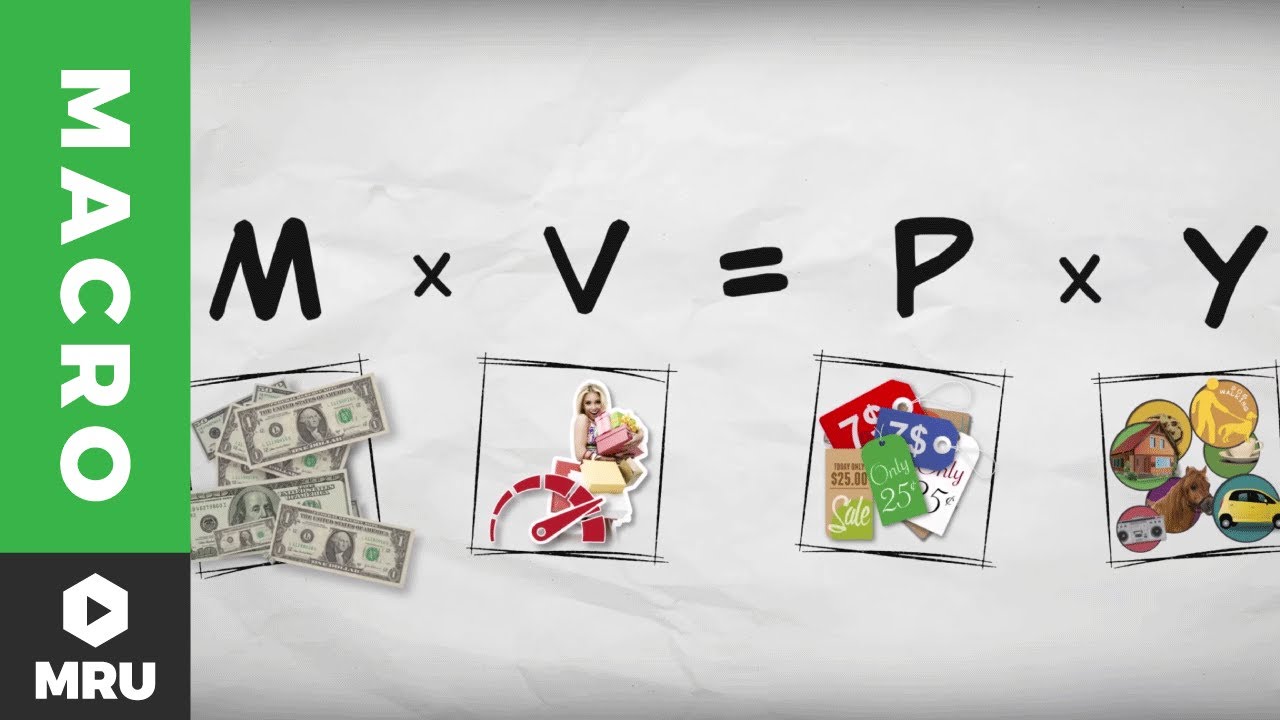ch 22 demand for money part 1 of 5 fisher 1
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses the Quantity Theory of Money and the role of money supply in economic transactions. It explores key economic theories from Irving Fisher, Milton Friedman, and others, focusing on how money velocity and the behavior of money supply affect aggregate income and economic activity. The lecture delves into the relationship between money, inflation, and the role of central banks in regulating money supply. Emphasis is placed on how changes in money supply and velocity influence economic outcomes, using examples to illustrate key concepts and the importance of monetary policy in the economy.
Takeaways
- 😀 The topic of the discussion revolves around the demand for money and the factors influencing the tendency to hold money.
- 😀 Various economic theories related to money demand are introduced, including those by Irving Fisher and Milton Friedman.
- 😀 Fisher’s Quantity Theory of Money explains the relationship between the money supply and aggregate income, highlighting the role of velocity in money circulation.
- 😀 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding how money circulates in the economy, particularly the velocity of money, which affects economic transactions.
- 😀 A key concept presented is the role of the central bank in controlling the money supply and its impact on economic activity and inflation.
- 😀 The importance of monetary policy, such as interest rate adjustments and money supply regulation, is highlighted in controlling economic variables.
- 😀 A distinction is made between real money and credit transactions, explaining how credit can affect the velocity of money in the economy.
- 😀 The script discusses the differences between Keynesian economics (advocating government intervention) and classical economics (arguing against intervention).
- 😀 Irving Fisher's theory suggests that the demand for money is not affected by interest rates, challenging traditional views on money demand.
- 😀 The practical examples used in the script help illustrate how the velocity of money affects economic transactions, with implications for inflation and output.
- 😀 A simulation is given to demonstrate how changes in the money supply and its velocity can influence the overall economic activity and nominal income.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lecture in the transcript?
-The main focus of the lecture is on monetary theory, particularly the quantity theory of money, and how factors like the velocity of money and money supply affect the economy.
What is the quantity theory of money, as discussed in the transcript?
-The quantity theory of money explains the relationship between the total money supply in an economy and its total spending, particularly focusing on how changes in money supply can influence aggregate income and prices.
What is the importance of velocity in the quantity theory of money?
-Velocity refers to how fast money changes hands within an economy, and it is crucial in determining how changes in the money supply affect aggregate income and economic activity.
What role do central banks play in the money supply, according to the transcript?
-Central banks control the money supply by regulating how much money is available in the economy, influencing factors like interest rates and the quantity of money circulating in the market.
How does Irving Fisher's theory relate to the demand for money?
-Irving Fisher's theory suggests that the demand for money is not influenced by interest rates but is determined by the overall economic activity and the velocity of money.
What is the difference between classical and Keynesian economic thought, as described in the script?
-Classical economics believes in minimal government intervention in the economy, while Keynesian economics advocates for government intervention to stabilize economic fluctuations.
What impact do institutions and credit systems have on the velocity of money?
-Institutions and credit systems, such as the use of credit cards or deferred payments, can reduce the velocity of money because transactions are conducted without actual money changing hands immediately.
What is the significance of the nominal GDP in understanding the economy's overall health?
-Nominal GDP represents the total value of goods and services produced in an economy at current prices, and it helps assess the overall economic activity, including the impact of money supply changes.
How does the quantity of money (M) influence economic transactions, based on the lecture?
-The quantity of money (M) affects the frequency and volume of economic transactions. When the money supply increases, more transactions can occur, but if velocity decreases, fewer transactions happen even with a larger money supply.
What does the example of credit card usage reveal about the relationship between money supply and transactions?
-The use of credit cards highlights that even if the money supply increases (M), the actual flow of money can be reduced because transactions may be conducted through credit, not immediately using cash.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)