Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (7 of 31) Differences Between Series and Parallel Current
Summary
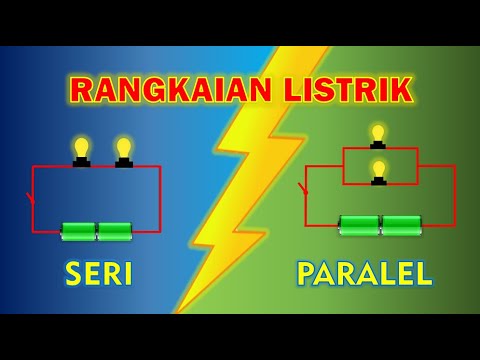
TLDRThis video explains the difference between series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit, elements are connected such that they share a node exclusively, resulting in the same current through all components. In a parallel circuit, multiple elements share the same two nodes, and the voltage across each branch is the same. The video highlights key characteristics of both circuit types, providing a foundational understanding of how they function, which will be useful for future circuit analysis.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Series circuits have components connected one after another, sharing exclusive nodes.
- 🔋 In a series circuit, current through all elements is the same because they share nodes exclusively with no other elements.
- 💡 Parallel circuits have components connected in such a way that they share the same two nodes.
- ⚡ In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each parallel branch is the same.
- 🔧 In a series circuit, resistor R1 and resistor R2 are in series if they share an exclusive node with no other shared components.
- 🔌 Resistors R2 and R3 in a series circuit are also in series if they share a node not connected to other elements.
- 🔋 The current through a series circuit remains constant through each element due to their connection.
- 💡 In a parallel circuit, resistors share two nodes, which makes them parallel, and the voltage remains the same across each branch.
- ⚡ In a series circuit, current remains consistent across all elements, while in a parallel circuit, voltage remains consistent.
- 🔧 Understanding the characteristics of series and parallel circuits is essential for circuit analysis in the future.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
-The main difference is that in a series circuit, elements share a node exclusively between two components, while in a parallel circuit, two or more elements share the same two nodes.
How can you identify if two resistors are in series?
-Two resistors are in series if they share a node that is not connected to any other elements in the circuit.
Why is the entire circuit considered a series circuit in the example provided?
-The entire circuit is considered a series circuit because every two elements share a node exclusively with each other and not with any other element.
How can you tell if two resistors are in parallel in a circuit?
-Two resistors are in parallel if they share the same two nodes.
What is the defining characteristic of a series circuit in terms of current?
-In a series circuit, the current is the same through every element of the circuit.
What is the defining characteristic of a parallel circuit in terms of voltage?
-In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across each branch.
Why can't the elements in a parallel circuit be considered in series?
-In a parallel circuit, elements share the same nodes with other elements, which breaks the rule for a series connection where nodes should not be shared with more than two elements.
What happens to the current in a series circuit when multiple elements are connected?
-The current remains the same through all elements connected in series.
What happens to the voltage in a parallel circuit when multiple branches are connected?
-The voltage remains the same across all branches connected in parallel.
Why is it important to understand the difference between series and parallel circuits?
-Understanding the difference is important because it helps in analyzing circuits, predicting the behavior of current and voltage in different components, and solving circuit-related problems efficiently.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)