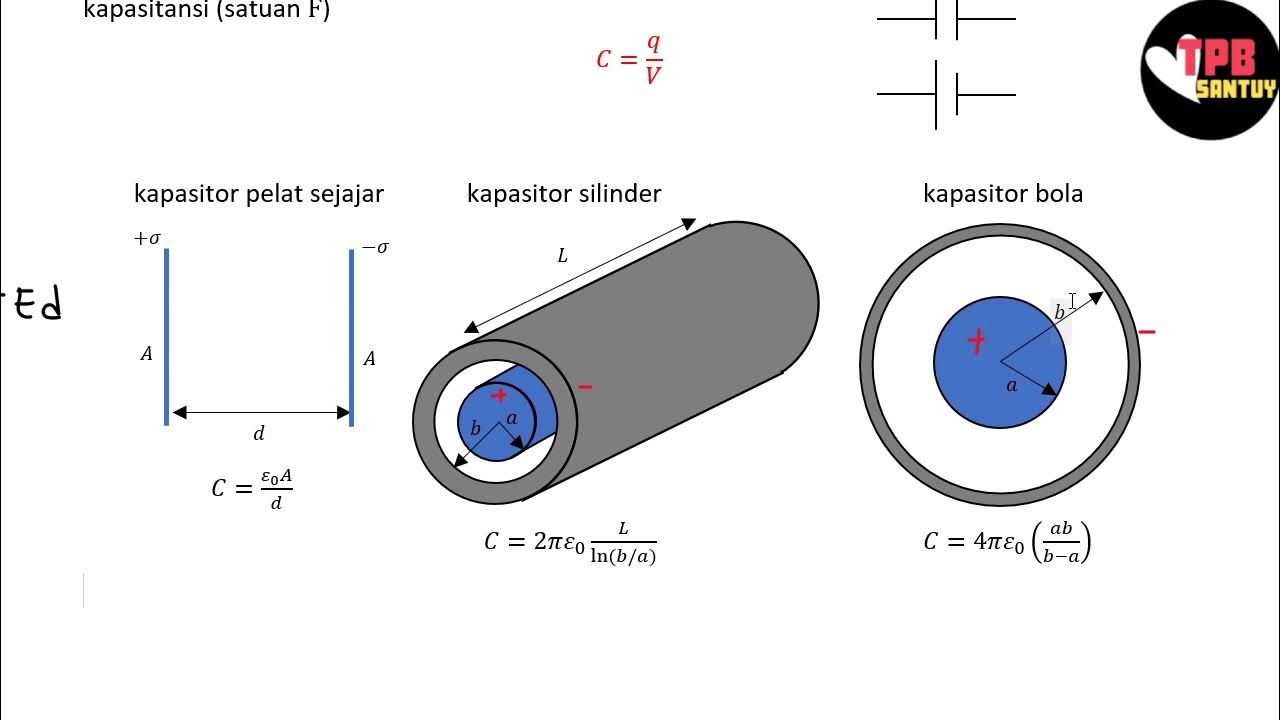
Capacitors in Series and Parallel Explained!
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamentals of capacitors in series and parallel circuits, highlighting key concepts such as equivalent capacitance, charge, voltage, and potential energy. It walks through practical examples with step-by-step calculations, like finding the total capacitance of parallel and series circuits, determining the voltage across individual capacitors, and calculating the energy stored in them. The script also emphasizes the differences between series and parallel configurations, helping viewers understand how to approach capacitor-related problems in both types of circuits. Ideal for anyone learning about capacitor behavior in electrical circuits.
Takeaways
- 😀 Capacitors in parallel have the same voltage across them, and their equivalent capacitance is the sum of all individual capacitances.
- 😀 To calculate the total charge in a parallel circuit, use the formula Q = C × V for each capacitor.
- 😀 The total charge in a parallel capacitor network is the sum of the charges stored on each individual capacitor.
- 😀 The energy stored in a capacitor is calculated using the formula E = 1/2 × C × V², where C is the capacitance and V is the voltage across the capacitor.
- 😀 In a series capacitor circuit, the charge on each capacitor is the same, but the voltage across each capacitor will differ depending on the capacitance.
- 😀 The equivalent capacitance of capacitors in series is found by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances.
- 😀 The voltage across each capacitor in a series circuit can be found by dividing the charge by the capacitance of each capacitor.
- 😀 To calculate the total charge in a series circuit, multiply the equivalent capacitance by the battery voltage.
- 😀 The sum of the individual voltages across capacitors in series must equal the total voltage of the battery.
- 😀 The energy stored in a series capacitor can also be calculated using the same formula E = 1/2 × C × V², where the voltage is the value specific to that capacitor.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)