IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (part 5 : Transformator)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of transformers (trafo) in physics, covering how they work to increase or decrease electrical voltage. It introduces the key components of transformers, such as the iron core and coils, and provides essential formulas relating the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils to the voltage. The video further explores types of transformers (step-up and step-down), efficiency, and ideal transformer equations. Several example problems are solved to help viewers understand transformer operation, including calculating secondary voltage, current, and efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transformers are devices used to change the voltage of electrical energy, either increasing or decreasing it.
- 😀 A transformer consists of two main components: a square or circular iron core and coils of wire wrapped around it.
- 😀 The primary coil (Np) receives input current, while the secondary coil (Ns) delivers the output current.
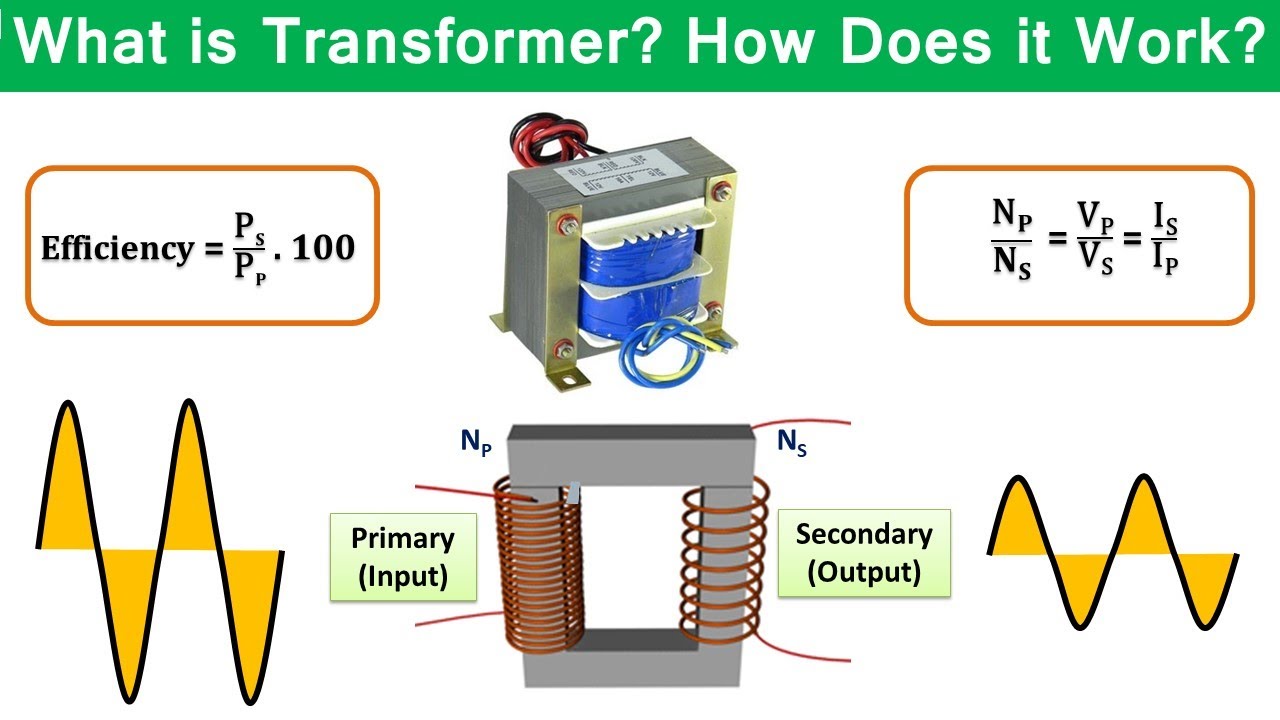
- 😀 The relationship between the number of turns and voltage in a transformer is given by the formula: (Np / Ns) = (Vp / Vs).
- 😀 A step-up transformer increases the output voltage, and a step-down transformer decreases it.
- 😀 For a step-up transformer, the secondary voltage (Vs) is higher than the primary voltage (Vp), and the number of turns in the secondary coil (Ns) is greater than in the primary coil (Np).
- 😀 A step-down transformer works the opposite: the secondary voltage (Vs) is lower than the primary voltage (Vp), and the number of turns in the secondary coil (Ns) is fewer than in the primary coil (Np).
- 😀 The efficiency of a transformer is the ratio of output power (Psecondary) to input power (Pprimary), expressed as a percentage: Efficiency = (Psecondary / Pprimary) × 100%.
- 😀 An ideal transformer has 100% efficiency, meaning all input power is converted to output power without any loss.
- 😀 When calculating current in an ideal transformer, the product of voltage and current on the primary side equals the product on the secondary side: (Vp × Ip) = (Vs × Is).
Q & A
What is a transformer (trafo), and what is its primary function?
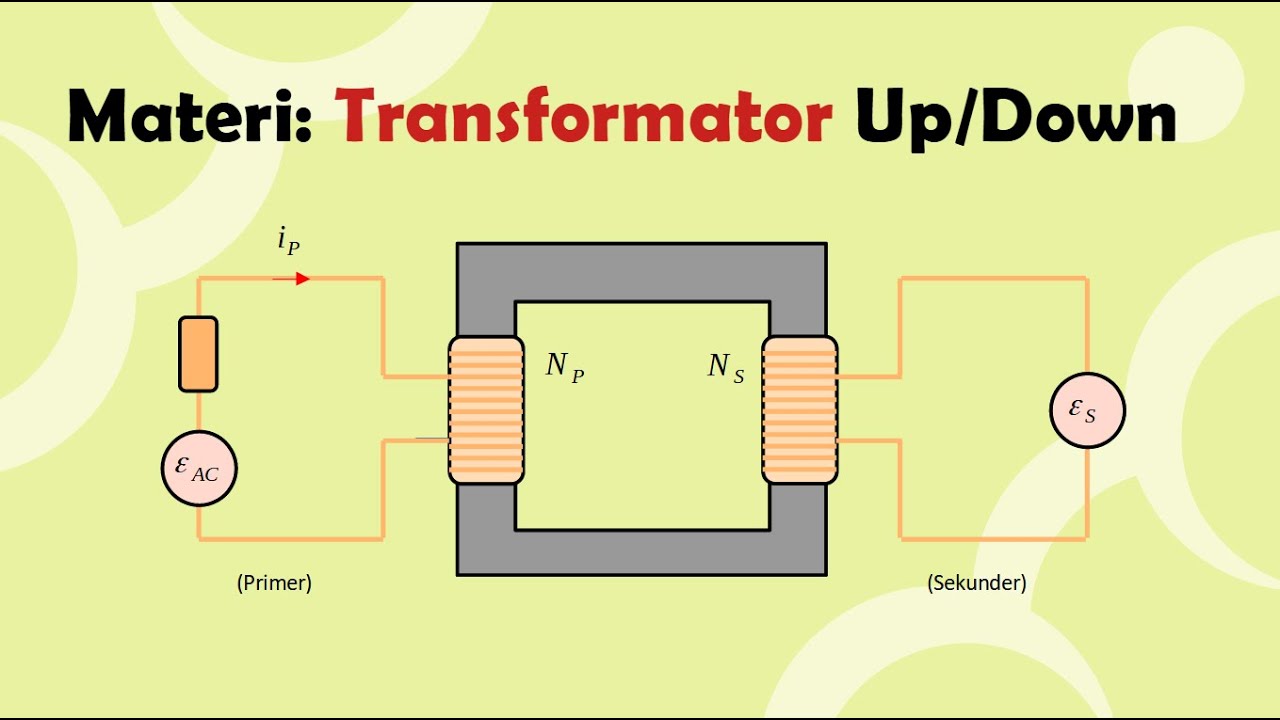
-A transformer (trafo) is an electrical device that is used to change electrical voltage. It can either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the voltage. It consists of two main components: an iron core and coils of wire wound around it, which are called the primary and secondary coils.
What are the primary and secondary coils of a transformer?
-The primary coil is the coil through which electrical current enters the transformer, and the secondary coil is where the electrical current exits. The primary coil is connected to the input power supply, while the secondary coil supplies power to electrical devices.
What is the relationship between the number of turns in the coils and the voltage in a transformer?
