APA ITU TRANSFORMATOR | CARA KERJA DAN CARA HITUNG TRAFO
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains the fundamental principles and calculations related to transformers (trafo). They discuss the two main types: step-up and step-down transformers, highlighting their operational mechanics based on the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils. Key components, including the magnetic core, are introduced, along with essential formulas for calculating output voltage and coil turns. Through practical examples, viewers learn how to apply these formulas to determine the characteristics of transformers, making the content accessible and informative for those interested in electrical engineering.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, transferring energy between circuits.
- 🔋 There are two main types of transformers: step-up (increases voltage) and step-down (decreases voltage).
- 🔄 A step-up transformer has fewer turns in the primary winding compared to the secondary winding.
- 🔽 A step-down transformer has more turns in the primary winding compared to the secondary winding.
- 🧲 All transformers contain an iron core that enhances the magnetic field created by the primary winding.
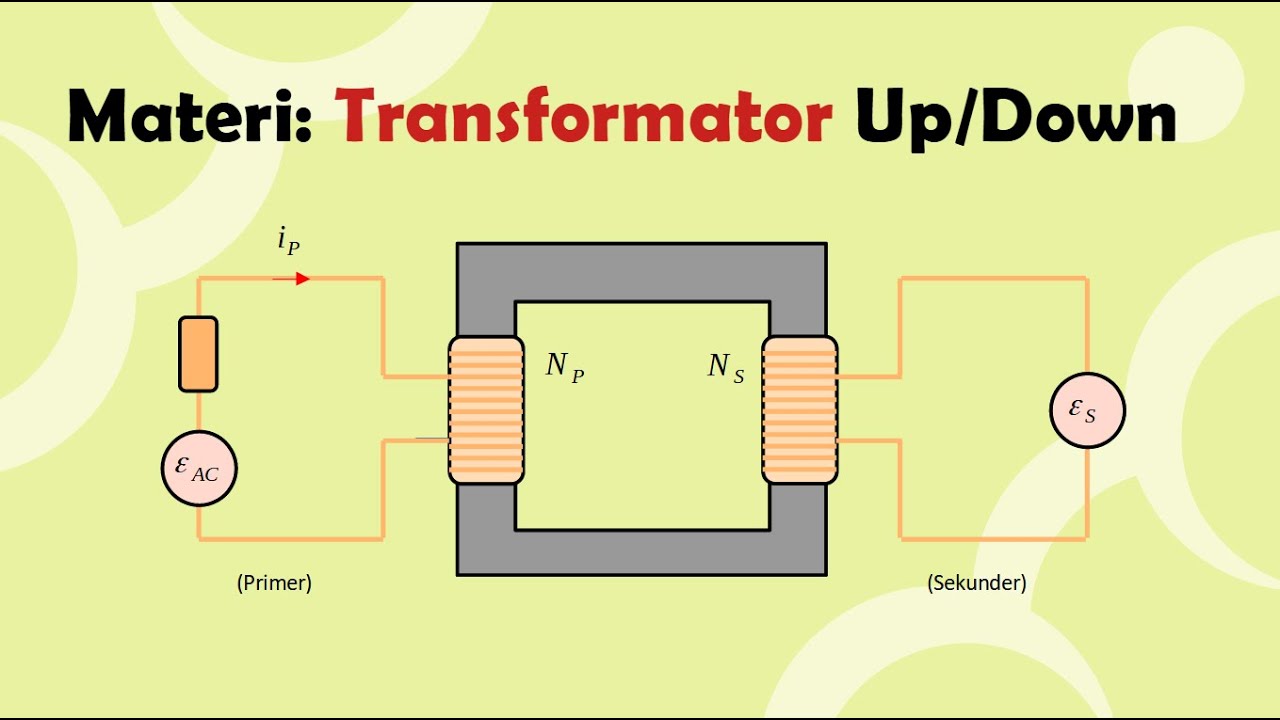
- 💡 The primary winding is where the input voltage is applied, creating a magnetic field.
- ⚡ The secondary winding produces the output voltage that can be supplied to a load.
- 📊 The voltage ratio between primary and secondary windings can be calculated using the formula: VP/VS = NP/NS.
- 🧮 Example calculations demonstrate how to find the number of turns in the secondary winding or the output voltage.
- 📬 Viewers are encouraged to engage with comments for additional questions or clarifications.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a transformer?
-The primary function of a transformer is to change the voltage levels in an electrical circuit, either increasing (step-up) or decreasing (step-down) the voltage.
What distinguishes a step-up transformer from a step-down transformer?
-A step-up transformer has fewer turns of wire in the primary coil compared to the secondary coil, resulting in an increase in voltage. In contrast, a step-down transformer has more turns in the primary coil than in the secondary coil, resulting in a decrease in voltage.
What are the main components of a transformer?
-The main components of a transformer are the magnetic core, the primary winding (coil), and the secondary winding (coil).
How does an AC voltage in the primary winding affect the transformer?
-When an AC voltage is applied to the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field in the core, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding through electromagnetic induction.
What formula is used to calculate the relationship between primary and secondary voltage in a transformer?
-The relationship is given by the formula: Vp/Vs = Np/Ns, where Vp is the primary voltage, Vs is the secondary voltage, Np is the number of turns in the primary winding, and Ns is the number of turns in the secondary winding.
If a step-down transformer has a primary voltage of 220V and a secondary voltage of 110V, what can be inferred about the number of turns in the windings?
-Since the transformer is a step-down transformer with a lower secondary voltage, it indicates that the primary winding has more turns than the secondary winding.
In the example provided in the video, if the primary winding has 1500 turns and the primary voltage is 220V, how many turns does the secondary winding have if the secondary voltage is 110V?
-The secondary winding has 750 turns, calculated using the transformer formula.
What is the significance of the magnetic core in a transformer?
-The magnetic core enhances the efficiency of the transformer by providing a path for the magnetic flux and concentrating the magnetic field, which increases the induction between the primary and secondary windings.
What happens to the voltage if the number of turns in the primary winding is increased while keeping the secondary turns constant?
-If the number of turns in the primary winding is increased while the secondary turns remain constant, the output voltage of the transformer will increase, resulting in a higher voltage at the secondary winding.
How can one determine the output voltage of a transformer if the primary voltage and the number of turns in the windings are known?
-The output voltage can be determined using the transformer ratio formula, rearranging it to find Vs = Vp * (Ns/Np), where Vs is the secondary voltage, Vp is the primary voltage, and Ns and Np are the respective number of turns in the secondary and primary windings.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Apa yang dimaksud transformator step up dan step down induksi elekromagnet kelas 12

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (part 5 : Transformator)

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Induksi Elektromagnetik: Fluks Magnetik dan GGL Induksi | GIA Academy

Transformers Explained - How transformers work

USAHA DAN DAYA | IPA KELAS 8

Transformadores Eléctricos Explicados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
