Transformers Explained - How transformers work
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the inner workings of transformers, essential devices in modern electrical systems that transfer and alter voltage levels. It explains how transformers operate only with alternating current, using coils and an iron core to efficiently step up or step down voltages for various applications, from small devices to entire cities. The script delves into the physics behind transformers, discusses energy losses, and provides a basic understanding of calculations related to transformer operation. Additionally, it touches on the use of transformers in rectifier circuits and the importance of apparent power in transformer ratings.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Transformers are essential devices that transfer electrical energy and are used to change voltage and current levels.
- 🔄 They only work with alternating current (AC), not direct current (DC).
- 🏠 Transformers are found in various sizes, from small ones in doorbells to large ones supplying entire cities.
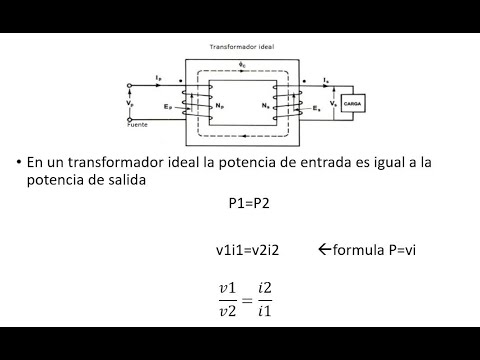
- 🌀 They consist of two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core, with one coil connected to the power supply (primary side) and the other to the load (secondary side).
- 🔋 Transformers are rated in volt-amps (VA) or kilovolt-amps (kVA), not watts, because they transfer power between coils.
- 🔧 Step-up transformers increase the voltage output, while step-down transformers decrease it, allowing for efficient power transmission over long distances.
- 🌐 By increasing voltage and reducing current, transformers minimize energy losses during transmission.
- 📉 Transformers have efficiency losses due to eddy currents and resistance in the coils, which generate heat and cause the characteristic humming sound.
- 🔧 The efficiency of transformers is enhanced by using laminated iron cores to reduce eddy currents.
- 🔄 Transformers are integral in rectifier circuits to convert AC to DC, with diodes and capacitors smoothing the output.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a transformer?
-A transformer is used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It can change the voltage and current levels, making it essential for transmitting electrical power efficiently.
Why do transformers only work with alternating current (AC) and not with direct current (DC)?
-Transformers only work with alternating current because AC generates a changing magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil. DC creates a constant magnetic field that does not induce a voltage in the secondary coil, except briefly when the DC is switched on or off.
What units are transformers rated in, and why?
-Transformers are rated in volt-amperes (VA) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA) because they transfer apparent power. The actual power (in watts) depends on the efficiency and the load connected to the transformer.
What are the typical applications of small and large transformers?
-Small transformers are commonly used in devices like doorbells and laptop chargers. Larger transformers supply power to homes and businesses, while the largest transformers can supply entire regions, towns, or cities.
How does a step-up transformer differ from a step-down transformer?
-A step-up transformer increases the voltage on the output side, typically used for long-distance power transmission to reduce energy loss. A step-down transformer decreases the voltage on the output side, used to lower high transmission voltages to safer levels for local distribution and household use.
Why is high voltage used for long-distance power transmission?
-High voltage is used for long-distance power transmission to reduce energy losses. Higher voltage reduces the current in the transmission cables, which in turn decreases the energy lost as heat due to the cable's resistance.
What are the key components of a transformer, and how do they function?
-The key components of a transformer are two separate coils of wire (primary and secondary) and an iron core. The primary coil receives electrical energy, creating a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil, thus transferring the energy.
What causes the humming sound in transformers?
-The humming sound in transformers is caused by the vibrations of the iron core. The alternating current causes the core's laminated sheets to expand and contract slightly, creating vibrations and the characteristic humming noise.
What are copper losses and iron losses in transformers?
-Copper losses refer to the energy lost due to the resistance in the transformer's wire coils, generating heat. Iron losses are due to eddy currents and hysteresis in the iron core, which also generate heat and reduce efficiency.
How does a transformer improve the efficiency of electrical power transmission?
-A transformer improves efficiency by allowing electrical power to be transmitted at high voltages and low currents, reducing energy losses due to the resistance of transmission cables. The voltage is then stepped down to usable levels closer to the point of consumption.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)