-There is a direct proportional relationship between the number of turns in the coils and the voltage. The formula is: Np/Ns = Vp/Vs, where Np and Ns are the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils, respectively, and Vp and Vs are the primary and secondary voltages, respectively.
What is the difference between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer?
-A step-up transformer increases the voltage, so the secondary voltage is higher than the primary voltage. A step-down transformer decreases the voltage, so the secondary voltage is lower than the primary voltage.
How do you determine the type of transformer (step-up or step-down)?
-You can determine the type of transformer by comparing the primary and secondary voltages. If the secondary voltage is greater than the primary voltage, it is a step-up transformer. If the secondary voltage is smaller, it is a step-down transformer.
How is the efficiency of a transformer defined?
-Efficiency of a transformer is defined as the ratio of the power output (secondary power) to the power input (primary power), multiplied by 100%. It can be expressed as: Efficiency = (Ps / Pp) * 100%, where Ps is the secondary power and Pp is the primary power.
What is an ideal transformer, and how does it differ from a real transformer?
-An ideal transformer is one with 100% efficiency, meaning no energy is lost during the conversion. In reality, all transformers have some loss due to factors like resistance in the wires and magnetic leakage, so they are never 100% efficient.
How do you calculate the secondary voltage in a transformer with given primary voltage and coil turns?
-The secondary voltage can be calculated using the transformer formula: Vs = (Ns / Np) * Vp, where Ns and Np are the number of turns in the secondary and primary coils, and Vp is the primary voltage.
How can you calculate the secondary current in an ideal transformer?
-In an ideal transformer, the power in the primary coil is equal to the power in the secondary coil. Using the formula P = V * I, the secondary current (Is) can be calculated using the relationship: Is = (Ip * Vp) / Vs, where Ip is the primary current, Vp is the primary voltage, and Vs is the secondary voltage.
How would you calculate the efficiency of a transformer with a known power output and input?
-To calculate the efficiency of a transformer, use the formula: Efficiency = (Ps / Pp) * 100%, where Ps is the power output (secondary power) and Pp is the power input (primary power). If the power output is 240W and the efficiency is 80%, the input power can be calculated as: Pp = Ps / Efficiency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
What is a Transformer? Transformers Explained - Working Principle (Transformer Tutorial)
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE PHYSICS - transformer

APA ITU TRANSFORMATOR | CARA KERJA DAN CARA HITUNG TRAFO
Apa yang dimaksud transformator step up dan step down induksi elekromagnet kelas 12

Materi Kuliah Transformer #1

Transformadores Eléctricos Explicados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)